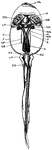
Tadpole Dissection
"Dissection of tadpole. DL., Lower lip; H., ventricle of heart; DE., oesophagus; NA., head kidney; A.,…
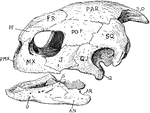
Turtle Skull
"Skull of turtle. "S.O., supra-occipital; PAR., parietal; FR., frontal; P.F., pre-frontal; PO.F., post-frontal;…
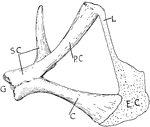
Turtle Pectoral Girdle
"Pectoral girdle of a Chelonian. G., Glenoid cavity; SC., scapula; P.C., procoracoid fused to the scapula;…
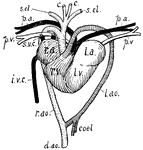
Tortoise Heart
"Heart and associated vessels of tortoise. r.a., Right auricle; superior venae cavae (s.v.c.) and inferior…
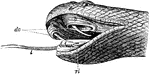
Snake Head
"Snake's head. dv., Poison fangs; b., sheath of fang; l., tongue; rl., muscles of tongue." -Thomson,…
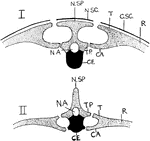
Mammal and Chelonian Backbones
"Vertical section through backbone and ribs of Chelonian (I.) and Mammal (II.). N.SP., neural spine;…
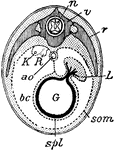
Bird Section
"Diagrammatic section of young bird. n., Spinal cord; v., vertebra; r., rib; L., liver; G., gut; som.…
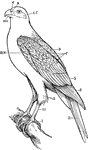
Falcon
"A falcon. mn., Mandible; C., cere; N., nostril; E.C., ear covert; th.W., thumb wing; C., wing coverts;…
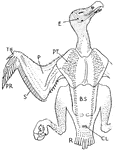
Lammergeier
"Young bearded griffin (Gypaetus barbatus). Showing the feather-tracts or pterylae, for instance those…
Feathers
"A., Filoplume. B., very young feather within its sheath (sh.); c., the core of dermis; b., the barbs.…
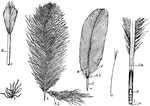
Feather Types
"Types of feathers. D., Down. 2, Developing feather in sheath (sh.). 3, Covert of heron showing aftershaft…
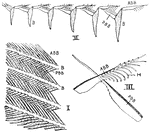
Feather Parts
"Parts of a feather. I., Four barbs (B.) bearing anterior barbules (A.BB.) and posterior barbules (P.BB.);…

