Lunge
"Executed in the same manner as the thrust, except that the left foot is carried forward about twice…

Left-Handed Rifle
"As additional instruction, the men may be permitted to wield the rifle left handed, that is on the…
Stock, top view
"The parts are the butt, A; small, B; magazine well, C; barrel bed, D; air chamber, E, which reduces…
Stock, right side view
"The parts are the butt, A; small, B; magazine well, C; barrel bed, D; air chamber, E, which reduces…

Guy Fawkes and his associates
"One of the most extraordinary events in the history of England is that commonly known by the name of…
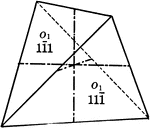
Positive and negative tetrahedrons
"If a positive and negative tetrahedron occured together with equal development, the resulting crystal…
Raised Fillet
A roman moulding, called Raised Fillet. Its projection is generally made equal to its height.…

Pistillate flower
"The stamens are situated on the calyx, and they may be artificially removed or suppressed by nature,…
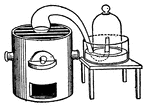
Retort
A retort is a primitive device used for distillation or dry distillation of substances. In the latter…
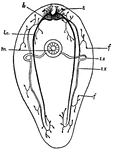
Turbellarian
This is a diagram of a Turbellarian, showing the general arrangement of the nervous structures and one…
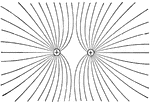
Electricity
This illustration represents the field between two equal positive charges; in this case the lines of…
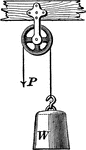
Fixed Pulley
"A fixed pulley is one whose block is not movable. In this case, if the weight W be lifted by pulling…
Barometer
"The barometer is simply a pressure gauge that registers the pressure of the air. In this case the cup…
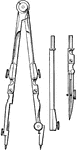
Compasses
"The compasses, next to the T square and triangles, are used more than any other instrument. A pencil…
Compasses
"The compasses, next to the T square and triangles, are used more than any other instrument. A pencil…
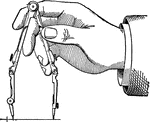
Compasses
"The compasses, next to the T square and triangles, are used more than any other instrument. A pencil…
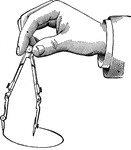
Compasses
"The compasses, next to the T square and triangles, are used more than any other instrument. A pencil…
Compasses
"The compasses, next to the T square and triangles, are used more than any other instrument. A pencil…
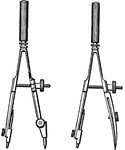
Compasses
"The compasses, next to the T square and triangles, are used more than any other instrument. A pencil…
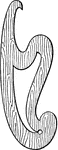
Irregular Curves
"Curves other than arcs of circles are drawn with the pencil or ruling pen by means of curved or irregular-shaped…
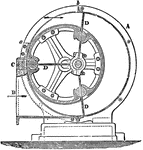
Blowing-Machine
"An American machine, introduced into England by Mr. Ellis. It consists of an iron cylindrical casing…
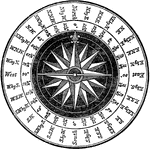
Compass Card
"Three principal parts, the card, the needle on its lower suface, and the case. The whole is enclosed…

Viollet-le-Duc
"A complete dress, with the exception of sides and sleeves, in which case it was either made to fit…
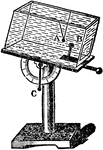
Sine Electrometer
"The sine electrometer of August, is a modification of the single pendulum electroscope, analogous in…
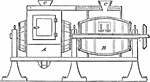
Glazing Barrel
"Glazing Barrels. A, elevation, showing door of case; C, hoppers for loading; B, section through barrel…
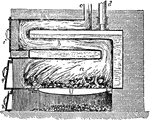
Saddle Boiler
"The fire is made under the principal arch a; the flame and smoke return through the flue b, and then…
Sulphurator
"Sulphurators are instruments for distributing flowers of sulphur, for the purpose of destroying mildew.…
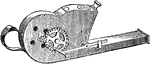
Epps's Sulphurator
"Sulphurators are instruments for distributing flowers of sulphur, for the purpose of destroying mildew.…
Suckering Iron
"Root suckers are young shoots from the roots of plants, chiefly woody plants, as may often be seenin…
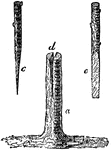
Cleft-Grafting
"Cleft-grafting is another method in common use. The stock a is cleft down from the horizontal cut d,…
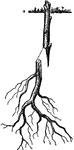
Root-Grafting
"In the case of large woody plants thus worked the grafted roots, after the operation is completed,…
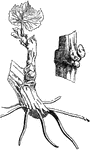
Single Eye
"This mode of propagation is performed by cutting the branches into short lengths, each containing one…
Pruning
"The nature of the cut itself in pruning is of more consequence, especially in the case of fruit trees,…

Pruning
"The nature of the cut itself in pruning is of more consequence, especially in the case of fruit trees,…
Pruning
"The nature of the cut itself in pruning is of more consequence, especially in the case of fruit trees,…
Pruning
"The nature of the cut itself in pruning is of more consequence, especially in the case of fruit trees,…
Pruning
"The nature of the cut itself in pruning is of more consequence, especially in the case of fruit trees,…
Pruning
"The nature of the cut itself in pruning is of more consequence, especially in the case of fruit trees,…

Summer Pruning
"Summer Pruning should be performed while the shoots are yet young and succulent, so that they may be…
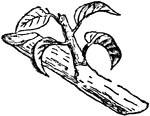
Summer Pruning
"Summer Pruning should be performed while the shoots are yet young and succulent, so that they may be…
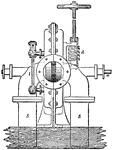
Reaction Turbine
"Professor James Thomson's inward flow or vortex turbine has been selected as the type of reaction turbines.…
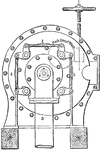
Reaction Turbine
"Professor James Thomson's inward flow or vortex turbine has been selected as the type of reaction turbines.…
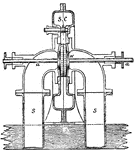
Reaction Turbine
"Professor James Thomson's inward flow or vortex turbine has been selected as the type of reaction turbines.…
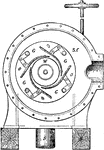
Reaction Turbine
"Professor James Thomson's inward flow or vortex turbine has been selected as the type of reaction turbines.…
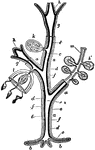
Hydromedusa
"Diagram showing possible modifications of persons of a gymnoblastic Hydromedusa. a, hydrocaulus (stem);…
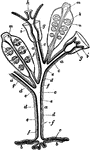
Hydromedusa
"Diagram showing possible modifications of the persons of a Calyptoblastic Hydromedusa. a, hydrocaulus…

Acropolis
"Acropolis, 'the highest point of the city.' Many of the important cities of Greece and Asia Minor were…
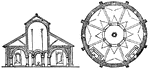
Baptistery
"A name given sometimes to a seperate building, sometimes to the portion of the church itself in which…