This human anatomy ClipArt gallery offers 240 illustrations of the human digestive system. This includes views of the gastrointestinal tract and organs involved in the breakdown and absorption of food. Included in this category are the oral cavity, salivary glands, stomach, esophagus, intestines, colon, and gallbladder.

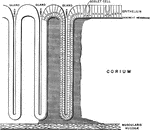
A Portion of the Mucous Membrane from the Small Intestine
Portion of the mucous membrane from the small intestine, magnified, showing the villi on its free surface,…

Mucous Membrane of the Small Intestine
Free surface of the mucous membrane of the small intestine, showing villi, solitary glands, and opening…
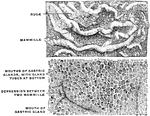
Mucous Membrane of the Stomach
The mucous membrane of the stomach. The top image is natural size and shows the rugae and he mamillated…
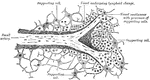
Gastropulmonary Mucous Membrane
Diagram of the gastropulmonary mucous membrane, showing the continuity of all its parts.
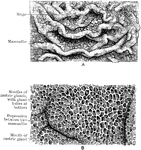
Stomach Mucous Membrane
The mucous membrane of the stomach. A, Natural size. B. Magnified. In A the rugae and the mammilated…
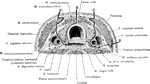
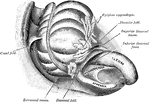
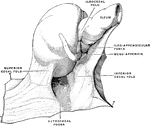
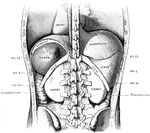
Cross Section of Neck at the 7th Cervical Vertebra
Modes of approach to the esophagus and the cervical sympathetic ganglion shown by means of a cross section…
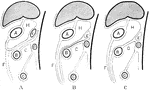
Development of the Great Omentum
Diagram to illustrate the development of the great omentum. A, shows the beginning of the great omentum…
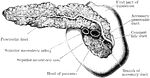
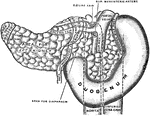
Pancreas and Duodenum from Behind
The pancreas and duodenum from behind, with the pancreatic duct exposed. The superior mesenteric vessels…
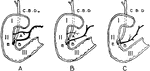
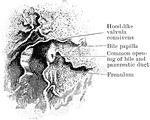
Variations in Termination of the Pancreatic and Bile Ducts
Showing the variations in the manner of termination of the pancreatic and bile ducts. A, Form in which…
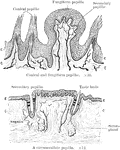
Papillae of the Tongue
The upper illustrations show conical and fungiform papillae, the lower a circumvallate papilla. Labels:…

Filiform Papillae
The epithelium covering the filiform papillae is extremely dense and thick, and projects from their…

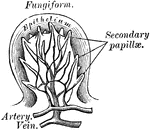
Fungiform Papillae
The fungiform papillae are scattered chiefly over the sides and tip, and sparingly over the middle of…

Peptic Gastric Gland
The peptic gastric glands are distributed throughout the entire fundus and body, and may be found even…
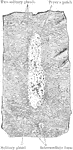
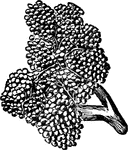
Peyer's Patch
A Peyer's patch consists of a large number of lymphoid nodules grouped closely together so as to form…
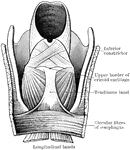
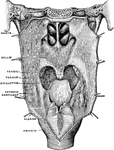
Pharynx and Esophagus
The lower part of the pharynx and the upper part of the esophagus have been slit up from behind, and…
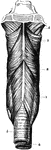
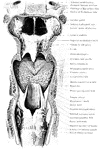
The Pharynx
The structure of the pharynx, a conical, musculo-membranous tube that forms the alimentary canal which…
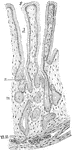
Pyloric Gland
Section showing the pyloric glands. Labels: s, free surface; d, ducts of pyloric glands; n, neck of…
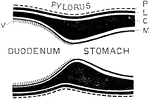
Formation of Pylorus
Diagram to show formation of pylorus. Labels: P, peritoneum; L, longitudinal layer of muscular fibers;…
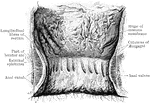
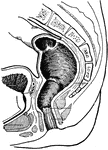
Rectum and Anal Canal
The interior of the anal canal and lower part of the rectum. Showing the column of Morgagni and the…
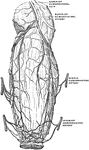
Blood Vessels of the Rectum and Anus
The blood vessels of the rectum and anus, showing the distribution and anastomosis on the posterior…

