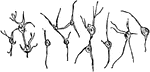The Cellular Biology ClipArt gallery offers 242 illustrations of biology at the cellular level for many species and parts of the body, including blood cells and bone tissue, and also contains general images of cell, cell structure, and cell reproduction.
Auerbach's Nerve Plexus
Auerbach's nerve plexus in the small intestine. The plexus consist of fibrillated substance, and is…
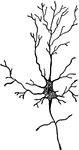
Neuron
"Showing a motor cell with its long, unbranched process (with two little lateral offshoots), with motor…
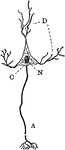
Diagram of a Neuron
Diagram of a neuron. Labels: A, axon arising from the cell-body and branching at its termination; D,…
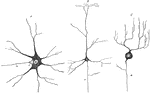
Various Forms of Neurons
Multipolar nerve cells of various forms. Labels: A, from spinal cord; B, from cerebral cortex; C, from…
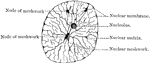
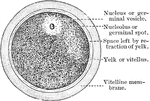
Nucleus at Rest
The nucleus when in a condition of rest is bounded by a distinct membrane, possibly derived from the…
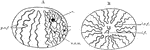
Nucleus Showing Chromatic Filaments
Diagrams of the nucleus showing the arrangement of chief chromatic filaments. A, Viewed from the side,…
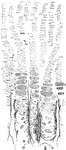
Ossifying Cartilage Showing Calcification
Longitudinal section of ossifying cartilage from the humerus of a fetal sheep. Calcified trabeculae…

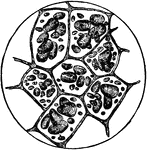
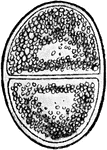
The Human Ovum Undergoing Segmentation
The diagram of a human ovum undergoing segmentation. Labels: a, human ovum; b, ovum divided into two;…

Pacinian Corpuscle of a Cat
The Pacinian bodies or corpuscles are elongated oval bodies situated on some of the cerebrospinal and…

Pacinian Corpuscle of a Human
The Pacinian bodies or corpuscles are elongated oval bodies situated on some of the cerebrospinal and…

Pacinian Corpuscles in a Human
The Pacinian bodies or corpuscles are elongated oval bodies situated on some of the cerebrospinal and…
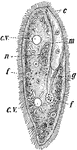
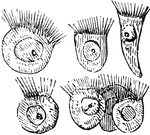
Paramecia
Paramecia (Slipper Animalcule), also known as Lady Slippers, due to their appearance, are a group of…
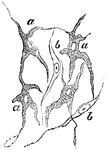
Pigment Cells
Ramified pigment cells, from the tissue of the choroid coat of the eye. Labels: a, cell with pigment;…
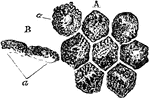
Pigment Cells from the Retina
Squamous epithelium is found arranged as a single layer of flattened cells as the pigmentary layer of…
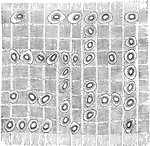
Pellionia Plant Cell
"Cell of Pellionia Daveauana, showing starch-grains. The black, crescent-shaped body on the end of each…
Protozoan
Gregarina, a protozoan, various species which live in the alimentary canal of crayfishes, centipeds,…
Protozoan
Gregarina, a protozoan, various species which live in the alimentary canal of crayfishes, centipeds,…
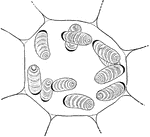
Protozoan
Gregarina, a protozoan, various species which live in the alimentary canal of crayfishes, centipeds,…
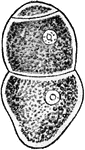
Protozoan
Gregarina, a protozoan, various species which live in the alimentary canal of crayfishes, centipeds,…
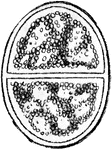
Protozoan
Gregarina, a protozoan, various species which live in the alimentary canal of crayfishes, centipeds,…

Protozoan
Gregarina, a protozoan, various species which live in the alimentary canal of crayfishes, centipeds,…

