
General Burnside
"Major General Burnside assuming command of the Army of the Potomac- issuing orders to his staff. 'Headquarters,…
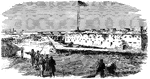
Fort Macon
"Surrender of Fort Macon, GA., April 26th, 1862. Exterior on side facing the Federal Batteries, showing…

Battle of Antietam
"Battle of Antietam, Md. Burnside's division carrying the bridge over the Antietam Creek and storming…

Fort Macon
"Surrender of Fort Macon, GA., April 26th, 1862- lowering the Confederate flag."— Frank Leslie,…

Killing's Cave
"Killing's Cave, on the banks of the Potomac, near Sharpsburg, the place of refuge of many citizens…

Bird's Point
"View of the fortifications erected by the Federal troops at Bird's Point, MO., opposite Cairo, Ill."—…

Army of the Potomac
"Advance of the Army of the Potomac. Occupation of Winchester, VA., and the abandoned Confederate Fortifications,…
Confederates
"Confederates in ambush firing on a reconnoitring expedition to Oyster Creek, Roanoke Island, N.C."—…

Fort Thompson
"Bombardment and capture of Fort Thompson, thirteen guns, near New Berne, on the Neuse River, by the…

Pocotaligo Bridge
"The Federal troops under Generals Brannan and Terry driving the Confederates under beauregard across…

Federal Baggage Train
"Federal baggage train on its way to the army at Falmouth, VA., December, 1862. Our illustration represents…

Admiral Silas H. Stringham
"Rear admiral Stringham, born in Middletown, Orange County, N. Y., November 7th, 1798; died in brooklyn,…

Masquerade of War
"The Masquerade of War. Ingenious method of disguising the masts and hulls of Commodore Porter's morter…

Columbus, Kentucky
"General view of Columbus, Ky., and its fortications, looking down the river, showing the 'Iron Bluffs'…

Paducah, Kentucky
"View of the town of Paducah, Ky., at the confluence of the rivers Ohio and Tennessee, the Northern…

General John Buford
"General Buford, born in Kentucky in 1825, died in Washington, D. C., December 16th, 1863, was graduated…

General Thomas L. Crittenden
"General Crittenden, born in Russellville, Ky., May 15th, 1815, studied law under his father, was admitted…

General George W. Morgan
"General Morgan, born in Washington County, Pa., September 20th, 1820, died at Old Point Comfort, Va.,…

General John G. Foster
"General Foster, born in Whitefield, N. H., May 27th, 1823, died in Nashua, H. H., September 2nd, 1874,…

Reconnoissance
"Reconnoissance by Colonel Max Weber's Turner rifles in the vicinity of Newmarket Bridge, on the road…

Battle of South Mountain
"Federal artillery taking up position at the Battle of South Mountain. The Federal movement was admirably…

The Forlorn Hope
"'The Forlorn Hope.' Volunteers storming party, consisting of portions of the Seventh Michigan and Nineteenth…

Naval Battle
"Naval action between the United States war steamer Mississippi and the Confederate iron-cased…

Confederate Schooner
"Bird's-eye view of the burning of a Confederate schooner in Quantico or Dumfries Creek, Potomac River,…

Encampment of Colonel Max Weber's Rifle Regiment
"Encampment of Colonel Max Weber's German Turner Rifle Regiment, Twentieth New York Volunteers, at Hampton…

Thoroughfare Gap
"Thoroughfare Gap, Va., a pass in the mountains on the Manassas Gap Railroad, near Strasburg, held by…

Campaign in Kentucky
"The campaign in Kentucky, Federal troops under General Johnston, advancing on the Louisville and Nashville…

Confederate Position
"Confederate position near Centreville, Va., at the crossing of the Orange and Alexandria Railway over…

Stockades at Newport News
"Erecting stockades at Newport News, Va., by the Federal Troops, June 1861."— Frank Leslie, 1896

Confederate Fortifications
"Interior of the principal Confederate fortifications near New Berne, N. C., after their capture by…

Destruction of Nashville
"Destruction of the famous Confederate privateer Nashville, in the Ogeechee River, Ga., by…
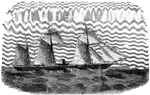
Steamer Alabama
"The Confederate privateer steamer Alabama (290). Captain Raphael Semmes. Our illustration…

Civil War Musical Entertainment
"Extempore musical and terpischorean entertainment at the United States arsenal, Baton Rouge, La., under…

Foraging spoils
"Return of a foraging party of the Twenty-fourth Regiment, Connecticut Volunteers, with their spoils,…

Federal Hill
"Federal Hill, Baltimore, taken from the North side basin, occupied by the Federal Troops."— Frank…
Fort Clinch
"Exterior view of Fort Clinch, on Amelia Island, Fla., commanding the Harbor of Fernandina, captured…

Vermont Regiment
"Encampment of the First Vermont Regiment, Colonel Phelps, at Newport News, Va."— Frank Leslie, 1896
Fort Clinch
"Interior view of Fort Clinch, on Amelia Island, Fla., commanding the Harbor of Fernandina, captured…

Federals Crossing
"Federal Volunteers crossing from Cincinnati to Covington on a bridge of coal boats, constructed for…

Battle of Antietam
"Battle of Antietam, Burnside's Division, left wing- brilliant and decisive bayonet charge of Hawkins's…

General Edward O. C. Ord
"General Ord, born in Cumberland, Md., October 18th, 1818, died in Havana, Cuba, July 22nd, 1883, was…

General Francis C. Barlow
"General Barlow, born in Brooklyn, N. Y., October 18th, 1834, was graduated at Harvard in 1855. In 1861…

General George H. Sharpe
"General Sharpe, born in Kingston, N. Y., February 26th, 1828, was graduated at Rutgers in 1847; studied…

Battle of Antietam
"Battle of Antietam- the opening of the fight- Hooker's division fording the Great Antietam Creek to…

Confederate Cavalry
"Confederate cavalry driving stragglers and skulkers back to their duty at the Battle of Antietam. One…

Bombardment of Fredericksburg
"Bombardment of Fredericksburg, Va., by the army of the Potomac, commanded by General Burnside, Thursday,…

Land Practice
"Land practice of sailors with the Dahlgren Howitzer Boat Gun, sponging out the gun."— Frank Leslie,…

Artillery Practice
"Artillery practice with the Dahlgren Howitzer boat gun- loading."— Frank Leslie, 1896

Artillery Practice
"Artillery practice with the Dahlgren Howitzer boat gun- officer giving the word of command to fire."—…

The Pirate's Decoy
"'The Pirate's Decoy' Captain Semmes, of the Confederate privateer Alabama, decoying ships…
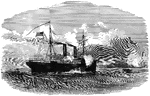
Quaker City
"The Quaker City, one of the Potomac Flotilla, engaging Confederate dragoons in Lynn Haven…
Charleston Harbor
"The harbor of Charleston, S. C.- Fort Moultrie, on Sullivan's Island."— Frank Leslie, 1896

Hilton Head
"Exterior view of fortifications erected by the Federal troops at Hilton Head, Port Royal. S. C. Hilton…

Castle Garden
"Reception of Brigadier General Corcoran by Mayor Opdyke and the citizens of New York, at Castle Garden,…

Grand Skedaddle
"The 'Grand Skedaddle' of the inhabitants from Charleston, S. C., when threatened by an attack from…

Battle of Baker's Creek
"Battle of Baker's Creek, May 16th, 1862- Defeat of the Confederates under Pemberton, by General Grant.…


