This human anatomy ClipArt gallery offers 240 illustrations of the human digestive system. This includes views of the gastrointestinal tract and organs involved in the breakdown and absorption of food. Included in this category are the oral cavity, salivary glands, stomach, esophagus, intestines, colon, and gallbladder.

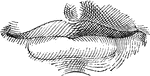
Gastric gland
"The inner coat of the stomach has its surface honeycombed with millions of little pits. We have all…
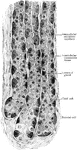
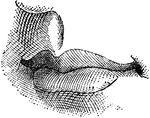
Gastric Gland from Fundus
Deeper portion of gastric glands from fundus, showing two varieties of lining cells and secretion capillaries…

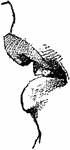
Branched Gastric Gland
Gastric glands are often branched at the bottom end. Labels: a, the peptic cells; b, the inert cells.
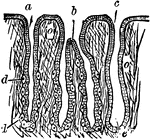
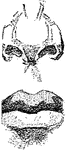
Section through the Gastric Mucous Membrane
A thin section through the gastric mucous membrane which lines the stomach, perpendicular to its surface,…
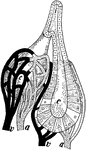
Gland
"Diagram to show the working parts of a gland. v and a are blood tubes with thin-walled branches around…
Gland of Lieberkuhn
The glands or crypts of Lieberkuhn are simple tubular depressions of the intestinal mucous membrane,…

Forms of Glands
Forms of glands. Labels: A, a simple secreting surface; a, its epithelium; b, basement membrane; c,…

Forms of Glands
Forms of glands. Labels: A, a simple secreting surface; a, its epithelium; b, basement membrane; c,…
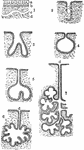
Diagram Showing Various Forms of Secreting Glands
Diagram showing various forms of secreting glands. Labels: 1, general plan of a secreating membrane;…
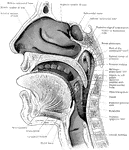
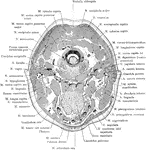
Section of the Head and Neck
Sagittal section through mouth, tongue, larynx, pharynx, and nasal cavity. The section was slightly…
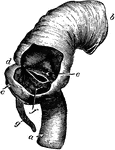
Ileo-caecal valve
The ileo-caecal valve, where the small intestine joins the large. Labels: a, ileum; b, ascending colon;…

Ileo-caecal Valve
Three forms of ileocaecal valve, from bodies hardened by intravascular injections of formalin.
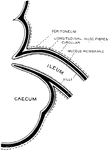
Formation of Ileo-caecal Valve
Diagrammatic Section through the junction of the ileum with caecum, to show the formation of the ileocaecal…
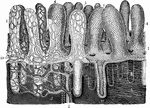
Mucous Membrane of the Ileum
The mucous membrane of the ileum. Labels: 1, cellular structure of the epithelium, or outer layer; 2,…
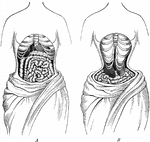
The Natural Position Compared to the Deformed Position of the Internal Organs
A, the natural position of the internal organs. B, when deformed by tight lacing. The liver and stomach…
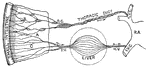
Intestinal absorption
"A, a fold of peritoneum; B, lacteals and lymphatic glands; C, veins of intestines;…
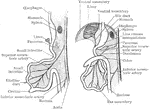
Development of the Intestinal Canal
Two diagrams to illustrate the development of the intestinal canal. The figure to the right shows the…
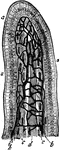
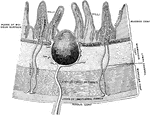
Intestinal Villus
An intestinal villus. They are little projections of the mucous membrane, covered with epithelium, and…
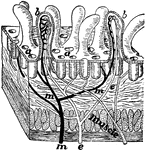
Section of Intestine wall
"A tiny block cut from the wall of the intestine showing villi and the mouths of glands at a; b, villus…

