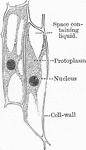
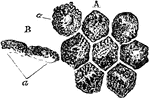
Eudorina
"Eudorina. The development of reproductive bodies within the colony from the ordinary vegetative cells…
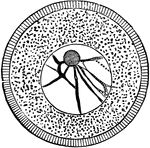
Flame Cell
"Diagram of flame cell, the internal terminus of the excretory tubules. c, cilia lining tubule; f, special…
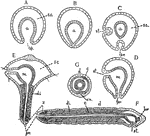
Polygordius
"Diagrams of stages in the metamorphosis of Polygordius, a primitive annelid. Ectoderm throughout is…
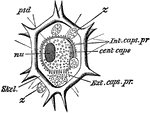
L. Annularis
"Liteocircus annularis. cent. caps, central capsule; ext. caps. pr, extra-capsular protoplasm; int.…
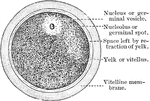
Sea Urchin Ovum
"Ovum of a Sea-Urchin, showing the radially striated cell-membrane, the protoplasm, containing yolk-granules,…
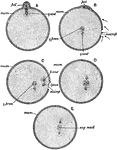
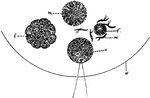
Ovum Fertilization
"Diagram illustrating the maturation and fertilization of the ovum. A, formation of first polar globule;…
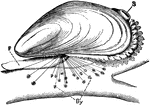
Blue Mussel
"Mytilus edulis, attached by byssus (By) to a piece of wood. F, foot; S, exhalant siphon." -Parker,…
Shipworm in Wood
"Teredo navalis, in a piece of timber. P, pallets; SS, siphons; T, tube; V, valve; of shell." -Parker,…
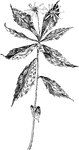
Sharp-Leaved Wood Aster
Of the Composite family (Compositae), the sharp-leaved wood aster (Aster acuminatus).

Fossil Wood
"Microscopical section of Fossil Wood, from clay iron-stone nodules; Oldham." -Taylor, 1904
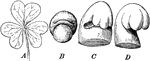
Oxalis Leaf Development
"Development of an oxalis leaf. A, full-grown leaf; B, rudimentary leaf, the leaflets not yet evident;…
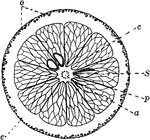
Orange
"Cross-section of an orange. a, axis of fruit with dots showing cut-off ends of fibro-vascular bundles;…

Manufacturing of Turpentine
Tar is made from the turpentine by the smothered burning of the wood. When burning the wood, it is placed…

The Gutta-percha tree
"It is a very large tree, the trunk being sometimes three feet in diameter, although it is of little…
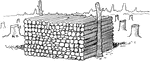
Cord of Wood
"A cord of wood is a solidly built pile of 8 feet long, 4 feet wide and 4 feet high. 1. How many cords,…

Sandal Wood
A tree belonging to the East Indies and the Malayan and Polynesian islands, remarkable for its fragrance.…
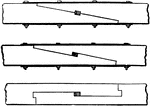
Scarfing Design
A particular method of uniting two pieces of timber together by the extremities, the end of one being…
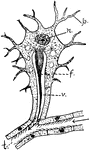
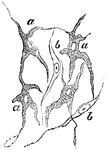
The Relation of Nerve Cells to Muscle
Diagram to show the relationship of nerve cell (NC) to Muscle (M) through its nerve fiber.

The Development of Muscular Fibers from Cells
The development of muscular fibers from cells. Labels: a, simple cell. b, a pair of cells fused together.…
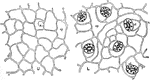
Leaf Epidermis
"Lizard's tail (Saururus cernuus). Portions of leaf-epidermis; U, upper epidermis; L, lower epidermis;…

