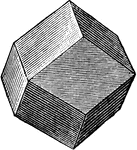
Rhombic Dodecahedron
A solid consisting of 12 similiar faces, each of which is rhomb, the angle between any two adjacent…
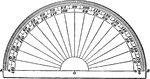
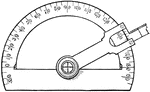
Protractor
"The outer edge is a semicircle, with center at 0, and is divided into 360 parts. Each division is one-half…
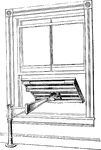
Painting Frame
"A patented frame that can be shoved out of the window and adjusted to any angle; it is made in different…
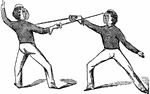
Carte
"Carte, Guard. Turn wrist with nails upwards; hand on a line with lower part of breast; arm somewhat…
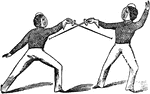
Seconde
"Seconde, Parade. Nails and wrist downward, hand opposed outward, and blade, pointing low, should form…
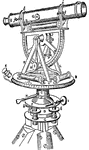
Theodolite
"An instrument much employed in land-surveying for the measurement of angles horizontal and verticle."…
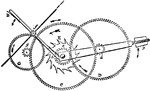
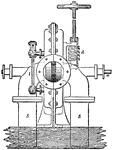
Gravity Train Remontoire
"E represents the scape-wheel turning in a minute, and e its pinion, which is driven by the wheel D…

Prothonotary Warbler
A beautiful bird of a rich yellow color, passing by degrees through olivaceous tints on te rump, wings,…
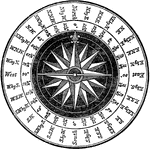
Compass Card
"Three principal parts, the card, the needle on its lower suface, and the case. The whole is enclosed…

Ball's Naturalists' Dredge
"The dredges on this pattern, used in Britain for ten years after their first introduction, about the…
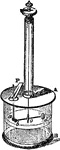
Torsion Balance
"ABCD is a cylinder of glass 1 foot in diameter and 1 foot high. This cylinder is closed by a glass…
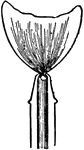
Burner
"Flat-flame burners, or burners which spread their flame in a broad thin sheet, are of two principal…
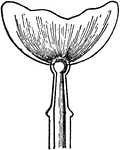
Burner
"Flat-flame burners, or burners which spread their flame in a broad thin sheet, are of two principal…
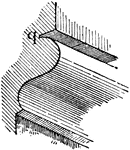
Quirk Molding
A molding characterized by a sharp and sudden return from its extreme projection to a reentrant angle.
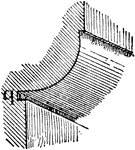
Quirk Molding
A molding characterized by a sharp and sudden return from its extreme projection to a reentrant angle.
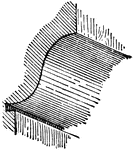
Quirk Molding
A molding characterized by a sharp and sudden return from its extreme projection to a reentrant angle.
Quirk Molding
A molding characterized by a sharp and sudden return from its extreme projection to a reentrant angle.
Pruning
"The nature of the cut itself in pruning is of more consequence, especially in the case of fruit trees,…

Pruning
"The nature of the cut itself in pruning is of more consequence, especially in the case of fruit trees,…
Pruning
"The nature of the cut itself in pruning is of more consequence, especially in the case of fruit trees,…
Pruning
"The nature of the cut itself in pruning is of more consequence, especially in the case of fruit trees,…
Pruning
"The nature of the cut itself in pruning is of more consequence, especially in the case of fruit trees,…
Pruning
"The nature of the cut itself in pruning is of more consequence, especially in the case of fruit trees,…
Montreuil Fan
"The Montreuil form of training. The principal feature is the suppression of the direct channel of the…
Reaction Turbine
"Professor James Thomson's inward flow or vortex turbine has been selected as the type of reaction turbines.…
Reaction Turbine
"Professor James Thomson's inward flow or vortex turbine has been selected as the type of reaction turbines.…
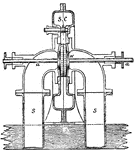
Reaction Turbine
"Professor James Thomson's inward flow or vortex turbine has been selected as the type of reaction turbines.…
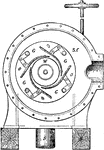
Reaction Turbine
"Professor James Thomson's inward flow or vortex turbine has been selected as the type of reaction turbines.…

