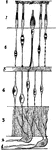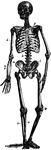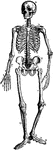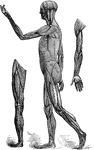
The Tympanic Ossicles
The tympanic ossicles, which are 3 small bones that form a chain across the tympanic cavity, connecting…
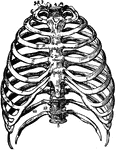
The Bones of the Thorax
Front view of the bones of the thorax, including the ribs, sternum and vertebrae. Labels: 1, first bone…
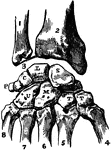
Bones of the Carpus
Articulations of bones of the carpus (wrist area). Labels: 1, ulna; 2, radius; 3, inter-articular fibro-cartilage;…

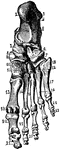
Upper Surface of the Left Foot
Bones of the upper surface of the left foot. Labels: 1, astragalus; 2, its anterior face; 3, os calcis;…
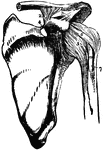
Bones and Ligaments of the Shoulder Articulation
Ligaments of the acromio-clavicular and scapulo-humeral articulations (joints of the shoulder). Labels:…
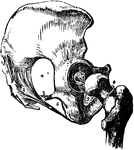
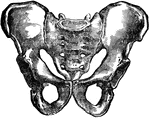
Bones and Ligaments of the Hip and Pelvis
Ligaments and bones of the hip joint and pelvis. Labels: 1, posterior sacro-iliac ligament; 2, greater…
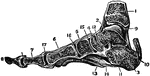
Ankle Joint and Foot
Vertical section of the ankle joint and foot. Labels: 1, tibia; 2, astragalus; 3, os calci; 4, scaphoides;…
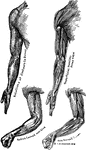
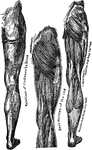
Bones and Muscles of the Arms
Showing relations of the muscles and bones of the arms from the inner side.
Bones and Muscles of the Arms
Showing relations of the muscles and bones of the arms from the outer side
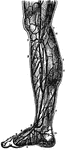
Veins of the Legs
Superficial veins of the legs. Labels: 1, saphena major; 2, collateral branch; 3, anastomosis of veins;…
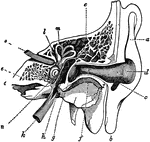
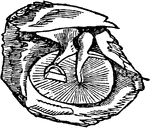
A Cross-Section of the Ear
Cross-section of the external and internal ear. a, b, and c: External ear. d: Entrance…

Bone Exposed to Acid and Twisted
This figure shows a thigh bone that has been softened by exposing it to acid, then twisted in a knot…

Teeth of an Herbivore
Teeth of an herbivore, showing the rough surface of some of these teeth. Herbivores have no tearing…
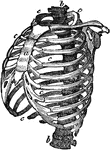
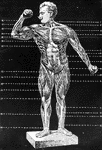
Structure of the Chest
Structure of the chest, showing the framework of the bones which are connected together chiefly by muscles.…
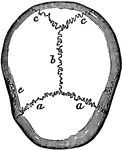
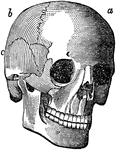
Cranial Sutures
The bones of the top of the head are fastened together by what are called sutures which are locked together…
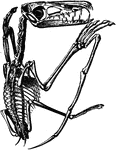
Vertebra of a Fish
The vertebra of a fish, which is very different from that of a human. It has but two processes, …
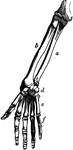
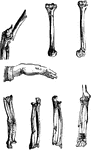
Bones of the Arm and Hand
Bones of the arm and hand. Labels: a, large end of ulna; b, radius; c, small end of the ulna; d, carpal…
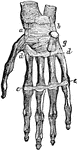
Bones and Ligaments of the Hand
Bones and ligaments of the hand. There are 27 bones in all, including 8 small bones called the carpal…

