The Mammal Anatomy: Internal Organs ClipArt gallery offers 192 views of the internal organs and other soft tissue of various species of mammals.
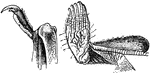
Mystacina Tuberculata
"Thumb and leg and foot of Mystacina tuberculata." —The Encyclopedia Britannica, 1903
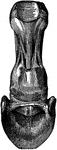
Navicular Ligaments
Navicular ligaments. Labels: a, superior, or broad, ligament; b, inferior ligament; c, lateral ligament.

Neck of a Horse Showing Arteries
Arteries of the neck exposed on the left side. Labels: a, anterior aorta; a', left brachial; a",…
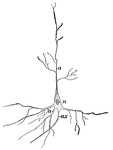
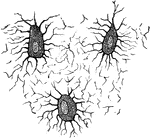
Nerve Cell
Nerve cell from the brain; a, processes by which it communicates with other cells near by;…
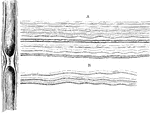
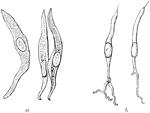
Gelatinous Nerve Fibers
Gray, pale, or gelatinous nerve fibers. A. From a branch of olfactory nerve of the sheep: two dark bordered…
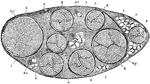
Nerve Trunk
Each nerve trunk is composed of a variable number of different sized bundle (funiculi) of nerve fibers…
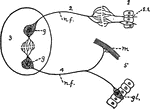
Nervous System
"Scheme showing the essential relations of the parts of a nervous system: 1, the sensory end organ (epithelial);…
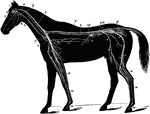
Nervous System of the Horse
The nervous system of the horse. Labels: 1, brain; 2, optic nerve; 3, superior maxillary nerve (5th);…

Neural Canal
The neural canal of first three cervical vertebrae, opened from above to show the internal ligaments.…
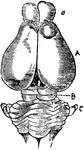
Opossum Brain
"The size of the hemispheres of the brain (A) is so small that they leave exposed the olfactory ganglion…
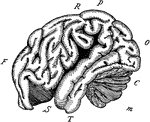
Orangoutang Brain
"The outline of the brain of an orang outang. Front portion F to O, cerebrum; C, cerebellum; M, medulla…
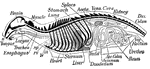
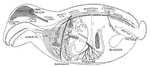
Organs
Diagram of the chief organs of a mammal. The bones are black. a, opening from the nasal cavity…
Osteoblasts
Nucleated none cells (osteoblasts) and their processes, contained in the one lacunae and their canaliculi…
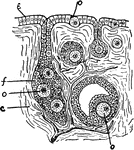
Ovary
"Section through ovary of a young Mammal. The eggs (o) are seen to be formed from the epithelium. c,…
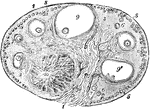
Ovary of the Cat
View of a section of the ovary of the cat. Labels: 1, outer covering and free border of the ovary; 1',…

Ovary of the Cat
Section of the ovary of a cat. Labels: A, germinal epithelium; B, immature Graafian follicle; C, stroma…
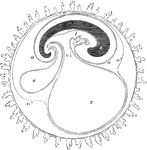
Membranes of the Ovum
Diagrammatic section showing the relation in a mammal between the primitive alimentary canal and the…
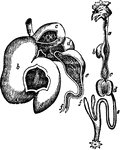
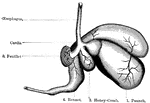
Ox Stomach
"Compound stomach of ox. a, esophagus; b, rumen, or paunch; c, reticulum, or second stomach; d, omasum,…
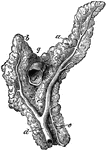
Pancreas of a Horse
Anterior view of the pancreas. Labels: a, left branch; b, right branch; c, inferior branch; d, duct…
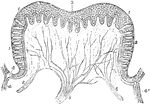
Papilla of a Calf
Vertical section of a circumvallate papilla of the calf. Labels: 1 and 3, epithelial layers covering…

Parotid and Molar Glands of a Horse
Parotid and molar glands of the left side. Labels: a, parotid gland; b, Steno's duct; c, superior molar…

Lobules of Parotid of a Sheep
In mammalia, each salivary gland first appears as a simple canal with bud-like processes, lying in a…

Peyer's Glands
The glands of Peyer occur chiefly but not exclusively in the small intestine. They are found in greatest…
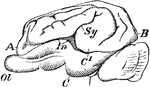
Pig Brain
"Brain of pig. Ol, olfactory lobe; A, B, C, frontal, occipital, and temporal lobes; C1, a portion of…
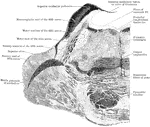
Section Through Pons Varolii
Section through the pons varolii at the level of the nuclei of the trigeminal nerve in an orangoutang.
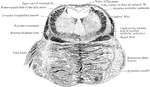
Section Through Pons Varolii
Section through the upper part of the pons varolii of the orangoutang above the level of the trigeminal…
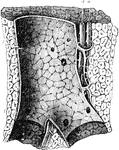
Portal Canal
Longitudinal section of a portal canal, containing a portal vein, hepatic artery and hepatic duct from…
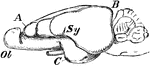
Rabbit Brain
"Brain of rabbit. Ol, olfactory lobe; A, B, C, frontal, occipital, and temporal lobes; Sy, Sylvian fissure."…
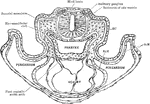
Transverse Section of a Rat Embryo
Transverse section of a rat embryo. Showing relation of the paraxial mesoderm of the head to the lateral…

