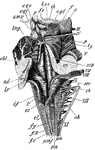
Medulla
Dorsal or posterior view of the medulla, fourth ventricle, and mesencephalon. Labels: p.n., line of…
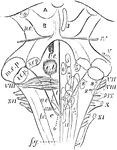
Fourth Ventricle with the Medulla Oblongata and the Corpora Quadrigemina
Fourth ventricle with the medulla oblongata and the corpora quadrigemina. The roman numbers indicate…
Chair of St. Peter Arm-Chair
The chair of St. Peter was made out of wood with ivory reliefs illustrating the story of Hercules in…

Roman Arm-Chair
The Roman Arm-chair had a decoration symbolic of Ceres, the Roman goddess of growing plants.
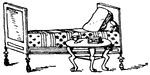
Roman Bedstead
This Roman bedstead had a Pompeian vase-painting. It included a head and foot board. It was made out…

Pinna Rudis (Linnaeus)
"The genus Pinna was so called from its resemblance to the plumelet which the Roman soldiers…

Pinna Nigrina (Lamarck)
"The genus Pinna was so called from its resemblance to the plumelet which the Roman soldiers…

Pinna Nobilis, with its byssus (Linnaeus)
"The genus Pinna was so called from its resemblance to the plumelet which the Roman soldiers…
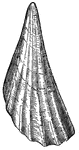
Pinna Bullata (Swainson)
"The genus Pinna was so called from its resemblance to the plumelet which the Roman soldiers…

Construction of a Portion of Appian Way
A famous road with many branches which connected Rome with Southern Italy
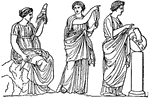
Fates
The three fates of Greek Mythology were three sisters who spun the thread of life named Clotho, Lachesis,…

Francis Joseph I
"Francis Joseph I (1830-1916), emperor of Austria and king of Hungary, and next to the last of the Hapsburg…

Frederick II
(1712-1786) King of Prussia from the Hohenzollern dynaasty, known as the founder of Germany's military…

Picciola
An illustration of the story, Picciola by X. B. Saintine. Count Charney was imprisoned by the Emperor…

Portrait of the Emperor Maximilian
"Portrait of the Emperor Maximilian. From a drawing by Dürer in the Albertina Gallery in Vienna."…

Apatura Ilia
"In the month of July, the Apatura Ilia and the Purple Emperor may be observed in the woods.…

The Pantheon at Rome
The Pantheon is a building in Rome which was originally built as a temple to all the gods of Ancient…

Hadrian's Wall
Hadrian's Wall is a stone and turf fortification built by the Roman Empire across the width of what…

St. Alban's Shrine
Saint Alban was the first British Christian martyr. Along with his fellow saints Julius and Aaron, Alban…

The City of Constantinople (Byzantium)
Byzantine Constantinople had been the capital of a Christian empire, see Christendom, successor to ancient…

Roman Amphitheatre at Arles
The Arles Amphitheatre is a Roman amphitheatre in the southern French town of Arles.

Roman Soldiers
The distinction between rank and unit type doesn't seem to have been as precise as in a modern-day army,…

St. Asaph Cathedral
St Asaph Cathedral, (Welsh: Eglwys Gadeiriol Llanelwy) at St Asaph, Denbighshire, north Wales, is sometimes…

Roman Lighthouse, and Part of St. Mary's Church, Dover
The lighthouse on the Eastern Heights still stands in the grounds of Dover Castle to 80 foot (24 m)…

St. Paul's Cathedral
St Paul's Cathedral, is the Anglican cathedral on Ludgate Hill, in the City of London, and the seat…

The Door of the Roman Bridge
This image depicts the door leading to the Puente Romano, a Roman bridge in Cordoba, Spain.

Hexham Abbey
There has been a church on the site for over 1300 years since Etheldreda, Queen of Northumbria made…

Bede's Tomb, Durham Cathedral
He is well known as an author and scholar, and his most famous work, Historia ecclesiastica gentis Anglorum…

Benedictine Monk
Within Roman Catholicism, a monk is a member of a religious order who lives a communal life in a monastery,…

Earls-Barton Saxon Tower
The influence is very much Roman, and this can be seen by looking at the doors and windows of the tower.…

Pope Gregory VII
Pope Saint Gregory VII (c. 1020/1025 – May 25, 1085), born Hildebrand of Soana (Italian: Ildebrando…

Odo of Bayeux
Odo of Bayeux (c. 1036 – February 1097, Palermo), Norman bishop and English earl, was the half-brother…

Rochester Castle
Rochester Castle stands on the east bank of the River Medway, in Rochester, Kent. It is one of the best-preserved…

St. John's Church, Lateran Palace, Rome
The Basilica of St. John Lateran (Italian: Basilica di San Giovanni in Laterano) is the cathedral of…
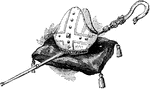
Mitre and Crosier
The mitre is a type of headgear now known as the traditional, ceremonial head-dress of bishops and certain…

General View of Rome
Rome is the capital city of Italy and Lazio, and is Italy's largest and most populous city, with more…

Cistercian Monk
The Order of Cistercians, sometimes called the White Monks, is a Roman Catholic religious order of enclosed…

Henry II
Henry II of England (5 March 1133 – 6 July 1189) ruled as King of England (1154–1189). Henry…

Costume of a Bishop (12th Century)
The pontifical vestments, also referred to as episcopal vestments or pontificals, are the liturgical…

Richard I
Richard I (8 September 1157 – 6 April 1199) was King of England from 6 July 1189 until his death.…

King John
John (24 December 1167 – 19 October 1216) reigned as King of England from 6 April 1199, until…

Henry III
Henry III (1 October 1207 – 16 November 1272) was the son and successor of John "Lackland" as…

Edward II
Edward II, (April 25, 1284 – September 21, 1327?) of Caernarfon, was King of England from 1307…

John Wycliffe
John Wycliffe (mid-1320s – 31 December 1384) was an English theologian, translator and reformist.…

Norman Doorway
The term Norman architecture is used to categorise styles of Romanesque architecture developed by the…

Early English Door
The most significant and characteristic development of the Early English period was the pointed arch…

Decorated Doorway
The most significant and characteristic development of the Early English period was the pointed arch…

Decorated Arch and Piscina
A piscina or sacrarium is a shallow basin placed near the altar of a church, used for washing the communion…
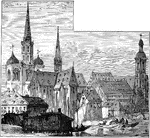
Constance Cathedral
The Cathedral of Constance (Konstanzer Münster in German) served as the central church of the diocese…