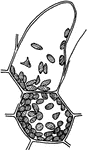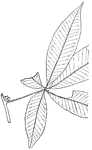
Genus Aesculus, L. (Buckeye, Horse Chestnut)
Leaves - compound (hand-shaped; leaflets, five); opposite; edge toothed. Outline - of leaflet, oval…
Dull Edge Pencil
The wood is cut away so that about 1/4 or 1/2 inch of lead projects. The lead can then be sharpened.
45 Degree Triangle
Triangles are made of various substances such as wood, rubber, celluloid, and steel.
30-60 Degree Triangle
Triangles are made of various substances such as wood, rubber, celluloid, and steel.

Type
A piece of wood or metal to stamp a letter or character. "(1) the body, (2) the face, (3) the shoulder,…
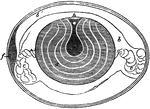
Egg Parts
"Section of a Hen's Egg before Incubation. a, yolk, showing concentric layers; a', its semi-fluid center;…
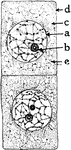
Onion Cells
"A, embryonic cells from onion root tip; d, plasmatic membrane; c, cytoplasm; a, nuclear membrane enclosing…
Onion Cells
"B, older (onion) cells farther back from the root tip. The cytoplasm is becoming vacuolate; f, vacuole."…
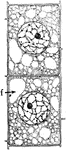
T. Zebrina Cell
In onion cells: "C, a cell from the epidermis of the mid-rib of Tradescantia zebrina, in its natural…
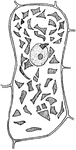
T. Majus Cell
"A, cell from the epidermis of the upper side of the calyx of Tropaeolum majus with crystalline chromoplasts."…
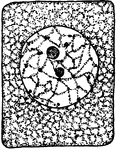
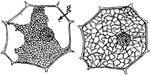
Plant Cell Division 1
First stage in plant cell division: Protophase 1; "Resting cell ready to begin division." -Stevens,…
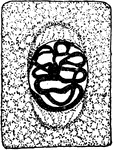
Plant Cell Division 2
Second stage in plant cell division: Protophase 2; "the nuclear reticulum is assuming the form of a…
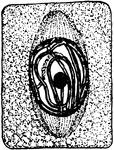
Plant Cell Division 3
Third stage in plant cell division: Protophase 3; "The nuclear thread has divided longitudinally throughout…

Plant Cell Division 4
Fourth stage in plant cell division: Protophase 4; "The nuclear membrane and the nucleolus have disappeared,…
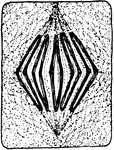
Plant Cell Division 5
Fifth stage in plant cell division: Metaphase; "The metaphase, where the longitudinal halves of the…

Plant Cell Division 6
Sixth stage in plant cell division: Anaphase; "The anaphase, or movement of the chromosomes toward the…
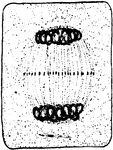
Plant Cell Division 7
Seventh stage in plant cell division: Telophase; "Telophase where the chromosomes have begun to spin…

Plant Cell Division 8
Eighth stage in plant cell division: "The connecting fibers have spread out and come into contact with…
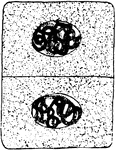
Plant Cell Division 9
Ninth and final stage in plant cell division: "A nuclear membrane has been formed about each daughter…
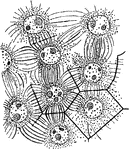
A. Eupatorium Cell
"Formation of endosperm in the embryo-sac of Agrimonia Eupatorium. Cell-walls are being formed between…
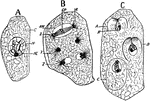
E. Communis Cell
"Free cell formation of spores in the ascus of Erysiphe communis. A, ascus with single nucleus; C, cytoplasm;…

S. Cerevisiae Cell Multiplication
"Various stages of cell multiplication by budding of Saccharomyces cerevisiae." -Stevens, 1916
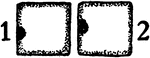
Collenchyma 1 and 2
Developmental stages of collenchyma: "1 and 2, cross and longitudinal section of a collenchyma cell…
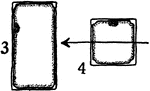
Collenchyma 3 and 4
Developmental stages of collenchyma: "3 and 4, longitudinal and cross sections of the same cell at a…
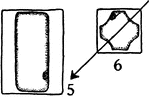
Collenchyma 5 and 6
Developmental stages of collenchyma: "5 and 6, longitudinal and cross sections of a mature cell. The…

