This human anatomy ClipArt gallery offers 76 illustrations of the human lower respiratory system, including organs involved in respiration. The human lower respiratory tract includes the trachea, bronchi, lungs, and diaphragm.
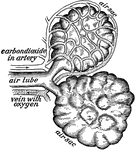
Diagrammatic view of an air sac
"A, epithelial lining wall; B, partition between two adjacent sacs, in which run capillaries;…
Air Sacs from the Lungs
Two of the air sacs from the lungs with the network of blood tubes shown about one.
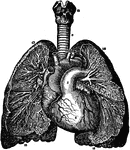
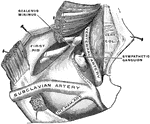
Branchi and Blood Vessels
Branchi of the lungs, the heart, and blood vessels. Labels: 1, left auricle; 2, right auricle; 3, left…
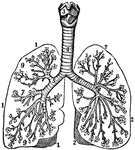
The Bronchia
The bronchia. Labels; 1, Outline of the right lung. 2, Outline of the left lung. 3, Larynx. 4, Trachea.…
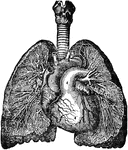
Bronchia and Veins of the Lungs
View of the bronchia and veins of the lungs, exposed by dissection, as well as the relative position…
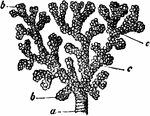
Bronchial Tube
A small bronchial tube, a, dividing into its terminal branches, c; these have pouched or sacculated…
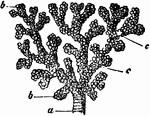
A Bronchial Tube
A small bronchial tube. Labels: a, dividing into its terminal branches, c; these have pouched or sacculated…
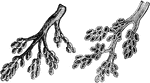
Bronchial Tubes Terminating in Air Vesicles
View of the bronchial tubes, terminating in air vesicles. On the left is the external view (1, bronchial…
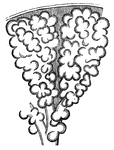
Bronchioles
This diagram shows the bronchial tubes, with clusters of cells. The bronchioles are the first airway…
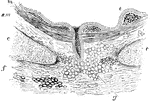
Section of the Bronchus
Transverse section of a bronchus. Labels: e, Epithelium (ciliated); immediately beneath it is the mucous…
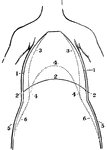
A Front View of the Chest and Abdomen in Respiration
A front view of the chest and abdomen in respiration. Labels: 1, The position of the walls of the chest…
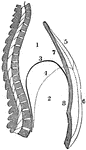
A Side View of the Chest and Abdomen in Respiration
A side view of the chest and abdomen in respiration. Labels: 1, The cavity of the chest. 2, The cavity…
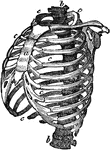
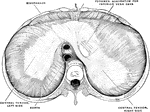
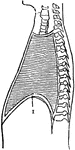
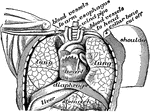
Structure of the Chest
Structure of the chest, showing the framework of the bones which are connected together chiefly by muscles.…
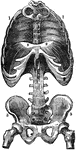
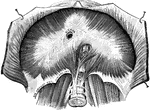
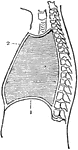
Diaphragm
View of the diaphragm; 1, cavity of the thorax; 2, diaphragm separating the cavity of the thorax from…

Diaphragm During Expiration
Diaphragm in the state of its greatest ascent in expiration; 2, muscles of the abdomen in action forcing…
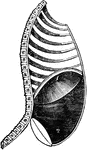
Diaphragm During Inspiration
Diaphragm in its state of greatest descent in inspiration; 2, muscles of the abdomen, showing the extend…
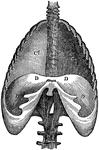
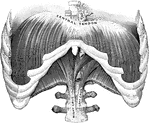
The Diaphragm
The diaphragm, which is the principal muscle that act sin breathing. Here you have the cavity of the…
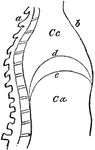
The Diaphragm
Diaphragm of the diaphragm and it's placement in the chest. Let a represent the spinal column,…

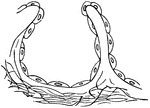
Infundibula
Two small infundibula or groups of air cells, a, with air cells, b, and the ultimate bronchial tubes,…

