Haddock
"The haddock. n.a., Nasal apertures (double on each side); d.f.1, d.f.2, d.f.3, dorsal unpaired fins;…

Carp
"External characters of a Teleostean--a carp (Cyprinus carpio). R., Dorsal unpaired fin; S., homocercal…
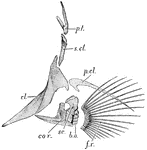
Cod Fin
"Pectoral girdle and fin of cod. fr., Fin-rays; b.o., brachial ossicles; cor., coracoid; sc., scapula;…

Teleostean Gill
"Section of a Teleostean gill. G.F., Gill-filament; A., artery (venous blood); V., vein (pure blood);…
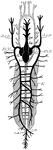
Teleostean Circulation
"Diagram of Teleostean circulation. A., auricle; V., ventricle; v.a., ventral aorta; a.br., afferent…
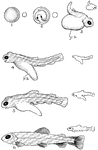
Salmon Development
"The early development of the salmon. 1, The fertilised egg; 2, the egg just before hatching; 3, the…
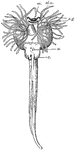
Young Skate
"Young skate. The yolk-sac has been cut off, the yolk-stalk is left. m., Mouth; ol.o., nostril, e.g.…
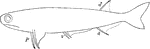
Acanthodes Sulcatus
"Outline of Acanthodes sulcatus. p., Pectoral fins; v., pelvis; a., anal; d., dorsal." -Thomson, 1916

Polypterus
"Larva of Polypterus. e.g., Large external gill of the hyoid arch; Pc., pectoral fins; Pv., pelvic fins.…
Sturgeon
"Sturgeon (Acipenser sturio). Note the elongated snout, the barbules bounding the ventral mouth, the…
South American Lungfish
"Lepidosiren showing (Pc.f.) pectoral fin and the tufted pelvic fin (Pv.f.) of the mature male." -Thomson,…
Queensland Lungfish Fin
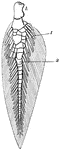
"Skeleton of Ceratodus fin. a., Central axis; r., radials; h., basal piece." -Thomson, 1916
African Lungfish Head
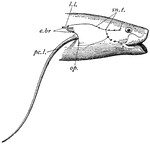
"Head region of Protopterus. sn.t., Sensory tubes; l.l., lateral line; e.br., external gills; pc.l.,…
African Lungfish Larva
"Larva of Protopterus. e.g., external gills; Pc., pectoral fin; Pv., pelvic fin." -Thomson, 1916
Octopus
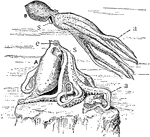
"The Devil-fish (Octopus). A, at rest; B, swimming. a, arms, with suckers on the inner aspect; e, eye;…
Fish Vertebrae
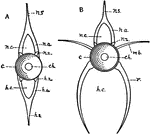
"Diagram of vertebrae of a bony fish. A, caudal; B, trunk. c, centrum or body of the vertebra; ch.,…
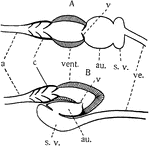
Vertebrate Heart
"Diagrams of the structure of the heart in the lower Vertebrates. A, primitive condition; B, the position…
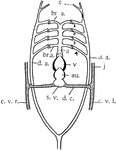
Teleost Heart
"Diagram of the heart, the branchial arches, and the principal veins in the Teleosts. Ventral view.…
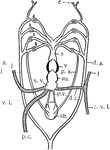
Queensland Lungfish Heart
"Diagram of heart and branchial arches in Ceratodus (one of the Dipnoi). a.b., air bladder (lung); p.a.,…
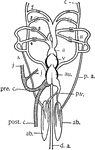
African Lungfish Heart
"Diagram of the heart and branchial arches in Protopterus (one of the Dipno). pre.c., precaval vein,…
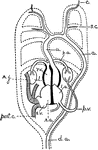
Mammal Heart
"Diagram of the heart and the branchial arches in Mammals. A dotted outline of the arches of the Fish…
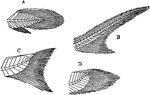
Fishtails
"Diagrams of some principal forms of tails in fishes. A, protocercal fin (as in Polypterus); B, heterocercal…
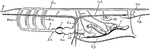
Fish Circulation Vessels
"Diagram of the principal vessels in the circulation of a Fish, lateral view. a, aorta; au., auricle;…
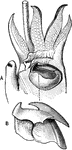
Cuttlefish Jaws
"Sepia officinalis, jaws. A, in situ; B, removed and slightly enlarged." -Parker, 1900
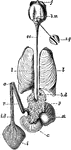
Cuttlefish Enteric Canal
"Sepia officinalis, enteric canal. a, anus; b. d, one of the bile ducts; b. m, buccal mass; c, caecum;…
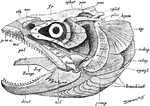
Fish Skull
"Salmo fario, the entire skull, from the left side. art, articular; branchiost, branchiostegal rays;…

