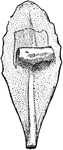
Sedum Leaf
"Leaf of a live-forever (Sedum sp.), with a portion of the epidermis peeled back. Underneath the epidermis…
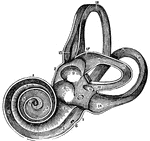
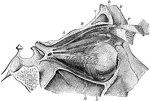
View of the Labyrinth Laid Open
A view of the labyrinth laid open. Labels: 1, The cochlea. 2, 3, Two channels that wind two and half…
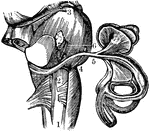
View of the Auditory Nerve
A view of the auditory nerve. Labels: 1, The spinal cord. 2, The medulla oblongata. 3, The lower part…
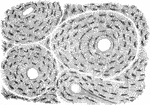
A Magnified View of a Bone
A thin slice of bone, highly magnified, showing the lacunae, the tiny tubs (canaliculi) radiating from…
The Spine
The spine showing the seven vertebrae of the neck, cervical; the twelve of the back, dorsal; the five…
Microscopic View of a Muscle
A microscopic view of a muscle showing, at one end, the fibrillae; and at the other, the disk, or cells…
Muscles of the Eye
The muscles of the right eye. Labels: A, superior straight; B, superior oblique passing through a pulley,…

Magnified View of the Cuticle
Magnified views of the cuticle. Labels: A, represents a vertical section of the cuticle. B, the lateral…
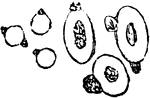
Corpuscles of Human and Animal Blood
A magnified view of corpuscles of human blood compared to animal blood. Labels: A, corpuscles of human…

Epithelium of the Rabbit's Cornea
The vertical section of the stratified epithelium of the cornea of a rabbit. Labels: a, Anterior epithelium…
Effect of Tannin on Red Blood Cells
When a 2 percent fresh solution of tannic acid is applied to frog's blood it causes the appearance of…
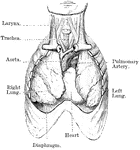
Heart and Lungs
View of heart and lungs in situ. The front portion of the chest wall, and the outer or parietal layers…
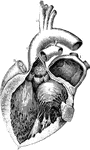
A Diagram of the Heart
The left auricle and ventricle opened and a part of their anterior and left walls removed. The pulmonary…

Surface View of an Artery
Surface view of an artery from the mesentery of a frog, ensheathed in a perivascular lymphatic vessel.…
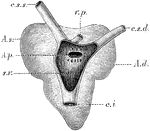
Heart of a Frog
The heart of a frog (Rana esculenta) from the back. Labels: s.v., sinus venosus opened; c.s.s., left…
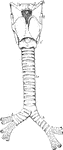
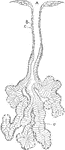
Front View of Respiratory Apparatus
Outline showing the general form of the larynx, trachea, and bronchi, as seen from front. Labels: h,…
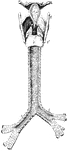
Back View of Respiratory Apparatus
Outline showing the general form of the larynx, trachea, and bronchi, as seen from behind. Labels: h,…
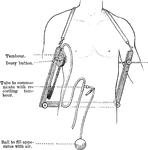
Stethometer
The stethometer consists of a frame formed of two parallel steel bars joined by a third at one end.…
Mucous Gland from Tongue
Section of a mucous gland from the tongue. Labels: A, opening of the duct on the free surface; C, basement…
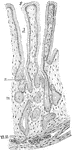
Pyloric Gland
Section showing the pyloric glands. Labels: s, free surface; d, ducts of pyloric glands; n, neck of…

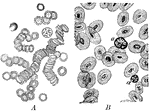
Types of Microorganisms
Types of microorganisms. Labels: a, micrococci arranged singly; in twos, diplococci- if all the micrococci…
Magnified Surface of a Hair
The hair is produced by a peculiar growth and modification of the epidermis. Externally it is covered…
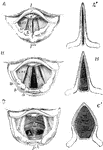
Movement of the Vocal Cords
Three laryngoscopic view of the superior aperture of the larynx and surrounding parts. Labels: A, the…
Upper Part of the Larynx
View of the upper part of the larynx as seen by means of the laryngoscope during the utterance of a…
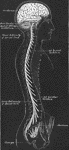
Central Nervous System
View of the cerebrospinal axis of the nervous system. The right half of the cranium and trunk of the…
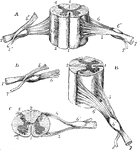
Views of a Spinal Cord
Different views of a portion of the spinal cord from the cervical region, with the roots of the nerves.…
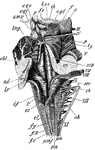
Medulla
Dorsal or posterior view of the medulla, fourth ventricle, and mesencephalon. Labels: p.n., line of…
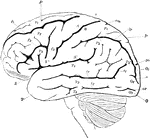
Lateral View of the Brain
Lateral view of the brain. F, Frontal lobe; P, Parietal lobe; O, Occipital lobe; T, Temporal lobe; S,…
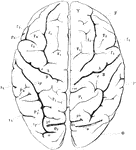
View of Brain from Above
View of brain from above. F, Frontal lobe; P, Parietal lobe; O, Occipital lobe; T, Temporal lobe; S,…
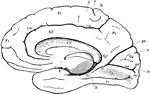
Right Hemisphere of the Brain
View of the right hemisphere in the median aspect. CC, corpus callosum longitudinally divided; Gf, gyrus…
Cortical Gray Matter of the Cerebrum
The five layers of the cortical gray matter of the cerebrum. 1, Superficial layer with abundance of…
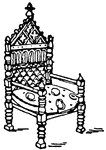
King David's Arm-Chair
King David's Arm-chair was designed in the 13th century. The Arm-chair was made from a relief portal…
Modern Cane Chair
The cane chair's seat or back is of woven cane-work or padded. The Chair is termed "cane" meaning upholstered.