Small Intestine with Mesentery and Vessels
A portion of the intestine, with mesentery and vessels. The peritoneal coat has been removed from the…
Large Intestine
Large intestine, A piece of transverse colon from a child two years old. The three chief characteristics…

Large Intestine
A piece of transverse colon from a child two years old. The three chief characteristics of the large…
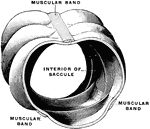
Structure of Large Intestine
Segment of large intestine showing the characteristic feature of its structure.
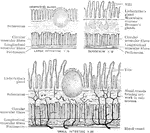
Structure of the Intestine
Diagram to show the structure of the small and large intestine and duodenum.
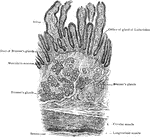
Transverse Section of Small Intestine
Transverse section of small intestine (lower part of duodenum), showing general arrangement of coats.
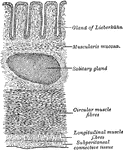
Transverse Section of the Wall of the Large Intestine
Transverse section of the wall of the large intestine.
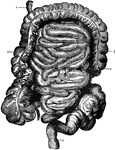
Intestines
The Intestines. 1: Begining of Duodenum; 2: Small inestine; 3: Large intestine; 4: Rectum.
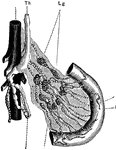
Lacteals
Showing the connection of the small intestine to the thoracic duct by the lacteals lying in the mesentery.…
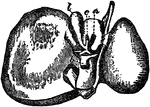
Liver
The large dlangular organ situated in the upper abdominal cavity of vertebrates, whose function is to…
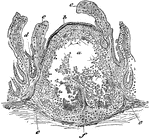
Lymphoid Tissue
Section through the lymphoid tissue of a solitary gland. Labels: a, center of the gland, with the lymphoid…
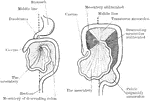
Development of the Mesenteries
Two diagrams to illustrate the development of the mesenteries. In the first figure the rotation of the…
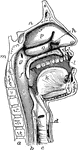
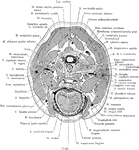
Mouth
"The mouth, nose and pharynx, with the commencement of the gullet and larynx, as exposed by a section,…
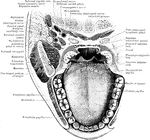
Horizontal Section Through Mouth and Pharynx
Horizontal section through mouth and pharynx at the level of the tonsils.
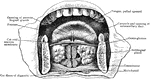
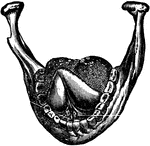
Anterior Part of Floor of Mouth
Section across anterior part of floor of mouth, showing relations of sublingual glands to mucous membrane…
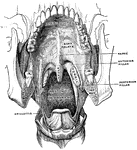
Mouth, Cavity of the
Antero-inferior surface of the soft palate. The tongue has been removed, so that the pharyngeal isthmus…
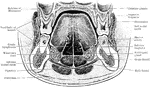
Section Through Mouth
Coronal section through the closed mouth. The slit liked character of the vestibule, the manner which…
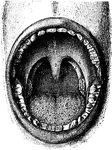
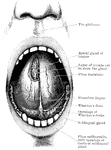
The Mouth
Interior of the mouth. Labels: 1, soft palate; 2, its median ridge; 3, uvula; 4, anterior, 5, posterior…
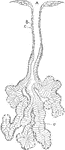
Mucous Gland from Tongue
Section of a mucous gland from the tongue. Labels: A, opening of the duct on the free surface; C, basement…

Mucous Membrane from the Jejunum
The mucous membrane from the jejunum. Labels: 1, Villi (folds of lining mucous membrane) in miniature.…