Roots in Soil
"Diagram to illustrate a root-hair (h) in the soil, and its relation to the soil-particles, the capillary…
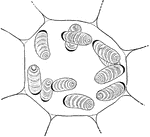
Pellionia Plant Cell
"Cell of Pellionia Daveauana, showing starch-grains. The black, crescent-shaped body on the end of each…
Cell with its Reticulum Disposed
A cell with its reticulum disposed radically; from the intestinal epithelium in a worm.
Intracellular Network of Blood Corpuscles
The intracellular network of colorless and colored blood corpuscles. Labels: A, The colorless blood…
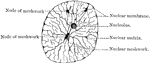
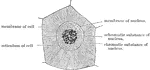
Nucleus at Rest
The nucleus when in a condition of rest is bounded by a distinct membrane, possibly derived from the…
Karyokinesis
Karyokinesis. Labels: a, ordinary nucleus of a columnar epithelial cell; B, C, the same nucleus in the…
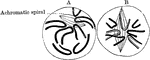
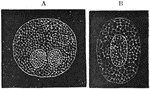
Early Stages of Karyokinesis
The early stages of karyokinesis. Labels: A, The thicker primary fibers remain and the achromatic spindle…
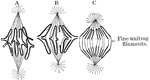
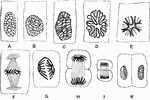
Metakinesis
Metakinesis- chromatic figure, spindle. Labels: A, early stage; B, later stage; C, latest stage-formation…
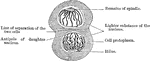
Final Stage of Karyokinesis
The final stage of karyokinesis. In the lower figure the changes are still more advanced than in the…
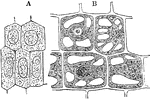
Vegetable Cell
A, A young vegetable cell, showing cell cavity entirely filled with granular protoplasm enclosing a…
Pigment Cells from the Retina
Squamous epithelium is found arranged as a single layer of flattened cells as the pigmentary layer of…
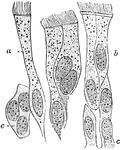
Ciliated Epithelium
Ciliated epithelium from the human trachea. Large fully formed cell. Labels: b, shorter cell; c, developing…
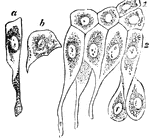
Epithelium of the Bladder
Epithelium of the bladder. Labels: a, one of the cells of the first row; b, a cell of the second row;…
Pigment Cells
Ramified pigment cells, from the tissue of the choroid coat of the eye. Labels: a, cell with pigment;…

Connective Tissue Cells from a Frog
Flat, pigmented, branched connective tissue cells from the sheath of a large blood vessel of a frog's…
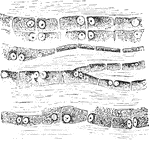
Structure of Tendon Cells
The cells in the tendons are arranged in long chains in the ground substance separating the bundle of…
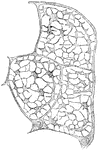
Branched Tendon Cells
The branched character of the cells is seen. Shown is a transverse section from a cross section of the…
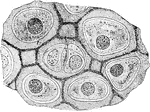
Hyaline Cartilage Cells
The matrix of hyaline cartilage has a dimly granular appearance like that of ground glass, and in man…
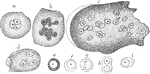
Cells of the Red Marrow
Red marrow occupies the spaces in the cancellous tissue; it is highly vascular, and this maintains the…
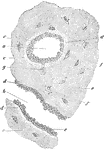
Formation of Compact Bone in a Human
Transverse section of femur of a human embryo about eleven weeks old. Labels: a, rudimentary Haversian…

Unstriped Muscle of a Newt
Unstriped muscle, or plain muscle, forms the proper muscular coats. Shown is unstriped muscle cells…
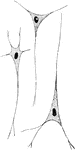
Ganglion Nerve Corpuscles
Nerve cells, also known as nerve corpuscles, comprise the second principle element of the nervous tissue.…
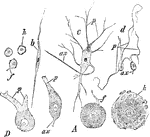
Different Forms of Ganglion Cells
Different forms of ganglion cells. A, a, round ball-shaped unipolar cell from the human Gasserian ganglion.…
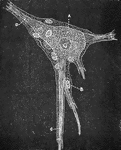
Ganglion Cell, Structure of
An isolated ganglion cell of a human, showing sheath with nucleated cell lining, B. A Ganglion cell,…

Effect of Acetic Acid on Red Blood Cells
Acetic acid (dilute) causes the nucleus of the red blood cells in the frog to become more clearly defined;…
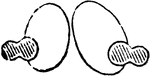
Effect of Boric Acid on Red Blood Cells
A 2 percent solution of boric acid applied to nucleated red blood cells of a frog will cause the concentration…