This human anatomy ClipArt gallery offers 265 illustrations of the central nervous system, including external and dissected views of the brain and spinal cord.
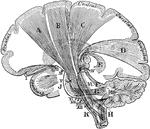
Projection Fibers of the Cerebrum
Diagram of the projection fibers of the cerebrum. Labels: B, motor (pyramidal) tract; C, body-sense…
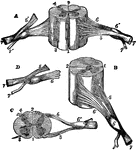
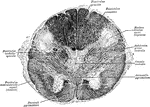
Sections of Cervical Spinal Cord
Views of section of cervical cord. Labels: A, anterior surface; B, right side; C, upper surface; D,…
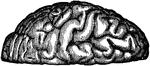
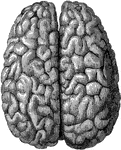
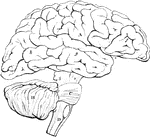
Convolutions of the Brain
View of the appearance of the tortuous elevations (convolutions) of the brain, seen from above.
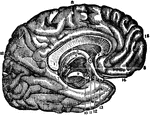
Corpus Callosum
Middle vertical section of the callous body (corpus callosum). The inner left side of the brain is also…
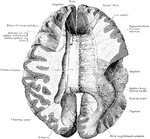
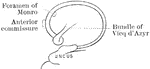
Corpus Collosum
The corpus callosum, exposed from above and the right half dissected to show the course taken by its…
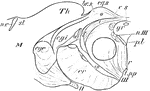
Corpus Quadrigeminum
Section through anterior corpus quadrigeminum and part of optic thalamus. Labels: s, aqueduct of Sylvius;…
Cortical Gray Matter of the Cerebrum
The five layers of the cortical gray matter of the cerebrum. 1, Superficial layer with abundance of…
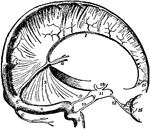
Dura Mater and Cranial Sinuses
The dura mater and cranial sinuses. 1, falx cerebri; 2, tentorium; 3, superior longitudinal sinus; 4,…
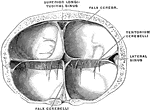
Dura of the Brain
Crucial prolongation of the dura. Frontal section passing through the tentorium cerebelli. The torcular…
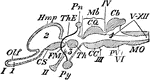
Encephalon
"Diagram of Vertebrate Encephalon ... in longitudinal vertical section. Mb, mid-brain; in front of it…
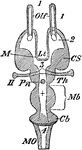
Encephalon
"Diagram of Vertebrate Encephalon ... in horizontal section. Mb, mid-brain; in front of it all is forebrain,…
Outline of the Encephalon
Plan in outline of the encephalon, as seen from the right side. The parts are represented as separated…
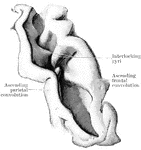
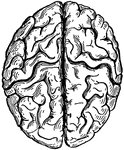
Fissure of Rolando
Fissure of Rolando fully opened up, so as to exhibit the interlocking gyri and deep annectant gyrus…
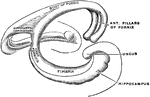
Fornix
The fornix is a paired structure consisting of bilaterally symmetrical halves composed of longitudinally…
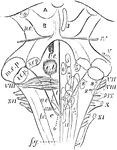
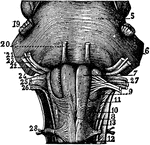
Fourth Ventricle with the Medulla Oblongata and the Corpora Quadrigemina
Fourth ventricle with the medulla oblongata and the corpora quadrigemina. The roman numbers indicate…
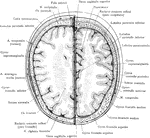
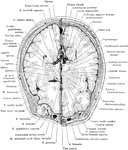
Cross Section of Head 3 cm above Supraorbital Border
Section of head 3 cm above supraorbital border.
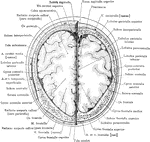
Cross Section of Head 4 cm above Supraorbital Border
Section of head 4 cm above supraorbital border.
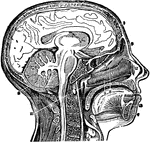
Head and Neck, Section of
Vertical middle section of head and neck showing the opening through the Eustachian tube, and its relations…
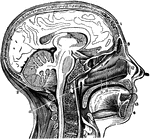
A Vertical Section of the Head and Neck
A vertical section of the head and neck through the mesial line, in order to show the opening of the…
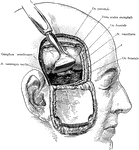
Incision of the Head Showing Gasserian Ganglion
Exposure of the Gasserian ganglion and middle meningeal artery though a flap incision of the scalp and…
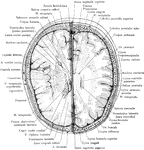
Cross Section of Head Through Lower Portion of Orbit
Section of the head through lower portion of orbit.