Respiratory Organs of a Horse
General view of the respiratory organs. Labels: a, septum nasi; b, posterior naris; c, larynx; d, trachea;…
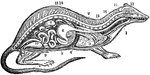
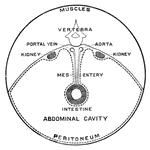
The Respiratory System of a Small Mammal
The respiratory apparatus of other mammals is similar to humans in both structure and function. The…
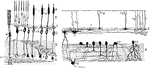
Section of Retina
Perpendicular section of mammalian retina. Labels: A, layer of rods and cones; B, outer nuclear layer;…
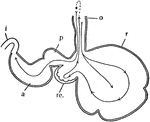
Ruminant Stomach
"Diagram of the stomach of a ruminant. o, esophagus; r, rumen or paunch; re., reticulum, or honeycomb;…
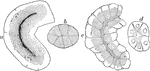
Serous Glands of a Rabbit
Serous glands. Labels: a, rabbit's pancreas "loaded" (resting); c, "discharged" (active) (observed in…
Sesamoidean and Digital Ligaments
Sesamoidean and digital ligaments- posterior aspect. Labels: a, suspensory ligament; b, external and…
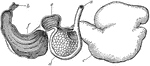
Sheep Stomach
"Stomach of sheep. a, OEsophagus; c, rumen or paunch; d, reticulum or honeycomb-bag; e, psalterium or…
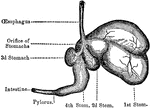
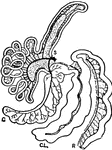
Sheep, Stomachs of
The four stomachs of the sheep, a grass-eating animal. The beginning of the intestines are also shown,…

Spleen of a Horse
Internal aspect of the spleen. Labels: a, superior extremity, or base; b, inferior extremity; c, internal…
Stifle Joint Ligaments
Ligaments of the stifle joint- posterior aspect. Labels: a, external lateral patellar ligament; b, external…
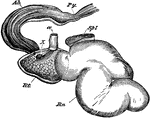
Stomach of a Deer
Stomach of a musk deer, left aspect- the last three compartments opened and reflected forwards. Rn,…
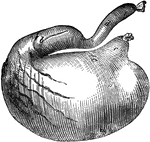
Stomach of a Dog
Stomach of a dog-inflated. Labels: a, cardiac portion; b, pyloric portion; c, esophageal orifice; d,…

Stomach of a Hog
Stomach of a hog- inflated. Labels: a, cardiac portion; b, its accessory cul-de-sac; c, pyloric portion;…
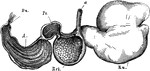
Stomach of a Sheep
Stomach of an sheep seen from the left side- the last three compartments are laid open and reflected…

Stomach of a Sheep
Compartments of a ruminant stomach, laid open. A, rumen- a, pillars; b, papilla; c, esophageal orifice.…
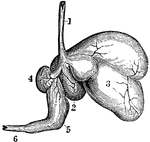
The Stomach of a Sheep
Ruminants (those animals that chew the cud), as the sheep, have a stomach with four cavities. Labels:…
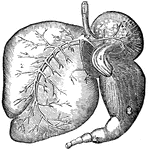
Stomach of an Ox
Ruminants (those animals that chew the cud), as the ox, have a stomach with four cavities. Labels: 1,…
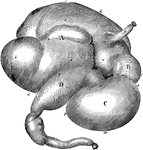
Stomach of an Ox
Stomach of an ox inflated-viewed from the right side. Labels: A, rumen; a, left sac; a', its anterior…

Horse Stomach
Posterior view of the stomach of a horse. Labels: a, left cul-de-sac; b, right cul-de-sac; c, greater…
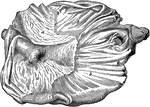
Horse Stomach
Internal aspect of a horse stomach, opened from below. Labels: a, cuticular mucous membrane; b, villous…
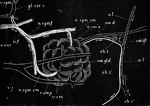
Submaxillary Gland of Dog with Nerves and Blood Vessels
Diagrammatic representation of the submaxillary gland of the dog with its nerves and blood vessels.…
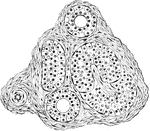
Sudoriferous Glands
Terminal tubules of sudoriferous glands, cut in various directions from the skin of the pig's ear.
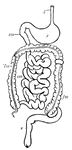
Digestive system
Digestive system of a mammal. (g) gullet; (s) stomach; (sm) small intestine; (lm) large intestine; (r)…
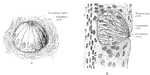
Taste bud of Rabbit
A, Three-quarter surface view of taste bud from the papilla foliata of a rabbit. B, Vertical section…
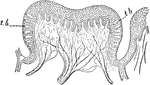
Sense of Taste
The sense of taste enables us to test in some degree the chemical constitution of substances we take…