Inner Wall of the Rectum and Anus
Inner wall of the lower end of the rectum and anus. On the right the mucous membrane has been removed…
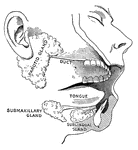
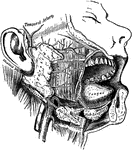
Salivary glands
"While the food is being chewed it is moistened by saliva, or spittle, which flows into the mouth from…
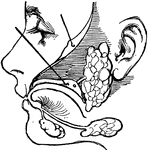
Salivary glands
"There are three pairs of salivary glands. One pair lies under the tongue; one pair is found under the…
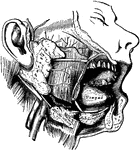
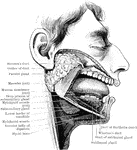
Salivary Glands
The salivary glands. One side of the lower jaw has been removed, and the face dissected, in order to…
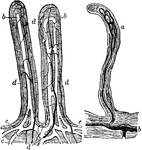
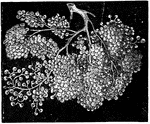
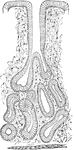
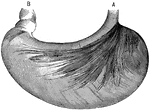
Small Intestine Villi
Villi of the small intestine, magnified about 80 diameters. In the left-hand figure the lacteals, a,b,c,…
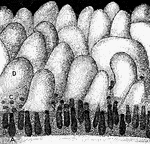
Glands and villi of the small intestine
"A, B, glands seen in vertical section with their orifices at C opening upon the membrane…
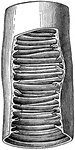
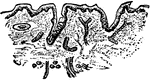
Piece of small intestine
"Piece of small intestine cut open to show wrinkling of inner coat bearing villi." —Davison, 1910
The Small Intestine
The small intestine, a convoluted, tubular, digestive organ, about 20 ft in length, extending from the…
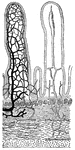
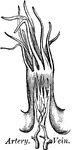
Transverse section of the small intestine
"In the figure on the left are seen the artery and vein of a villus. In the right figure are represented…

The Spleen
The spleen, a soft, brittle, highly vascular organ, of dark purplish color, in size about 5 x 3 x 1.5…
Stomach
"The stomach is a half-gallon sac, with an outer wall of muscle lined within by mucous membrane, made…
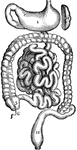
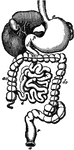
Stomach
The stomach and intestines. 1: Stomach. 2: Duodenum. 3: Small intestine. 4: Termination of the ileum.…
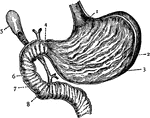
Stomach
Section of the Stomach. 1: Cardiac orifice; 2: Folds of mucous membrane; 3: Muscular wall; 4: Pylorus;…
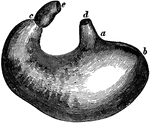
The Stomach
The stomach. Labels: d, lower end of the gullet; a, position of the cardiac aperture; b, the fundus;…
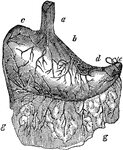
Stomach
The human stomach. Labels: a, the esophagus or gullet; b, the cardiac portion; c, the left extremity;…
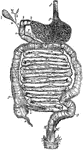
Stomach
The digestive system. This figure represents the whole tract of the intestinal canal, not exactly in…
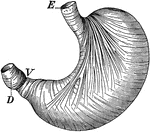
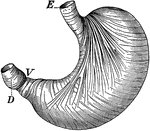
Stomach
The stomach showing the muscles which churn the food. Labels: E, where food enters; V, entrance into…