This human anatomy ClipArt gallery offers 265 illustrations of the central nervous system, including external and dissected views of the brain and spinal cord.
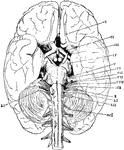
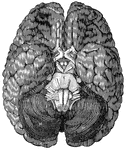
Base of the Brain
The base of the brain. The cerebral hemispheres are seen overlapping all the rest. Labels: I, olfactory…
Base of the Brain
Base of the Brain. Labels: 1,2, longitudinal fissure; 3, anterior lobes cerebrum; 4, middle lobe; 5,…
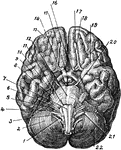
Base of Brain
The base of the brain. Labels: 1, eleventh or spinal accessory nerve; 2, right hemisphere of cerebellum;…
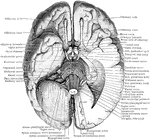
Base of the Brain
The base of the brain. The under part of the left temporal and occipital lobes has been sliced off so…
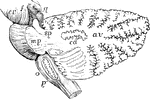
The Cerebellum of the Brain
Outline sketch of a section of the cerebellum, showing the corpus dentatum. The section has been carried…
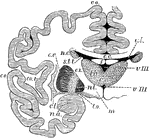
The Cerebrum and Basic Ganglia of the Brain
Vertical section through the cerebrum and basic ganglia to show the relation of the latter. Labels:…
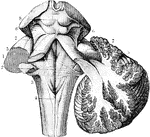
The Cerebrum and Fourth Ventricle of the Brain
The cerebellum in section and fourth ventricle, with the neighboring parts. Labels: 1, median groove…
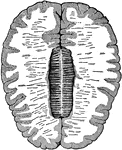
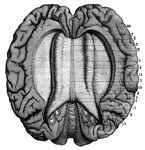
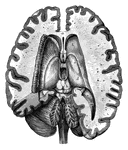
Cross-Section of the Brain
Cross-section of the brain. Here the upper half of the brain is cut off, and you see the upper cut surface…
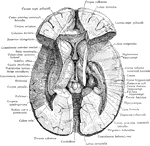
Dissection of the Brain
Dissection of the brain showing basal ganglia, third ventricle and adjacent structures viewed from above.
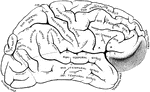
Gyri and Sulci on the Brain
Gyri and sulci, on the outer surface of the cerebral hemisphere. Labels: f1, sulcus frontalis superior;…
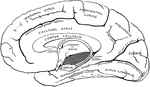
Gyri and Sulci on the Brain
The gyri and sulci on the mesial aspect of the cerebral hemisphere. Labels: r, fissure of Rolando; r.o,…
Gyri and Sulci on the Brain
The gyri and sulci on the tentorial and orbital aspects of the cerebral hemispheres.
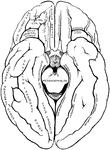
Human Brain
A top view of a dissection of the human brain showing the lateral fourth and fifth ventricles.
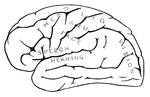
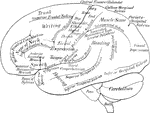
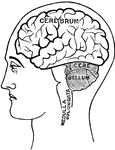
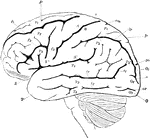
Human Brain
Side diagram of the human brain showing which parts of the brain control hearing, speech, vision, legs,…
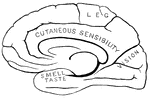
Human Brain
Side diagram of the human brain showing which areas perform the sense of taste, smell, and vision.
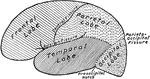
Lateral View of the Brain
Lateral view of the brain. F, Frontal lobe; P, Parietal lobe; O, Occipital lobe; T, Temporal lobe; S,…
Left Half of the Brain
"A,frontal love of the cerebrum; B, parietal lobe; C, parieto-occipital lobe;…
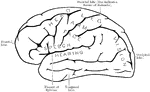
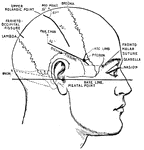
Motor Centers of the Brain
Diagram to indicate position of centers on the external surface of the brain.
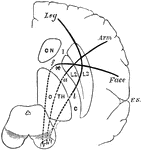
Motor Tracts of the Brain
Diagram to show the relative position of several motor tracts in their course from the cortex to the…
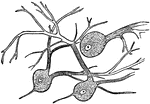
Nerve Cells of the Brain
"Wherever nerve cells are abundant, the nerve tissue has a gray color; in other places, it looks white.…
Precentral Gyrus in the Brain
The convolutionary projections of the precentral gyrus, and their relationship to motor areas.
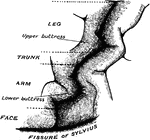
Principle Fissures of the Brain
Showing the lines which indicate the position of the principal fissures of the brain.
