John Brown
In 1859, John Brown collected a small body of men, white and black, in the mountains of Maryland. He…

Atlantic Cable
"Laying the Atlantic Cable. In 1866, a previous attempt in 1858 having failed, a telegraphic cable was…

Amphora
"A jar with two handles; Among the Greek and Roman, a vessel, usually tall and slender having two handles…

Amphora
"A jar with two handles; Among the Greek and Roman, a vessel, usually tall and slender having two handles…

Date Palm
"Date Palm is a genus of palms, the most important species of which is the common date palm, the palm…

Torque
"A Torque, in archæology, is a twisted collar of gold, or other metal, worn around the neck, in…

Statue of Liberty
"The Statue of Lberty is a colossal statue on Bedloe's Island, N.Y. On Oct. 28, 1886, after more than…

Egyptian Water Lily
"Lotus is a name given to various flowers, including several beautiful species of water lily, especially…

Passion Flower
"Pasiflora is the passion-flower. Generally climbing herbs or shrubs. Fruit succulent, seeds many. Found…

Theocritus
"The fame of Theocritus, the prince of bucolic poetry, depends on his faithful pictures of natural scenery…
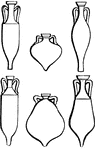
Amphorae
"A vessel used for holding wine, oil, honey. The following cut represents amphorae in the British Museum.…

Julian
"Thus the prince, both when present and when coming, was alike victorius: and these things he achieved…
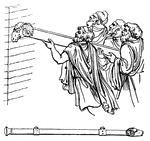
Aries
"The battering-ram, was used to batter down the walls of besieged cities. It consisted of a large beam,…
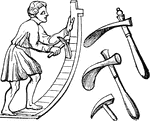
Ascia
"An adze. Muratori has published numerous representations of the adze, as it is exhibited on ancient…
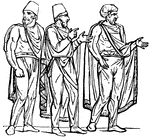
Bracae
"Trowsers, pantaloons, were common to all the nations which encircled the Greek and Roman population,…

Calceus
"A shoe or boot, anything adapted to cover and preserve the feet in walking. The use of shoes was by…
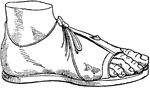
Calceus
"A shoe or boot, anything adapted to cover and preserve the feet in walking. The use of shoes was by…

Cantharus
"A king of drinking cup, furnished with handles. It was the cup scred to Bacchus, who is frequently…
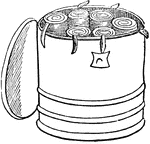
Capsa
"A box for holding books among the Romans. These boxes were of cylindrical form. There does not appear…
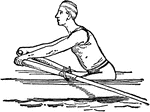
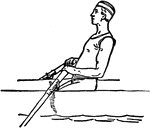
Positions in Rowing
"Rowing is the propulsion of a boat by oars. The oarsman sits with his face to the stern of the boat,…
Positions in Rowing
"Rowing is the propulsion of a boat by oars. The oarsman sits with his face to the stern of the boat,…
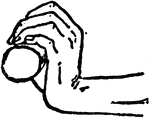
Wrist Positions in Rowing
"Rowing is the propulsion of a boat by oars. The oarsman sits with his face to the stern of the boat,…
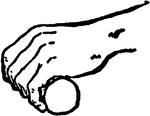
Wrist Positions in Rowing
"Rowing is the propulsion of a boat by oars. The oarsman sits with his face to the stern of the boat,…
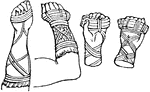
Cestus
"The thongs or bands of leather, which were tied round the hands of boxers, in order to render their…

Roller Skating
A group of people rollerskating indoors. The man in front is about to fall. All of the people are wearing…

Cock-Fighting
"Two players are made to sit on the ground draw their legs up, and clasp their hands together over their…
Whizzer
"Get a circular piece of tin, three inches or more in diameter, and cut it round the edges in the form…
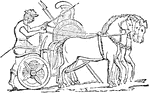
Greek Chariot
"In the battles, as depicted by Homer, the chiefs are the only important combatants, while the people…

Bust of Pericles
"The enormous influence which Pericles exercised for so long a period over an ingenious but fickle people…

Halteres
"Halteres were certain masses of stone or metal, which were used in the gymnastic exercises of the Greeks…
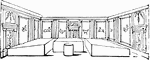
Banqueting room
"The Roman people reclined at their meals. On each couch there were commonly three persons. They lay…

Sacrifice of Iphigenia
"The cut represents a painting from a wall at Pompeii, the subject of which is the sacrifice of Iphigenia,…

Malleus
"A hammer, a mallet. In the hands of the farmer the mallet of wood served to break down the clods and…

Marsupium
"Marsupium, a purse. The purse used by the ancients was commonly a small leathern bag, and was often…

Cavalryman Charging
Charging cavalryman pictured trampling an enemy soldier and holding a spear in the Gallic War.

Pedum
"A shepherd's crook. On account of its connection with pastoral life, the crook is often seen in works…
Pons Cestius
"A bridge. As the rivers of Greece were small, and the use of the arch known to them only to a limited…
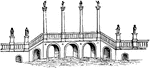
Pons Aelius
"A bridge. As the rivers of Greece were small, and the use of the arch known to them only to a limited…
Pons Ariminum
"A bridge. As the rivers of Greece were small, and the use of the arch known to them only to a limited…
Pons Trajan
"A bridge. As the rivers of Greece were small, and the use of the arch known to them only to a limited…
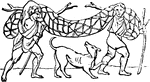
Retis
"In this woodcut, two men are carrying the net home after the chase, and hold in their hands two of…

Rostra
"The Beaks, was the name applied to the stage in the Forum, from which the orators addressed the people.…

Foreign Lands
Up into the cherry tree, who should climb but little me? I held the trunk with both my hands and looked…

Chimpanzee
A large West African Ape. A dark blackish brown hair, flesh-colored hands and feet, arms reaching to…
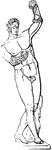
Boxer with cestus
"The cestus was used by boxers from the earliest times. It consisted of thongs of raw ox-hide, or of…
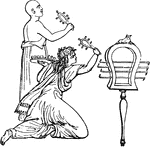
Sistrum
"The sistrum was an Egyptian instrument of music, used in certain ceremonies by that people, and especially…
Parade Rest
"Carry the right foot 6 inches straight to the rear, left knee slightly bent; clasp the hands, without…
Order Arms Standing
"The butt rests evenly on the ground, barrel to the rear, toe of the butt on a line with toe of, and…
Port Arms
"With the right hand raise and throw the piece diagonally across the body, grasp it smartly with both…