Paleozoic Animals
"Fish, trilobites, brachiopods, corals, and graptolites of the Palaeozoic epoch." -Taylor, 1904
Gar-Pike
"The gar-pike (Lepidosteus osseus), a Ganoid fish, now living in North American rivers." -Taylor, 1904

The Sea horse
The Sea horse is a remarkable fish found near our South American coasts. It belongs to the singular…

Singular Star Fish
" The most singular of all the star fishes is the splendid Astrophyton. Its center is not unlike the…

Remora Fish
A genus of fished included in the Goby family, and of which the common remora or sucking fish, is the…

Rudd
A fish of the carp family, having the back of an olive color; the sides and belly yellow, marked with…

Saccopharynx
A genus of eels, family Murraenidae. It inhabits the depths of the Atlantic, is of a perfectly black…

Ctenoid, Scale
Fishes are sometimes classed, in accordance with the structure of their scale, into Ctenoid, Ganoid,…

Cycloid Scale of the Carp
Fishes are sometimes classed, in accordance with the structure of their scale, into Ctenoid, Ganoid,…

Ganoid Scales of Dipterus
Fishes are sometimes classed, in accordance with the structure of their scale, into Ctenoid, Ganoid,…

Placoid Scale of Ray
Fishes are sometimes classed, in accordance with the structure of their scale, into Ctenoid, Ganoid,…

Skeleton of a Haddock
The skeleton of a haddock. In some species such as the haddock, there is a modified form of the coracoid…
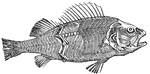
The Muscles of a Fish
In fish the chief masses of the muscular system are disposed on each side of the trunk in a series of…
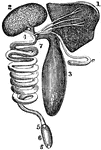
The Alimentary Canal of the Swordfish
In some species of fish the small intestine is in two to eight coils. The large intestines are short…

The Alimentary Canal of the Herring
There are two predominant forms of stomach in fish- one is like a bent tube (siphonal), and the other…
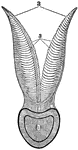
Section of a Branchial Arch of a Cod
In breathing, the mouth and gills of a fish open alternately; the water entering the mouth escapes by…
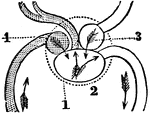
A Diagram of the Circulation of the Blood Through the Branchial Leaflets in a Fish
A diagram of the circulation of the blood through the branchial leaflets in a fish. Labels: 1. A section…
A Diagram of the Heart of a Fish
A diagram of the heart of a fish. Labels: 1, Pericardium. 2, The ventricle that receives the blood from…
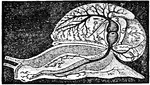
The Heart and Arteries of a Snail
In high orders of Mollusca the circulation resembles that of fish. Shown is the heart and arteries of…
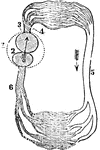
Circulation of a Fish
A diagram of the circulation of a fish. Labels: 1, The pericardium. 2, The single auricle. 3, The single…
Brain of a Fish
The brain of fish are small, it does not fill the whole cranial cavity, there being found within it…

Small-Mouthed Black Bass
"1. Spiny portion of dorsal fin. 2. Soft portion of dorsal fin. 3. Caudal fin. 4. Anal fin. 5. Pectoral…