Bones of the Foot
Bones of the foot. At e d f g h are the 7 bones of the tarsus; at a are the 5 bones…
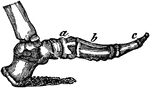
Side View of the Bone of the Foot
Bones of the foot, side view. In this figure the bones of the tarsus extend from the heel to a;…
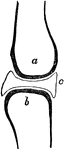
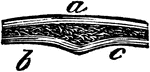
Joint
A joint between two bones (a and b). The ends of all bones are tipped with cartilage so that they may…
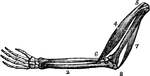
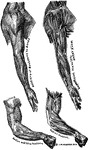
Arm Muscles
Two of the principal muscles f the arm (4 and 7). Between these is the bone of the arm (1) and the bones…
Tendons of a Finger
The arrangement of the tendons of a finger. At a b c are the 3 bones of the finger. At f…
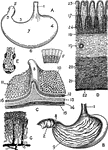
Views of the Stomach
Views of the stomach. Labels: A. stomach (human). B. Same, anterior wall removed. C. Portion of stomach,…
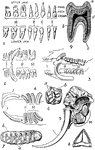
Teeth of Man and Several Animal Species
1. Dentition (teeth) of man. 2. Dentition of hyena. 3. Dentition of pig. 4. Dentition of Patagonian…
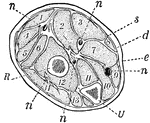
Forearm, Section of
A section across the forearm a short distance below the elbow-joint. R and U, its two supporting bones,…
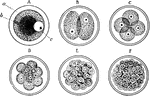
Cell Development
Every human body begin as a single nucleated cell. This cell, known as the ovum, divides or segments…
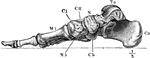
Bones of the Foot
The bones of the foot. Labels: Ca, calcaneum, or os calcis; Ta, articular surface for tibia on the astragalus;…
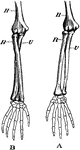
Bones of the Arm
Bones of the arm. Labels: A, arm in supination; B, arm in pronation. H, humerus; R, radius; U, ulna.
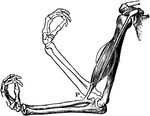
The Biceps Muscle and Arm Bones
The biceps muscle and arm bones, to illustrate how, under ordinary circumstances, the elbow-joint is…
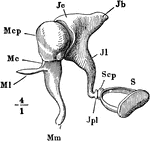
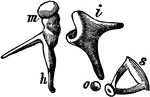
The Auditory Ossicles
The auditory ossicles of the right ear, seen from the front. Labels: M, malleus; J, incus; S, stapes;…
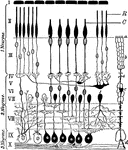
Retinal Structure
Diagram of the structure of the human retina. Labels: I, pigment layer; II, rod and cone layer; R, rods;…
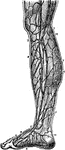
Veins of the Leg
Veins of the leg. Labels: 1, saphenous; 2, collateral branch; 3, anastomosis; 4, internal saphenous;…
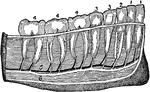
Teeth
Image of teeth in a human jaw. "1, incisors; 2, canine; 3, bicuspids; 4, molars (the molar at the left…
Bone Structure
If we divide any of the long bones longitudinally, we find two kinds of structure, the hard or compact,…
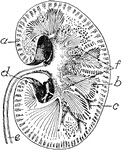
Kidney
Transverse section of the human kidney: "(a) cortex; (b) medulla; (c) small branch of the renal artery;…

Palanquin
A covered human-powered wagon used in Eastern countries where passengers were inside while two men would…
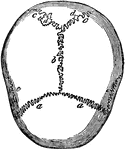
Skull Sutures
Sutures of the skull. Labels: a,a, the coronal suture, from the Latin corona, crown, so called from…
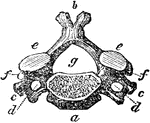
Vertebra of the Neck
A vertebra of the neck. Labels: a, body of the bone; b, the spinal process; c, d, the transverse processes…
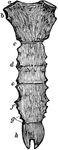
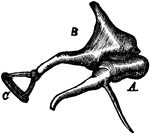
Sternum
The sternum in this cut consists of two bones. The first is broad and thick above, and contracts as…