Stone Cells 1
First developmental stage of stone cells: "1, in the primary meristem condition." -Stevens, 1916
Stone Cells 2
Second developmental stage of stone cells: "2, the cells have enlarged and the walls have begun to thicken…
Stone Cells 3
Third and final developmental stage of stone cells: "3, The walls are completed. The primary wall is…

Bast Fibers 1 and 2
Developmental stages of bast fibers: "1 and 2, cross and longitudinal sections of primary meristem cells…
Bast Fibers 3 and 4
Developmental stages of bast fibers: 3 and 4, cross and longitudinal sections of meristem cells becoming…
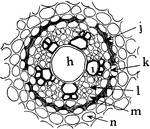
A. Ascalonicum Root
"Portion of a cross section of a root of Allium ascalonicum. h, large central, tracheal tube; i, xylem,…
Plant Cell Development 1
First developmental stage of sieve tubes, companion cells, and phloem parenchyma. "A, a and b, two rows…
Plant Cell Development 2
Second developmental stage of sieve tubes, companion cells, and phloem parenchyma. "B, c, companion…
Plant Cell Development 3
Third developmental stage of sieve tubes, companion cells, and phloem parenchyma. "The pits in the cross-walls…
Xylem Development 1
"Stages in the development of the elements of the xylem. A, progressive steps in the development of…
Xylem Development 2
Stages in the development of the elements of the xylem. "B, stages in the formation of tracheids from…
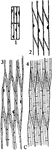
Xylem Development 3
Stages in the development of the elements of the xylem. "C, steps in the development of wood fibers…
Xylem Development 4
Stages in the development of the elements of the xylem. "D, steps in the formation of wood parenchyma…

Plant Tissues
"Diagram showing the relation of this year's leaves to the wood of the current year." -Stevens, 1916
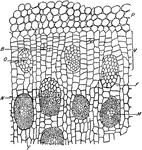
D. Marginata Stem
"Portion of a cross section throughout the stem of Dracaena marginata. P, parenchyma of cortex. V, meristematic…
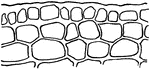
Multiple Epidermis
"Multiple epidermis of leaf of mangrove in cross section. This serves as a water reservoir, and the…
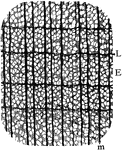
Yellow Poplar Wood
"Cross section of yellow poplar wood. E, early; L, late growth; m, medullary ray." -Stevens, 1916
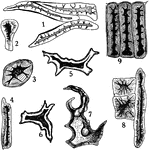
Stone Cells
"Stone cells from different sources. 1, from coffee; 2, 3, and 4, from stem of clove; 5 and 6, from…
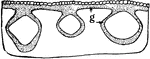
Cornstalk Bast Fibers
"Camera-lucida outline of portion of cross section of cornstalk, showing at g bast fiber zone beneath…
Palm Stem
"Cross section of a portion of palm stem. e, xylem; f, phloem portions of vascular bundle; g, sclerenchyma…
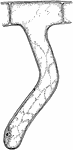
Plant Root Hair
"A single root hair on a large scale, showing that it is an outgrowth of an epidermal cell, and the…
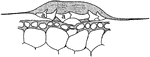
T. Usneoides Cell
"Cross section through a water-absorbing scale of Tillandsia usneoides; a, a, water-absorbing cells…

Magnified Pine
"Diagrammatic representation of a block of pine wood highly magnified. a, Early growth; b, late growth;…
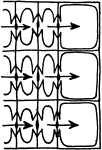
Water Flow in Pine
"Diagram to show the radial flow of water in pine wood, from the tracheids of the late growth of one…
Water Flow in Pine
"Diagram indicating by arrows how the water in the tracheids of pine passes longitudinally from one…
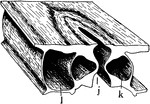
Stoma
"A typical stoma in cross section and surface view combined. k, guard cell; j, the gap or stoma between…
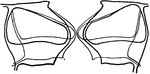
Stoma Guard Cells
"A, diagram showing relative position of the guard cells in cross section in the open and closed positions;…
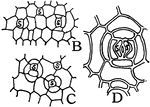
Stomata Formation
"B and C, early stages in the formation of stomata; at s, mother cells of guard cells are shown. D,…
Guard Cell Experiment
"Diagram of apparatus showing how the guard cells draw apart; j, j, position of the rubber tubing when…

Palisade Cell
"Diagrammatic representation of a single palisade cell, with chloroplasts lining the walls." -Stevens,…
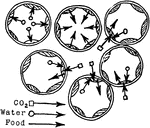
Palisade Cell Intake
"Diagram to show the intake of carbon dioxide by the palisade cells from the intercellular spaces, the…