The Fluid Mechanics ClipArt gallery offers 75 images of the study of liquids and gasses, how they move, and how they react to forces on them. Many additional examples may be found in the Fluid Pumps gallery in the Business and Industry section.
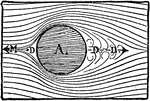
Circle Aerodynamic
A circle in a aerodynamic chamber where the airflow hitting the object. The area at point DD is large…
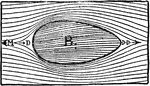
Ellipse Aerodynamic
Aerodynamic of the ellipse where the area at point DD is small. The small area creates less resistance…
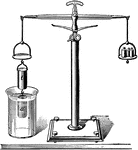
Archimedes Principle
"From on pan suspend a hollow cylinder of metal t, and below that a solid cylinder a of the same size…
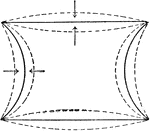
Capillary Water Surface Variation
"Variation in the direction and magnitude of the pressure of the capillary surface due to the form of…
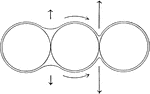
Capillary Water Surfaces
"Diagram showing three soil grains surrounded by water films: Straight arrows indicate direction and…
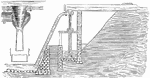
Centrifugal pump
This figure represents a small centrifugal pump as mounted for use. The largest class of centrifugal…
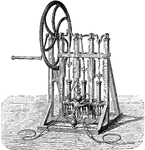
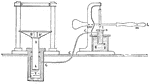
Connected Pumps.
This figure consists of three pumps, the piston rods of which are jointed to three cranks on a horizontal…
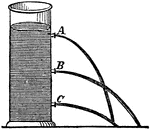
Course of Streams
"As the liquid flows out of each orifice, each stream follows a parabolic path based upon pressure of…
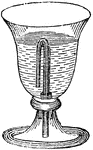
Tantalus's Cup
"Whenever liquid reaches the bottom of the short leg on the siphon inside the cup, the liquid is discharged…

Fire engine pump
The ordinary fire-engine is formed by the union of two forcing-pumps which play into a common reservoir,…
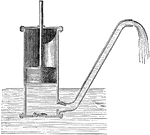
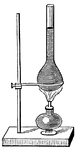
Forcing-pump
The forcing pump consists of a pump-barrel dipping into water, and having at the bottom a valve opening…
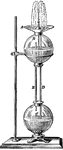
Hero's Fountain
Hero's fountain is named after its inventor, Hero, who lived in Alexandria 120 B.C. It is dependent…

Heron's Fountain
An illustration of Heron's fountain. Heron's fountain is a hydraulic machine invented by the first century…

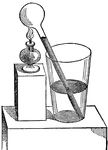
Pulp Glass
An instrument intended to exbihit the ebullition of liquid at low temperatures, constructed like a cryophorus.

Hero's Fountain
"It consists of a brass dish A and two glass globes B and C. The dish communicates with the lower part…
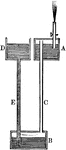
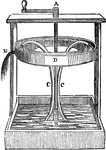
Hiero's Fountain
"After preparing the fountain, water is added into D, and later, the tube is opened to allow the air…
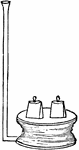
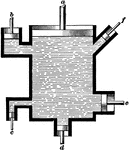
Hydraulic Bellows
"An instrument called the hydrostatic bellows, also shows, in a striking manner, the great force of…

Hydraulic Water Ram
"The hydraulic ram uses alternating water pressure, air pressure, and suction to provide a steady stream…
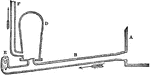
Hydraulic Ram
"Pumps water in bursts. Water enters pipe B and is forced into D then up the tube F. Any excess water…
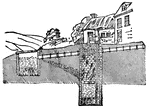
Leaky Drain
This illustration shows how putrefying animal matters from a leaky drain and an overflowing cess-pool…
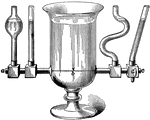
Water Level
The pressure at the bottom of an apparatus due to the weight of the liquid is dependent of the height…

Locks
"The lock C is a controllable compartment with raise-able and lower-able gates D and E. Since water…
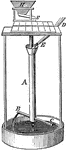
Barker's Mill
"Grain enters the mill at H down into D and into tube A. The grain passes down through the holes B and…

