Isaac Rice
Isaac Rice was the name of our octegenarian guide. Like scores of those who fought our battles for freedom,…

Parakeet Macaw
Native to South America, the parakeet macaw is renowned for its powers to imitate human speech.
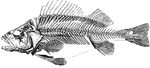
Perch skeleton
"The bones of fishes are of a less dense and compact nature than in the higher order of animals; in…

Sleepy Hollow
"Bridge over Sleepy Hollow Creek. Ichabod, according to Irving, in the Legend, returning from…

Camp Zagonyi
"Camp Zagonyi, encampment of Fremont's army on the prairie, near Wheatland, Mo., October 14th, 1861.…

Camp Zagonyi
"Camp Zagonyi, encampment of Fremont's army on the prairie, near Wheatland, Mo., October 14th, 1861.…

Camp Zagonyi
"Camp Zagonyi, encampment of Fremont's army on the prairie, near Wheatland, Mo., October 14th, 1861.…
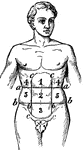
Abdominal
"In human anatomy, certain regions into which the abdomen is arbitrarily divided for the purpose of…

Martin Luther
"Martin Luther was born at Eisleben in 1483. He was the son of a poor miner, had entered the Augustinian…
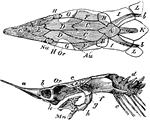
Sturgeon Skull
"Top and side views. The cartilaginous cranium shaded, is supposed to be seen through the unshded canial…

Buffalo
"The Buffalo. As the game upon which they depended moved about the country, so the Indians roved in…

Bombadier Beetle
"The bombadier beetle has a large oval abdomen, which secretes a caustic fluid. They live in societies,…

Death's Head Moth
"The most remarkable species is the Death's Head Moth, Acherontia Atropos, a large kind,…
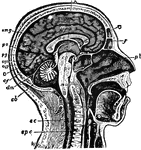
Human Brain
"The Brain is the encephalon, or center of the nervous system and the seat of consciousness and volition…

Collie
"Collie is a breed of the dog of obscure origin, which is highly valued. Many anecdotes are told of…
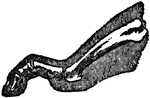
Side View of Bones in Foot
"The Foot is that part of the lower extremity below the leg on which we stand and walk. It is composed…
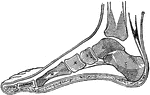
Side View of Bones in Foot
"The Foot is that part of the lower extremity below the leg on which we stand and walk. It is composed…
Larval Frog Hopper
"Frog Hoppers are ranked under the homopterous sub-order of insects. The name of frog hopper refers…
Frog Hopper on Leaf
"Frog Hoppers are ranked under the homopterous sub-order of insects. The name of frog hopper refers…
Adult Frog Hopper
"Frog Hoppers are ranked under the homopterous sub-order of insects. The name of frog hopper refers…

Female Gorilla
"The Gorilla is a celebrated anthropoid ape, generally belived to come nearer than any known one to…

Tomato Plant
"Tomato, or Love Apple, is a plant of the natural order Solanaceæ. It is one of a genus of several…

Tomato
"Tomato, or Love Apple, is a plant of the natural order Solanaceæ. It is one of a genus of several…

Tomato
"Tomato, or Love Apple, is a plant of the natural order Solanaceæ. It is one of a genus of several…