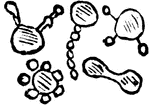
Effect of Acetic Acid on Red Blood Cells
Acetic acid (dilute) causes the nucleus of the red blood cells in the frog to become more clearly defined;…
Effect of Boric Acid on Red Blood Cells
A 2 percent solution of boric acid applied to nucleated red blood cells of a frog will cause the concentration…

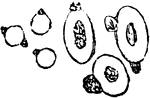
Effect of Gases on Red Blood Cells
If the red blood cells of a frog be first exposed to the action of water vapor (which renders their…
Effect of Heat on Red Blood Cells
The effect of heat on red blood cells up to 50-60 degrees C. (120-140 degrees F.) is to cause the formation…
Effect of Tannin on Red Blood Cells
When a 2 percent fresh solution of tannic acid is applied to frog's blood it causes the appearance of…
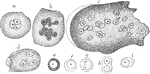
Cells of the Red Marrow
Red marrow occupies the spaces in the cancellous tissue; it is highly vascular, and this maintains the…
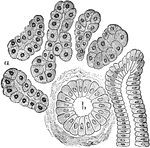
True Salivary Gland
From a section through a true salivary gland. Labels: a, the gland alveoli, lined with albuminous "salivary…
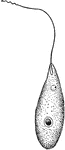
Sarcomastigophora
The phylum Sarcomastigophora belongs to the Protist kingdom and it includes many unicellular or colonial,…
Sieve Cell
A sieve cell is a tubular cell having its wall one or more sharply circumscribed thin areas which are…
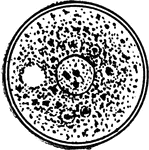
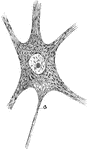
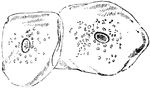
Spherical Cell
"Spherical cell (resting stage of Amoeba) illustrating general or universal symmetry. Any plane passing…
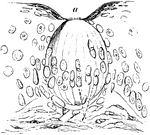
Taste Goblet from Dog's Epiglottis
Taste goblet from dog's epiglottis (laryngeal surface near the base) , precisely similar in structure…
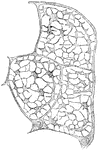
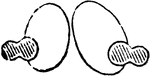
Branched Tendon Cells
The branched character of the cells is seen. Shown is a transverse section from a cross section of the…
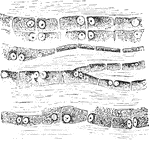
Structure of Tendon Cells
The cells in the tendons are arranged in long chains in the ground substance separating the bundle of…
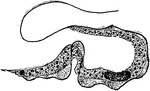
Trypanosoma
Trypanosoma are of the class kinetoplastida, a monophyletic group of unicellular parasitic protozoa.…
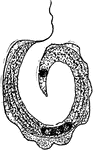
Trypanosoma
Trypanosoma are of the class kinetoplastida, a monophyletic group of unicellular parasitic protozoa.…
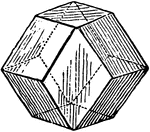
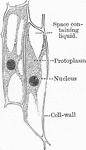
Vegetable Cell
Diagram of a vegetable cell, such as it would be if when spherical it were equally pressed by similar…
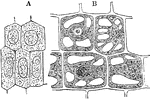
Vegetable Cell
A, A young vegetable cell, showing cell cavity entirely filled with granular protoplasm enclosing a…
Vorticella
The Bell Animalcule (Vorticella) (fig 10) in certain respects resembles the Slipper Animalcule. It is…
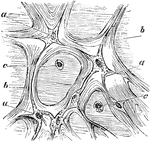
The Tissue of Whartonian Jelly
Tissue of the jelly of Wharton from a umbilical cord. Labels: a, connective tissue corpuscles; b, fasciculi…

White Blood Corpuscle
A white blood corpuscle sketched at successive intervals of a few seconds to illustrate the change of…
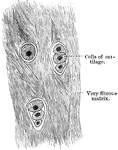
White Fibrocartilage
White fibrocartilage is composed of both cells and a matrix, but is almost exclusively composed of fibers…
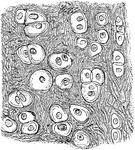
Yellow Elastic Cartilage
The cells in yellow elastic cartilage are rounded or oval, with well marked nuclei and nucleoli.