Modern cane chair
The cane chair's seat or back is of woven cane-work or padded. The Chair is termed "cane" meaning upholstered.

German 17th Century Chair
The German 17th century chair had openings for the hand that were carved into the wooden back of the…

German 17th Century Chair
The German 17th century chair had openings for the hand that were carved into the wooden back of the…

German 17th Century Chair
The German 17th century chair had openings for the hand that were carved into the wooden back of the…

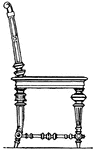
Modern Chair
The modern chair's top of the back is horizontal and is crowned with a cornice or an ornament.

Tablet Frame
This modern Tablet Architectural frame was in the style of the Italian Renaissance. It had the general…

Pulpit Frame
The pulpit Architectural frame was a German frame that was dated between 1595 to 1597. It had the general…

Ancient Persian Throne
The Ancient Persian Throne was decorated to represent a king sitting on his throne borne-up by slaves.

Cerebellum of Dog's Brain
Vertical section of dog's cerebellum. Labels: p m, pia mater; p, corpuscles of Purkinje, which are branched…
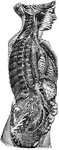
Sympathetic System
Diagrammatic view of the Sympathetic cord of the right side, showing its connections with the principal…
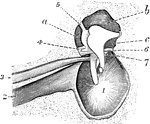
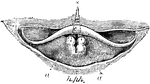
Tympanum
Interior view of the tympanum, with membrana tympani and bones in natural position. 1, Membrana tympani;…
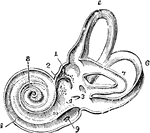
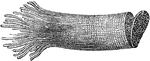
Interior of the Left Labyrinth
View of the interior of the left labyrinth. The bony wall of the labyrinth is removed superiorly and…
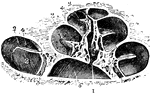
Osseous Cochlea
View of the osseous cochlea divided through the middle. Labels: 1, central canal of the modiolus; 2,…

Magnified Rabbit's Cornea
Vertical section of rabbit's cornea. Labels: anterior epithelium, showing the different shapes of the…
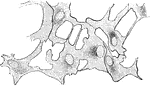
Lamella of Kitten's Cornea
Surface view of part lamella of kitten's cornea, prepared first with caustic potash and then with nitrate…

Section of Rabbit's Cornea
Vertical section of rabbit's cornea, stained with gold chloride. Labels: e, Laminated anterior epithelium.…
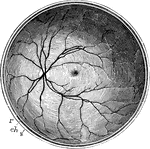
Posterior Half of the Retina
The posterior half of the retina of the left eye, viewed from before; s, the cut edge of the sclerotic…
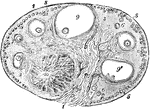
Ovary of the Cat
View of a section of the ovary of the cat. Labels: 1, outer covering and free border of the ovary; 1',…

Hair-Cap Moss
"Hair-cap moss (Polytrichum commune). A, male plant; B, same, proliferating; C, female plant, bearing…
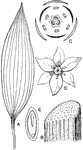
Monocotyledonous Morphology
"Morphology of typical monocotyledonous plant. A, leaf, parallel-veined; B, portion of stem, showing…
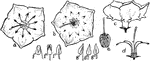
Mountain Laurel
"Mountain laurel (Kalmia latifolia). a, stamens in their original position, with the anthers in the…
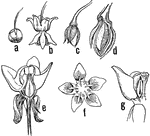
Milkweed Stages
"Milkweed (Asclepias sp.). a, flower-bud; b, flower; c, very young pod; d, older pod in section, showing…
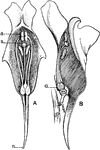
Common Toadflax
"Sections of flowers of the toad-flax (Linaria vulgaris). A, front view; a, anthers; s, stigma; n, nectar-gland.…
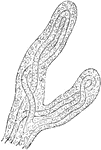
Magnified View of Chorion Villi
Very soon after the entrance of the ovum into the uterus, in the human subject, the outer surface of…
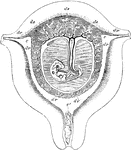
Uterus at Seventh Week of Pregnancy
Diagrammatic view of a vertical transverse section of the uterus at the seventh week of pregnancy. Labels:…
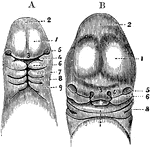
Head of an Embryo
A, Magnified view of the head and neck of a human embryo of three weeks. Labels: 1, anterior cerebral…