Oriole
"A very beautiful American, bird, found in all parts of the United States, and as far north as 55 degrees…
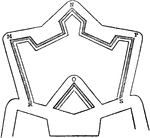
Crown-Work
"Crown-work, in Fortification, is formed to strengthen a weak front, or to occupy ground which might…
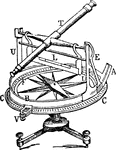
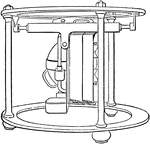
Declinometer
"Upon a tripod provided with levelling screws stands the pillar P, to which is fixed the graduated azimuthal…
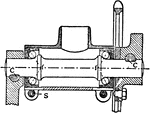
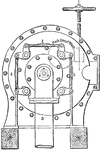
Crank-axle Bearing
"The usual form of crank-axle bearing which has inward-cups and is cup-adjusting. The end of the bracket…
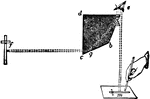
Camera Lucida
"An optical instrument employed to facilitate the sketching of objects from nature by producing a reflected…

Ipecacuanha Plant
"The root used in medicine under this name is obtained from Cephaelis Ipecacuanha, A. Rich, a small…
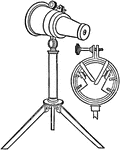
Polyangular Kaleidoscope
"Another form is called the polyangular kaleidoscope. The only essential difference in it is that the…
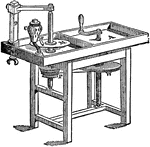
Lapidary's Mill
"In the ordinary pattern of a lapidary's bench the handle turns in a horizontal plane, where W is the…
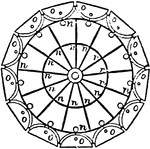
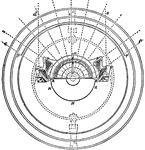
Revolving Light
"In order to produce, on the catoptric system, a fixed light showing all round the circle, a number…
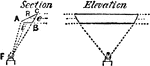
Reflecting Prism
"Fresnel next conceived the admirable improvement of employing the principle of "total" or internal…

Dioptric Holophote
"Perfect Form of Dioptric Holophote for an Oil Flame.—By combining the back prisms ga, hc just described…
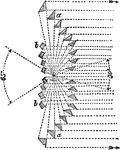
Swans Designs
"Professor Swan's Designs.—Among several ingenious arrangements and new forms of agents proposed by…
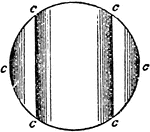
Differential Lens
"Differential Lens.—Horizontal divergence may be obtained to any required amount by varying the radius…
Differential Lens
"Differential Lens.—Horizontal divergence may be obtained to any required amount by varying the radius…
Differential Lens
"Differential Lens.—Horizontal divergence may be obtained to any required amount by varying the radius…
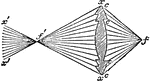
Condensing Apparatus
"Condensing Apparatus for Steamer's Side Lights.—By means of this application of the condensing…
Condensing Apparatus
"Condensing Apparatus for Steamer's Side Lights.—By means of this application of the condensing principle…
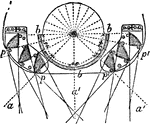
Condensing Quadrant
"Condensing Quadrant.—The fixed apparatus bbb, with spherical mirror behind, throws its rays directly…
Condensing Octant
"Condensing Octant.—The central fixed apparatus bb with spherical mirror dd throws its rays directly…
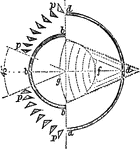
Condensing Octant
"Condensing Octant.—The central fixed apparatus bb with spherical mirror dd throws its rays directly…
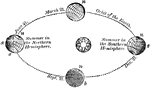
Seasons
"Suppose the Earth to be in her Summer solstice, which takes place on the 21st of June. At this period…
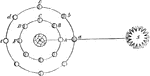
Moon Phases
"Let S be the Sun, E the Earth, and A, B, C, D, F, the Moon in different parts of her orbit. Now when…
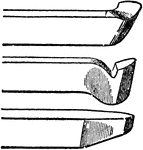
Slide-Rest Tools
"The middle one an ordinary hook tool, suited for outside work on wrought iron or steel, and the one…
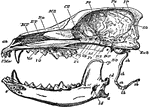
Dog Skull
"Longitudinal and Vertical section of the skull of a dog, with mandible and hyoid arch. an, anterior…

Micrometer
"The original Merz micrometer of the Cape Observatory, made on Fraunhofer's model. S is the head of…
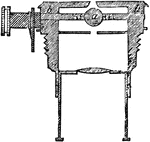
Micrometer
"a is the sphere, placed in half-holes on the axis bb, so that when its principal axis is parallel to…
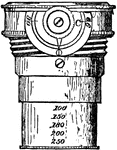
Micrometer
"a is the sphere, placed in half-holes on the axis bb, so that when its principal axis is parallel to…
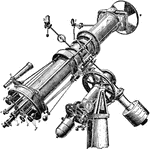
Micrometer
"The circles for position angle and declination are read by micrometer microscopes illuminated by the…

Still Life with Globe and Telescope
Still life arrangement including a globe, telescope, book, right angle, rolled map, and dividers.
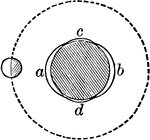
Lunar Tide
If the earth were uniformly covered with a layer of water, the passage of the moon over any place as…