This ClipArt gallery offers 396 images of the Roman Empire including culture, people, everyday life, coats of arms, and more. See also the Roman Coins, Roman Architecture, Roman Ornament, Roman Mythology, and Ancient Roman Musical Instruments ClipArt galleries.
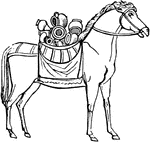
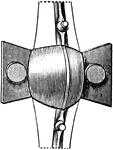
Clitellae
"A pair of panniers, and therefore only used in the plural number. In Italy they were commonly used…

Clovis, King of the Franks, is Baptized by Saint Remigius
Illustration of King Clovis kneeling before Saint Remigius. Clovis' wife, Clotilde, kneels next to him.…
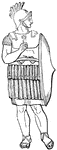
Roman Clypeus
"The following cut represents a Roman clypeus, from the column of Trajan. The projection in the centre…

Bust of Commodus
Lucius Aurelius Commodus Antoninus (31 August 161 – 31 December 192) was a Roman Emperor who ruled…

Roman Console
This Roman console is shown in the front and side view. It is a design that includes two decorative…
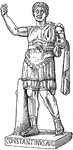
Constantine the Great
Emperor of Rome from 306 to 337. He is best known for being the first Christian Roman emperor.

Arch of Constantine
The Arch of Constantine was erected to celebrate Constantine's victory of Maxentius at the Battle of…
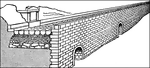
Construction Layers of a Section of the Appian Way
Illustration of the various layers of a Roman road. This is a section of the Appian Way, built across…

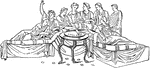
Consul and Lictors
The consul was the highest elected office of the Roman Republic. They were elected every year. The lictors…

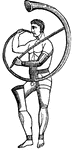
Cymbalum
"A musical instrument, in the shape of two half globes, which were held one in each hand of the performer,…
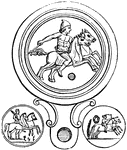
Desultor
"A rider in the Roman games, who generally rode two horses at the same time, sitting on them without…
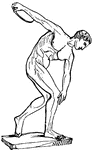
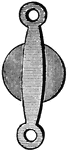
Discus
"A circular plate of stone or metal, made for throwing to a distance as in exercise of strength and…

Column of Duilius
Restoration of the column of Gaius Duilius, a Roman politician and admiral in the First Punic War.
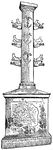
Column of Duilis
"The column was adorned with the brazen beaks of the captured Carthaginian vessels. Part of the inscription…
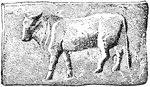
Early Roman Bar Money
"A bar of copper marked with the figure of a bull. Dates from the fourth century B.C."—Webster,…
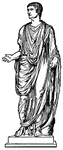
Emperor Tiberius Wearing a Toga
Illustration of the Roman Emperor Tiberius wearing a draped toga, which was fashionable in the first…

An Ertuscan Arch
"The Italian city of Volterra still preserves in the Porta dell' Arco an interesting relic of Ertuscan…
Fasces of a Roman Magistrate
"In Rom. antiq., bundles of rods, usually of birch, with an ax bound in with them, the blade projecting,…

Lictors with Fasces
"The symbolic fasces borne by these officers were probably of Ertuscan origin. The Tarquins are said…

Frankish Weapons, Including a Shield, Germanic Spear, Angon, Sword, Knife, and Short Axe
A collection of weapons used by the Germanic tribe called the Franks. These are all of their most typically…

Franks Crossing the Rhine to Establish Themselves on the West Bank as Allies of Rome
A group of Franks, mainly men with a couple of women and children, cross the Rhine River on a wooden…

Roman galley
"Elated by the victory, the Romans now determined to drive Carthage out of the island altogether. This,…
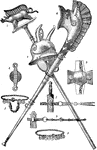
Gallic Remains
"1 and 3, necklaces with amber and coral pendants; 2, military standard; 4, bronze trumpet; 5, iron…

Gallic Soldier Wearing Trousers and a Horned Helmet
A soldier from Gaul carrying a sword in his right hand and shield in his left. He is wearing a cloak…

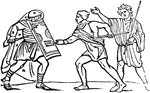
Gladiators
This illustration shows various types of gladiators, each type with with his specific weapons attributed…

Pompey the Great
Also known as Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus. He was a military and political leader of the late Roman Republic.