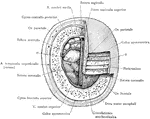
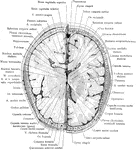
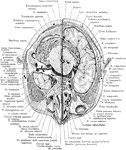
Cross Section of Head
Section two inches above supraorbital border. Upper surface. The (*) on right indicates subaponeurotic…
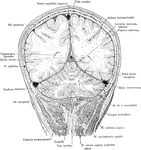
Frontal Section of the Head
Frontal section of the head passing through the parietal and occipital cerebral lobes and he cerebellar…
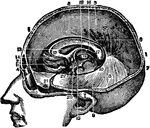
Head, Section of
Section of the head showing the greater scythe, the horizontal apophysis of the dura mater between the…
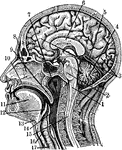
Sectional view of the Head
Section through the Head and Neck on the Median Line. 1. Medulla Oblongata 2. Pons 3. Right lobe of…
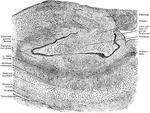
Frontal Section Through Hippocampus and Gyrus and Dentatus
Part of frontal section across left hippocampus and gyrus dentatus, showing arrangement of cell layers.
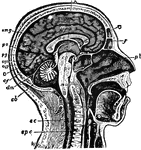
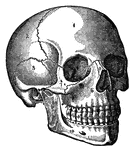
Human Brain
"The Brain is the encephalon, or center of the nervous system and the seat of consciousness and volition…
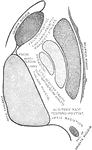
Internal Capsule
Diagrammatic representation of the internal capsule (as seen in horizontal section).
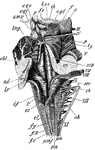
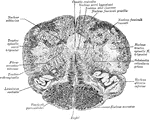
Medulla
Dorsal or posterior view of the medulla, fourth ventricle, and mesencephalon. Labels: p.n., line of…
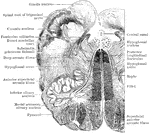
Section Through Medulla in Olivary Region
Transverse section through the human medulla in the lower olivary region.
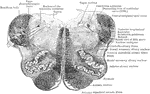
Section Through Medulla in Olivary Region
Transverse section through the the middle of the olivary region of the human medulla or bulb.
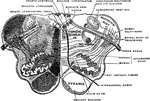
Medulla Oblongata
"The spinal cord and medulla oblongata. A, from the ventral, and B, from the dorsal aspect; C to H,…
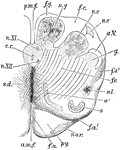
Medulla Oblongata
Anterior or dorsal section of the medulla oblongata in the region of the superior pyramidal decussation.…
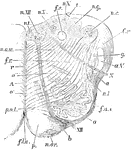
Medulla Oblongata
Section of the medulla oblongata at about the middle of the olivary body. f.l.a., anterior median fissure;…
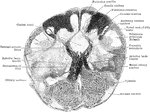
Transverse Section Through Closed Part of Medulla
Transverse section through the closed part of the human medulla immediately above the decussation of…
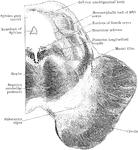
Section of Mesencephalon at Inferior Quadrigeminal Body
Transverse section through the mesencephalon at the level of the inferior quadrigeminal body.
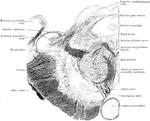
Section of Mesencephalon at Superior Quadrigeminal Body
Transverse section through the mesencephalon at the level of the superior quadrigeminal body.
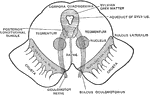
Section of Mesencephalon
Diagrammatic view of the cut surface of a transverse section through the upper part of the mesencephalon.
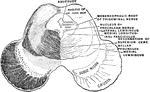
Section Through the Midbrain
Section of the midbrain through the level of the inferior quadrigeminal body.
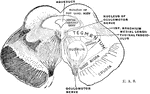
Section Through the Midbrain
Section of the midbrain through the level of the superior quadrigeminal body.
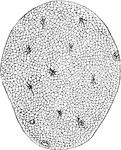
Muscle of the Hippocampus
Transverse section of one of the trunk muscles of the Hippocampus, stained in chloride gold.
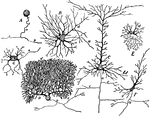
Nerve Cells
Forms of nerve cells. Labels: A, from spinal ganglion; B, from ventral horn of spinal cord; C, pyramidal…
Nerve Ganglia (Spinal)
Nerve Ganglia, or Knots (sing. Ganglion; Knot) occur as collections of nerve cells on the course of…
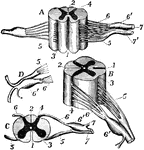
Nerve Roots
"The spinal cord and nerve-roots. A, a small portion of the cord seen from the ventral side; B, the…
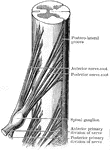
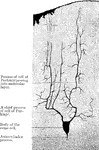
Seventh Dorsal Nerve
Throughout the dorsal region, the spinal cord presents a uniform girth and a very nearly circular outline…

Nerves
The cord-like structures composed of delicate filaments by which sensation or stimulative impulses are…