Dove Wing
"Wing of dove. h., Humerus; s.f., secondary feathers; r., radius; u., ulna; c., carpals; mc., carpo-metacarpus;…
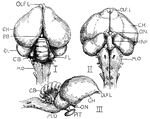
Pigeon Brain
"Brain of pigeon (I. dorsal, II. ventral, III. lateral aspects). OLF.L., Olfactory lobes; C.H., cerebral…
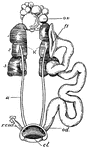
Female Pigeon Urogenital Organs
"Female urogenital organs of pigeon. K., Kidney with three lobes; u., ureter; cl., cloaca; ov., ovary;…
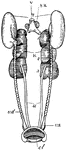
Male Pigeon Urogenital Organs
"Male urogenital organs of pigeon. T., testes; V., base of inferior vena cava; S.R., suprarenal bodies;…
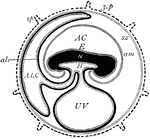
Mammal Fetus
"Diagram of foetal membranes. E., Embryo; H., gut lined by hypoblast, dotted-- the dark is mesoblast;…
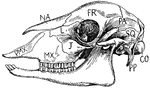
Sheep Skull
"Side view of sheep's skull. PMX., Premaxilla; MX., maxilla; NA., nasal; J., Jugal; L., lachrymal; FR.,…
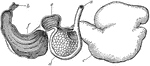
Sheep Stomach
"Stomach of sheep. a, OEsophagus; c, rumen or paunch; d, reticulum or honeycomb-bag; e, psalterium or…
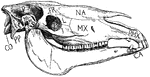
Horse Skull
"Side view of horse's skull. P., Parietal; FR., frontal; NA., nasal; PMX., premaxilla; MX., maxilla;…
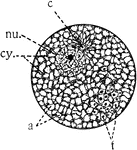
Cell Parts
"Diagram showing the principal parts of the cell as it appeaers when killed and stained. The protoplasm…
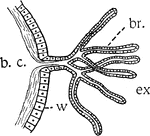
Gills or Branchiae
"Diagram illustrating gills or branchiae. b.c., cavity in which the body fluids circulate; br., branchial…
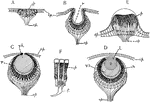
Invertebrate Simple Eye
"Diagrams showing some of the stages in the increasing complexity of the simple eye in Invertebrates.…
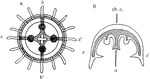
Medusa
"Diagram of Medusa, illustrating radial symmetry. A, viewed from the oral end of the principal axis;…
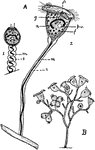
Vorticella
"A, Vorticella, a stalked ciliate Infusorian; I, contracted; 2, extended. f, food "vacuoles"; g, gullet;…
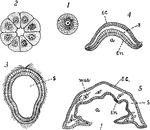
Simple Sponge Development
"Diagrams to illustrate the development of one of the simpler types of sponge: I, the egg; 2, section…
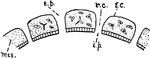
Ascon Sponge
Diagram showing the Ascon type of sponge. ec., ectoderm; r.c., radiating canals; i.p., internal pores;…
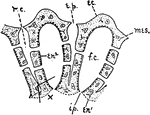
Sycon Sponge
Diagram showing the Sycon type of sponge. ec., ectoderm; r.c., radiating canals; i.p., internal pores;…
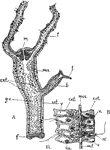
Hydra
"A, Longitudinal section through the body of Hydra (diagrammatic). B, small portion of the wall more…
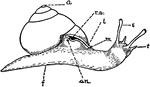
Helix Snail
"Helix. B, the relation of the animal to the shell when extended...a, apex of shell; an., anus; e, eyestalk;…
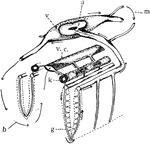
Bivalve Circulation
"Diagram showing the heart and general course of the circulation in the lamellibranchs. Only a short…
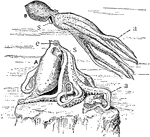
Octopus
"The Devil-fish (Octopus). A, at rest; B, swimming. a, arms, with suckers on the inner aspect; e, eye;…
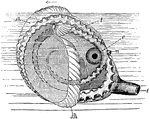
Paper Nautilus
"The Paper Nautilus (Argonauta argo). e, eye; m, mouth; f, siphon; sh, shell; t, tentacles." -Galloway,…
Lancelet
"Diagram of the anatomy of Amphioxus, drawn as a semi-transparent object. a, anus; a.p., atrial pore;…
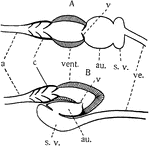
Vertebrate Heart
"Diagrams of the structure of the heart in the lower Vertebrates. A, primitive condition; B, the position…
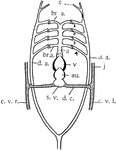
Teleost Heart
"Diagram of the heart, the branchial arches, and the principal veins in the Teleosts. Ventral view.…
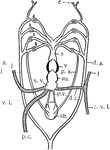
Queensland Lungfish Heart
"Diagram of heart and branchial arches in Ceratodus (one of the Dipnoi). a.b., air bladder (lung); p.a.,…
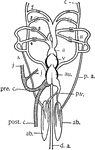
African Lungfish Heart
"Diagram of the heart and branchial arches in Protopterus (one of the Dipno). pre.c., precaval vein,…
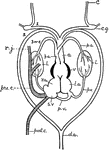
Frog Heart
"Diagram of the heart and branchial arches in the Frog. c.g., carotid gland; l., lungs; l.a., left auricle;…
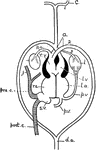
Reptile Heart
"Diagram of the heart and branchial arches in a Reptile...a, aorta; au., auricle; c, carotid; c.v.,…
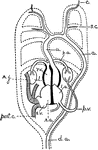
Mammal Heart
"Diagram of the heart and the branchial arches in Mammals. A dotted outline of the arches of the Fish…
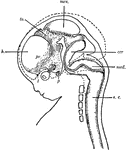
Human Fetus
"Diagram of head and brain of human foetus six weeks old (heavy boundaries). The dotted line indicates…
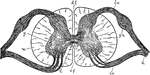
Spinal Cord
"Diagram of a cross-section of the spinal cord through the roots of spinal nerves. c, central canal;…
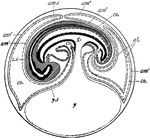
Fowl Embryo
"Diagram of a longitudinal section through the embryo of a fowl, showing formation of amnion and allantois…
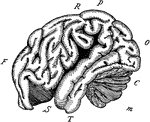
Orangoutang Brain
"The outline of the brain of an orang outang. Front portion F to O, cerebrum; C, cerebellum; M, medulla…

Bayberry
The bayberry or Myrica cerifera is small tree native to North America and used in candlemaking and for…

Yellow Lady's Slipper
The yellow lady's slipper or Cypripedium parviflorum is an orchid used for medicinal purposes.

Spotted Wintergreen
The spotted wintergreen or Chimaphila maculata is a perennial herb used for medicinal purposes.

Dog's Bane
The dog's bane or Apocynum androsemifolium is a flowering plant used for medicinal purposes.

Indian Tobacco
The Indian Tobacco or Lobelia inflata is an herbaceous plant used for medicinal purposes.

Butterfly Weed
The butterfly weed or Asclepias tuberosa is a milkweed plant used for medicinal purposes.