Viscacha
"Viscacha is a stout-built rodent, resembling a marmot, from 18 inches to two feet long, exclusive of…
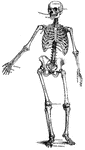
Human skeleton
"There are in all two hundred and six seperate bones in the adult skelton. The teeth are not bones,…
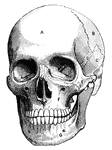
Human skull
"A, frontal bone; B, parietal bone; C, temporal bone; D, sphenoid bone; E, malar bone; F, upper jawbone;…
Spinal column
"The spine or backbone, serves as a support for the whole body. It is made up of a number of…
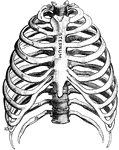
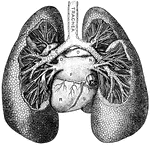
Thorax
"The ribs are long, flat, and curved bones which bend round the chest somewhat like the hoops…
Humerus
"The humerus, a long, hollow bone, rests against a shallow socket on the shoulder blade. It…
Ulna and Radius
"The ulna, or elbow bone, is the larger of these two bones. It is joined to the humerus by…
Tibia and Fibula
"The leg consists, like the forearm, of two bones. The larger, a strong, three-sided bone with…
Bones of the Foot
"The foot is built in the form of a half-dome or half-arch. This is to afford a broad, strong support…
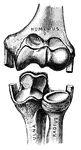
Elbow Joint
"Showing how the Ends of the Bones are shaped to form the Elbow Joint. The cut ends of a few ligaments…

Powerful Ligament at the Hip Joint
"The bones are fastened together, kept in place, and their movements limited, by tough and strong bands,…

Ligaments of the Foot and Ankle
"The bones are fastened together, kept in place, and their movements limited, by tough and strong bands,…
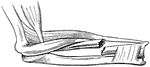
Broken Radius
"When a bone is broken, blood trickles out between the injured parts, and afterwards gives place to…
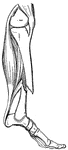
Broken Tibia
"When a bone is broken, blood trickles out between the injured parts, and afterwards gives place to…
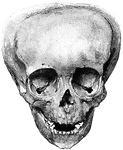
Deformed skull
"Showing how the Bones of the Skull may be artificially deformed by "head-binding." From the photograph…

Superficial Muscles of the Body
"A single muscle rarely or never contracts alone, but always in harmony with a number of other muscles.…
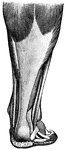
Achillles tendon
"Tendons are white, glistening cords, or straps, which connect the muscles with the bones." —…
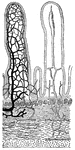
Transverse section of the small intestine
"In the figure on the left are seen the artery and vein of a villus. In the right figure are represented…
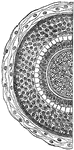
Cross-section of a human hair
"Cross-section of One Half of a Human Hair. A hair is made up of horny cells of the outer layer of the…
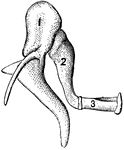
Bones of the Ear
"1, malleus, or hammer; 2, incus, or anvil; 3, stapes, or stirrup." — Blaisedell, 1904
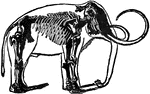
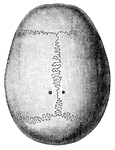
Skeleton of the Mammoth
"Mammoth is a species of extinct elephant, the fossil remains of which are found in European, Asiatic…

Mandrake
"Mandrake is a perennial herb. From the rude resemblance of the bifurcated root to the human figure…

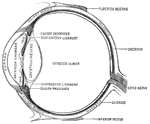
Compound microscope
"A Compound Microscope. The appearance of the various structures and tissues of the human body as revealed…

Lucian
"Lucian, the humorous satirist, was a native of Samosata, in Syria, and flourished towards the end of…
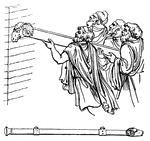
Aries
"The battering-ram, was used to batter down the walls of besieged cities. It consisted of a large beam,…

Raven
"The Raven is a large bird of the crow family. The raven has played an important part in mythology and…

Water Rice
"Rice is a well known genus of grasses, having panicles of one-flowered spike-lets, with two very small…

Sphinx
"Sphinx is a Greek word signifying 'strangler,' applied to certain symbolical forms of Egyptian origin,…

Swordfish
"Swordfish is a popular name for any individual of the Xiphiidæ. They are pelagic fishes, widely…
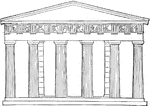
Thesium restored
"The Theseum is situated on a height to the north of the Areopagus, and was built to receive the bones…