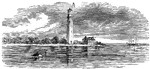
James Island
"Repulse of the Confederates at James Island, near Charleston, S. C., June 10th, 1862, in the attempt…

Jefferson City, Missouri
"Jefferson City, capital of Missouri. The arrival of General Fremont's division, September 26th, 1861.…

Jefferson City Railroad Depot
"Jefferson City, capital of Missouri. The arrival of General Fremont's division, September 26th, 1861.…
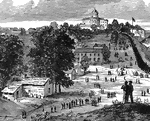
Jefferson City Capitol Building
"Jefferson City, capital of Missouri. The arrival of General Fremont's division, September 26th, 1861.…
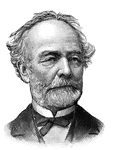
General Joseph E. Johnston
"General Johnston, born in Cherry Grove, near Farmville, Va., February 3rd, 1807; died at Washington,…

General Joseph E. Johnston
"General Joseph E. Johnston was involved in the Battle of Bull Run."—E. Benjamin Andrews 1895

General Joseph E. Johnston
Confederate General Joseph E. Johnston, who surrendered two weeks after Lee.

General Joseph Eggleston Johnston
General Joseph Eggleston Johnston, also known as General J. E. Johnston (1807 - 1891) was a U.S. Army…

Joseph E. Johnston
(1807-1891) Soldier that fought in the Mexican War and in the Confederate side of the Civil War.

Kelley's Ford
"Kelley's Ford, on the Rappahannock, the scene of the Battle of the 17th of March, and of General Stoneman's…

Kentucky Raid
"The Confederate raid into Kentucky- the fight at the Licking Bridge, Cynthiana, between the Federal…

Kentucky Raid
"The raid in Kentucky- the Confederate Morgan with his guerillas bivouacking in Courthouse Square, Paris,…

Kentucky Raid Rally
"The Confederate raid into Kentucky--excitement at Convington--gathering of armed Federal citizens at…

Kentucky Shore
"The Federal Army, under General Pope, landing on the Kentucky Shore, opposite New Madrid, April 1st,…

Campaign in Kentucky
"The campaign in Kentucky, Federal troops under General Johnston, advancing on the Louisville and Nashville…

Killing's Cave
"Killing's Cave, on the banks of the Potomac, near Sharpsburg, the place of refuge of many citizens…

General Judson Kilpatrick
"General Kilpatrick, born near Deckertown, N. J., January 14th, 1836, died in Valparaiso, Chili, December…

General Rufus King
"General King, born in New York city, January 26th, 1814, died there, October 13th, 1876, was graduated…

Captain Knapp
"Captain Knapp's Battery engaging the Confederates at the battle of Cedar Mountain, August 9th, 1862-…

Lafayette Parish
"The war in Louisiana- General Franklin's army crossing the prairie in Lafayette Parish, November 16th,…

Lake Providence
"Lake Providence, La., headquarters of General McPherson and the Federal division under his command.…

Land Practice
"Land practice of sailors with the Dahlgren Howitzer Boat Gun, sponging out the gun."— Frank Leslie,…

Landing of Captain Bailey and Lieutenant Perkins in New Orleans
Captain Bailey, bearing a flag of truce, put off in a boat, accompanied by Lieutenant George H. Perkins,…

Laurel Hill
"Advance of General Rosecrans's division through the forests of Laurel Hill to attack the Confederate…

Lee's Army
"Lee's army crossing the Potomac at Williamsport, in scows guided by wires, after the invasion of Maryland."—…

General Fitzhugh Lee
"General Lee, born in Clermont, Fairfax County, Va., November 19th, 1835, was graduated at the United…

Robert E. Lee
(1807-1870) A famous U.S. Army office and general of the Confederate forces during the American Civil…

General Robert E. Lee
General Robert E. Lee (1807 - 1870) was a career United States Army officer and one of the most celebrated…

Interior of Libby Prison
"Interior of Libby Prison, Richmond, Va., with prisoners from General Lee's army confined after the…

Lick Creek Bottom
"Advance of Federal troops on Corinth- the Carnival of Mud- scene at Lick Creek Bottom, between Pittsburg…

Lick Creek Bottom - Horse and Rider
"Advance of Federal troops on Corinth- the Carnival of Mud- scene at Lick Creek Bottom, between Pittsburg…

Lick Creek Bottom - In the Mud
"Advance of Federal troops on Corinth- the Carnival of Mud- scene at Lick Creek Bottom, between Pittsburg…

Lick Creek Bottom - Marching through the Mud
"Advance of Federal troops on Corinth- the Carnival of Mud- scene at Lick Creek Bottom, between Pittsburg…

Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln, sixteenth president of the United States, and president of the Union during the Civil…