Infundibula of the Lung
Two infundibula of the lung much magnified. Labels: b, b, hollow protrusions of the alveolus, opening…
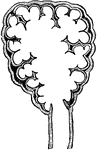
Pulmonary lobule
"Section of a pulmonary lobule, showing its division into pulmonary vesicles." — Tracy, 1888
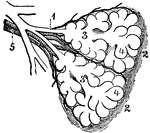
Diagram of the Two Primary Lobules of the Lung
Diagram of the two primary lobules of the lungs, magnified. Labels: 1, Bronchial tube. 2, A pair of…
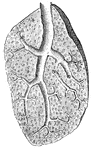
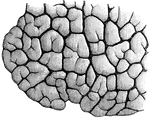
Lobule of a Lung
"Showing the structure of a lobule of the lung. The lobule has been injected with mercury, afterwards…
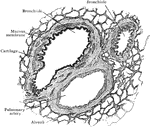
Section of Lung Showing Air Tubes
Section of lung, showing small air tubes and branch of pulmonary artery.
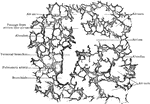
Section of Lung Showing General Relations of Divisions of Air Tubes
Section of lung, showing general relations of division of air tubes.

Section of Lung
Section of lung with distended blood vessels, highly magnified. Labels: c,c, partitions between alveoli;…
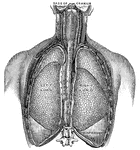
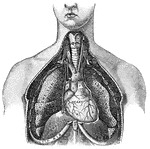
Lungs
"Relative Postion of the Lungs, the Heart, and Some of the Great Vessels belonging to the latter. A,…
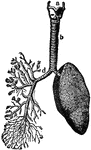
Lungs
The lung is the essential organ of respiration in air-breathing vertebrates. Its principal function…
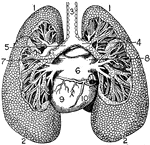
Lungs
"The Lungs. 1, Summit of lungs. 2, Base of lungs. 3, Trachea. 4, Right bronchus. 5, Left bronchus. 6,…
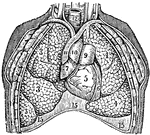
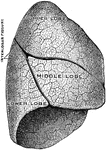
The Lungs
The lungs. Labels: 3, The lobes of the right lung. 4, The lobes of the left lung. 5, 6, 7, The heart.…
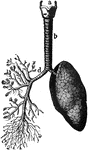
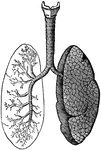
Lungs and Air Passages
The lungs and air passages seen from the front. On the left of the figure the pulmonary tissue has been…
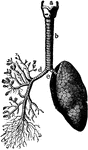
The Lungs and Air Passages
The lungs and air passages seen from the front. On the left of the figure the pulmonary tissue has been…
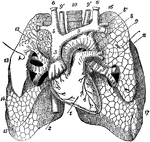
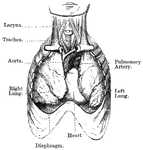
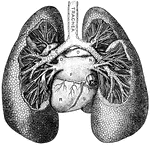
Anterior View of the Lungs and Heart
Anterior view of the lungs and heart. Labels: 1, heart; 2, inferior vena cava; 3, superior vena cava;…
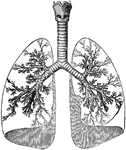
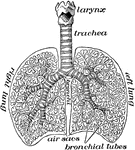
Lungs and Trachea
The lungs and windpipe (trachea). Labels: 1, larynx; 2, windpipe (trachea); 3, right lung, showing bronchi…
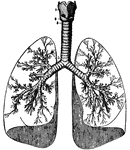
Human Lungs
Human lungs. 1 and 2 make up the larynx, or voice box. 1 is thyroid cartilage, 2 is cricoid cartilage.…
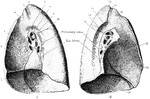
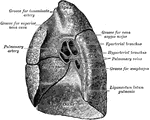
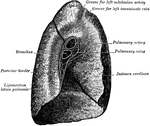
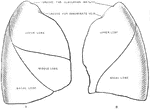
Mediastinal Surfaces of the Lungs
Mediastinal surfaces of the two lungs of a subject hardened by formalin injection. A, right lung. B,…
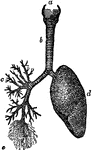
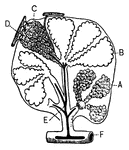
Structure of the Lungs
Diagram showing the structure of the lungs. At d is the left lung, and at c are represented…

Structure of the Lungs
Structure of the lung. The lung has a serous coat; a sub-serous, elastic areolar tissue, investing the…
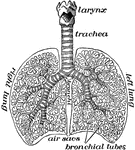
The lungs
"The lungs fill up most of the cavity of the chest. One lies on either side of the heart which is in…
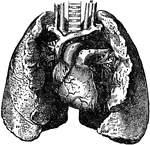
The Lungs
The lung, which are the two essential organs of respiration contained in the cavity of the thorax.