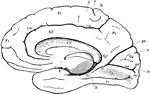
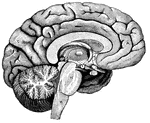
Right Hemisphere of the Brain
View of the right hemisphere in the median aspect. CC, corpus callosum longitudinally divided; Gf, gyrus…
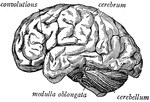
Side view of the brain
"The brain seen from the side, showing the three principal divisions." — Ritchie, 1918
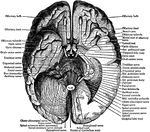
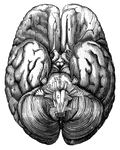
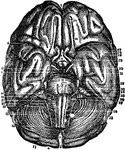
Under Surface of the Brain
View of the under surface of the brain, with the lower portion of the temporal and occipital lobes,…
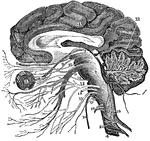
Vertical Section of the Brain
A vertical section of the cerebrum, cerebellum, and the medulla oblongata, showing the relation of the…
Nerve Cell
A simple nerve cell, or neuron. N is the nucleus of the cell, NC is the cytoplasm, D are dendrites which…
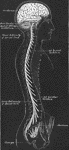
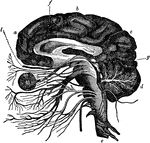
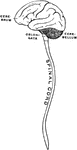
Central Nervous System
View of the cerebrospinal axis of the nervous system. The right half of the cranium and trunk of the…
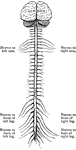
Central Nervous System
"Brain and spinal cord, with the thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves." — Tracy, 1888
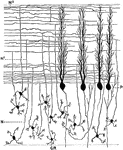
Sagittal Section Through Cerebellar Folium
Section through the molecular and granular layers in the long axis of a cerebellar folium. Labels: P,…
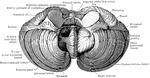
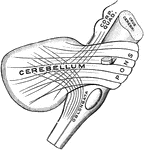
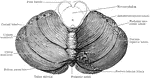
Lower Surface of Cerebellum
The lower surface of the cerebellum. The tonsil on the right side has been removed so at to display…
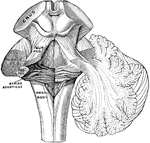
Peduncles of the Cerebellum
The peduncles of the cerebellum. On the left the three peduncles have been cut at their entrance into…
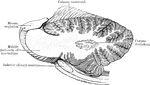
Sagittal Section Through Cerebellum
Sagittal section through the left lateral hemisphere of the cerebellum. Showing the "arbor vitae" and…
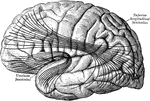
Cerebral Cortex
The most important association tracts of the brain. The fibers are projected upon the external surface…
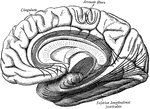
Cerebral Cortex
The most important association tracts of the brain. The fibers are projected upon the mesial (medial)…

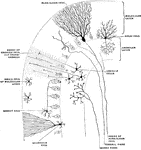
Minute Structure of Cerebral Cortex
Diagram to illustrate minute structure of the cerebral cortex. Labels: A and B, neuroglia cells; C,…
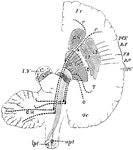
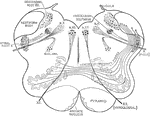
Cerebral Hemisphere
Diagram of the motor tract as shown in a diagrammatic horizontal section through the cerebral hemispheres…
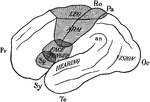
Cerebral Hemisphere Showing Localization of Function
Diagram of the outer surface of left cerebral hemisphere to illustrate the localization of functions.…
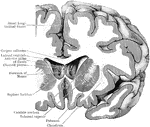
Coronal Section Through Cerebral Hemisphere
Coronal section through the right cerebral hemispheres as to cut through the anterior part (putamen)…
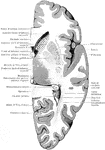
Section Through Cerebral Hemisphere
Horizontal section through the right cerebral hemisphere at the level of the widest part of the lenticular…
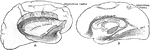
Association Bundles of the Cerebral Hemispheres
Diagram of the leading association bundles of the cerebral hemisphere. A, Outer aspect of hemisphere.…
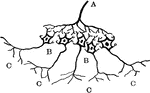
Diagram of the Relation between Cerebrospinal and Sympathetic Neurons
Diagram showing the relation of the cerebrospinal to the sympathetic neurons. Labels: A, a medullated…
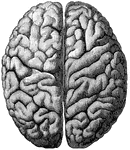
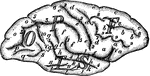
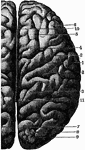
Cerebrum
"The Upper Surface of the Cerebrum. Showing its division into two hemispheres, and also of the convolutions."…
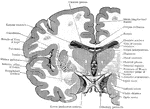
Coronal Section Through the Cerebrum
Coronal section through the cerebrum, so as to cut through the three divisions of the lenticular nucleus;…