David Glasgow Farragut
David Glasgow Farragut (July 5, 1801 – August 14, 1870) was a flag officer of the United States Navy…

Charles Wilkes
(1798-1877) American Naval officer and explorer who brought Great Britain on the Confederate side of…

Sir Peter Parker
Admiral of the Fleet Sir Peter Parker, 1st Baronet (1721 – 21 December 1811) was a Royal Navy officer.…

John Barry
(1745-1803) Naval officer that became the senior captain in the navy and commanded all US ships in the…

Secretary of Navy, 1923
Flag of the Secretary of Navy, 1923. For Asst. Secretary, white flag with blue stars and anchor.

The Consititution Capturing the Cyane and Levant
The Constitution engaging two British ships, the Cyane and Levant.

Action between the Weehawken and Confederate Iron-clad Atlanta
Naval battle between the Union Weehawken and Confederate Atlanta.
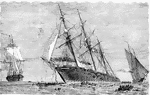
Kearsarge Sinking the Alabama
The sinking of the Alabama by the Union Kearsarge. Some Confederates aboard the Alabama escaped to England…
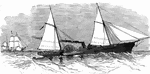
The Spanish Man-of-War Tornado Chasing the American Steamer "Virginius"
American steamship being chased by Spanish man-of-war.

The Great Naval Battle on the Mississippi
First day's bombardment, Federal Schooners off Forts Jackson and St. Philip, commanding the passage…

The Great Naval Battle of the Mississippi
Passage of the second division of the Federal Squadron past Fort St. Philip. On April 24, 1862 at three…

Infernal machine
"Infernal machine designed by the Confederates to destroy the Federal Flotilla in the Potomac discovered…

First naval battle
"First naval battle in Hampton Roads between the Confederate iron-plated steamers Merrimac, Yorktown,…

Zouaves
"Encampment of Colonel Ellsworth's New York Fire Zuoaves, on the heights opposite the Navy Yard, Washington,…

Admiral Silas H. Stringham
"Rear admiral Stringham, born in Middletown, Orange County, N. Y., November 7th, 1798; died in brooklyn,…
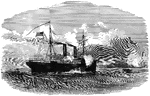
Quaker City
"The Quaker City, one of the Potomac Flotilla, engaging Confederate dragoons in Lynn Haven…

Admiral David G. Farragut
"Admiral Farragut, born at Campbell's Station, near Knoxville, Tenn., July 5th, 1801, died in Portsmouth,…

Rear Admiral Charles Wilkes
"Rear Admiral Wilkes, born in New York city, April 3rd, 1798, died in Washington, D. C., February 8th,…
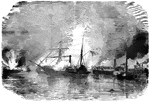
Harriet Lane
"Daring and desperate attack- surprise and capture of the United States gunboat Harriet Lane…

Rear Admiral John A. Winslow
"Rear Admiral Winslow, born in Wilmington, N. C., November 19th, 1811, died in Boston, Mass., September…

Rear Admiral James Alden
"Rear Admiral Alden, born in Portland, Me., March 31st, 1810, died in San Francisco, Cal., February…

General William Mahone
"General Mahone, born in Southampton County, Va., December 1st, 1826; died at Washington, D. C., October…

Naval Practice
"Naval Practice Battery, navy yard, Washington, D. C. We present to our readers a sketch of what was…

Trafalgar Monument
"Trafalgar Monument, Battle of Trafalgar (1805). During the early part of the Napoleonic wars, England's…

Great Harry
"The Great Harry, the First Famous Ship of the English Navy, built in 1512."—Scudder, 1897

Badge of the Loyal Legion
"The Military Order of the Loyal Legion is the first society formed by officers honorably discharged…

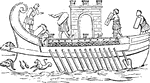
Roman galley
"Elated by the victory, the Romans now determined to drive Carthage out of the island altogether. This,…
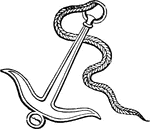
Anchor
The anchor used by the ancients was for the most part made of iron and its form... resembled that of…

Greek Boat
"The masts were usually taken down when the vessel arrived in port, and raised again when it was about…
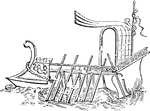
Ship with rudder
"The following cut represents a ship with its rudder. The pole by which it is fastened to the ship's…