This human anatomy ClipArt gallery offers 825 illustrations of the human skeletal system, including images of both the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. The human axial skeleton includes 80 bones formed by the vertebral column (spine), the thoracic cage (e.g., ribs, sternum), and the skull. The axial skeleton is responsible for the upright position of the body. The human appendicular skeleton is composed of 126 bones formed by the pectoral girdles, the upper and lower limbs, and the pelvic girdle. These bones function in locomotion as well as protection of vital organs.
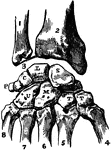
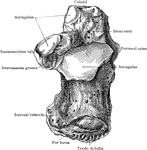
Bones of the Carpus
Articulations of bones of the carpus (wrist area). Labels: 1, ulna; 2, radius; 3, inter-articular fibro-cartilage;…

Cartilage
"Cartilage or gristle is fibrous tissue glued together by a substance containing chondrine." —…
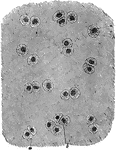
Cartilage Tissue
A thin slice of cartilage highly magnified, showing the cartilage cells (a,b) scattered through an almost…
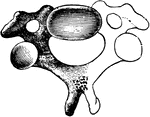
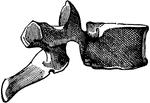
A Cervical Vertebra
A cervical vertebra. Labels: Frt, vertebral foramen; Pai, anterior articular process; R, rudimentary…
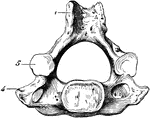
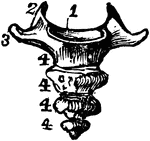
Human Cervical Vertebra Bone
A cervical vertebra of the spine, inferior surface. Labels: 1, spinous process, slightly bifid; 4, transverse…
The First and Second Cervical Vertebrae
B, the first cervical vertebra, the atlas. A, the atlas, and the second cervical vertebra, the axis;…
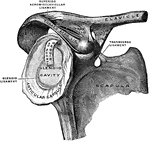
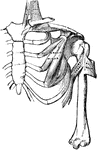
Clavicle and Scapula with Ligament
Right clavicle and scapula with ligament, from without and somewhat in front.
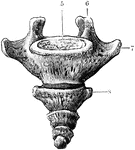
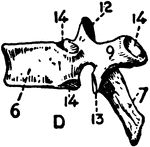
Coccyx, Anterior Surface of the
Anterior surface of the coccyx. Labels:5, sacrum; 6, cornu; 7, transverse process; 8, transverse process.
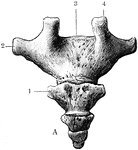
Coccyx, Posterior Surface of the
Posterior surface of the coccyx. Labels: 1, transverse process; 2, transverse process; 3, sacrum; 4,…

Compact Bone
"Compact bone consists of a series of concentric layers of bone disposed around a canal called the Haversian…
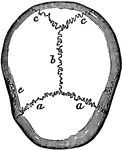
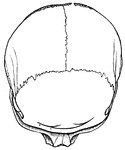
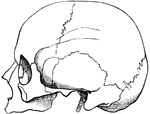
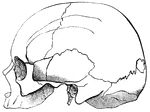
Cranial Sutures
The bones of the top of the head are fastened together by what are called sutures which are locked together…
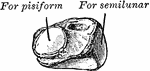
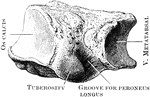
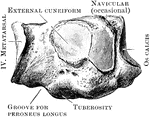
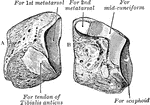
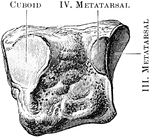
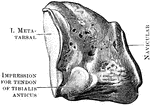
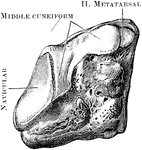
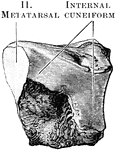
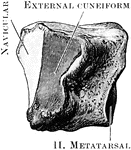
Cuneiform Bone
The cuneiform may be distinguished by its pyramidal shape, and by its having an oval, isolated facet…
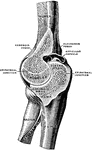
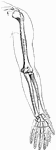
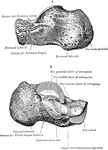
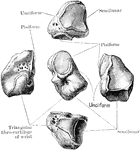
Elbow Joint
Right elbow joint, cut through at right angles to the axis of trochlea humeri, from the ulnar side.
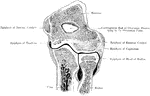
Frontal Section Through Elbow Joint
A view from behind of a frontal section through the right elbow joint.
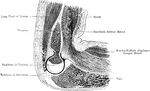
Sagittal Section Through Elbow Joint
A sagittal section through the left elbow joint of a child. View from the inner side.
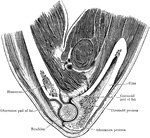
Vertical Section Through Elbow Joint
Vertical section through the trochlear part of the elbow joint.
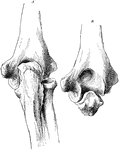
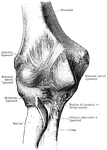
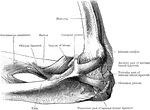
Posterior View of Elbow
Posterior view of elbow, showing relative position of condyles and olecranon. A, in extension; B, in…
Eleventh Rib
The eleventh and twelfth ribs have each a single articular facet on the head, which is of rather large…