Pascal's Law and Water Pressure
"...let the area of the piston a be 1 square inch; of b, 40 square inches. According to Pascal's law,…
Delivery Pipe
The part of the pipe that is above the highest piston travel point is the delivery pipe and the part…

Piston and Barrel of Deleuil's Air-pump
"To avoid friction and heat, the piston is not in contact with the cylinder in which it works."
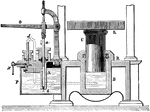
Hydraulic press
"Pascal's law finds an important application in the hydraulic press, in the more common forms of which…
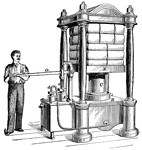
Hydraulic Press
A hydraulic press which uses a hydraulic cylinder to generate force. The inventor of the device, Joseph…
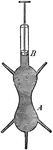
Pressure of Liquids
"The tightly fitted piston at the top of a glass vessel of water is driven down. The contained liquid…
Hydraulic Machine Exerting Pressure
Illustration of a hydraulic machine. "A principle known as Pascal's Law states that pressure exerted…
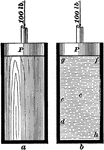
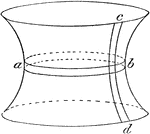
Water versus Wood Pressure
"The vessel a is fitted with a wooden bock of the same size as, and free to move in, the cylinder; the…
Water Pressure Demonstration
"Let the are of the piston a be 20 square inches; of b, 7 sq. in.; of c, 1 sq. in.; of d, 6 sq. in.;…
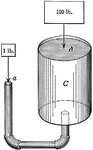
Centrifugal Pump
"The shaft A and B is attached to tubes, C. When the crank is turned, centrifugal force in the tubes…
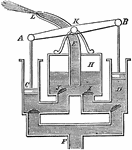
Fire Engine Pump
"Liquid is drawn up pipe F by pistons C and D. Once the liquid passes through the first set of valves,…
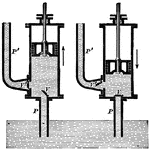
Force Pump
A force pump differs from a lifting pump for many reasons, with the main reason being that the force…
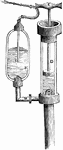
Forcing Pump
"Liquid is drawn up the pipe through the valve H. Piston G pushes the liquid through pipe, M, and into…
Lifting Pump
"Liquid is pumped up through pipe A, through valve H. The airtight piston G allows the liquid to pass…
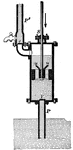
Lifting Pump
A lifting pump is used when water needs to be raised to a greater height than what can be done with…
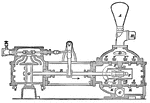
Steam Pump
A typical steam pump. A steam pump is a force pump operated by steam acting on the pistons of a steam…

Hydraulic Ram
A hydraulic ram. It is used to raise the level of water from a point below water level of a spring to…
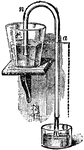
Siphon
A bent tube with limbs of unequal length, used for drawing liquids from one vessel into another.
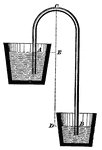
Siphon
"The action of the siphon illustrates the effect of atmospheric pressure. It is simply a bent tube having…
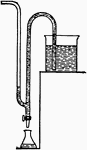
Siphon
"A bent tube with one limb longer than the other, by means of which a liquid can be drawn off to a lower…
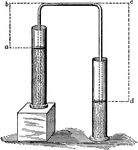
Siphon
"The vertical distance form the level of the upper liquid to the highest point of the tube (ab) is the…
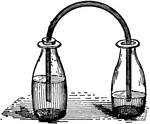
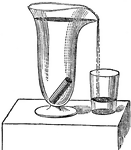
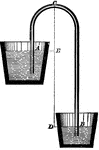
Bottle Siphon
"Partly fill two bottles with water. Connect them by a bent tube that fits closely into the mouth of…
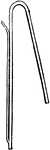
The Siphon
"A siphon is used to draw off liquids from a higher elevation to a lower one. The siphon uses the vacuum…

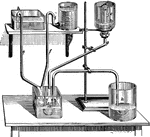
Still
"Impure water is vaporized in the boiler, A. It travels to the vat and down pipe R where it condenses…
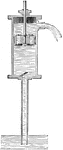
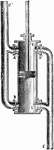
Suction-pump
The suction-pump consists of a clindrical pump-barrel traversed by a piston, and communicating by means…