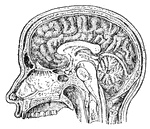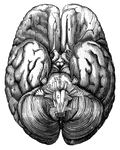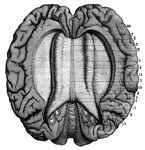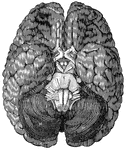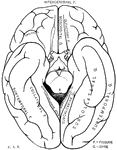
Human Brain
A top view of a dissection of the human brain showing the lateral fourth and fifth ventricles.
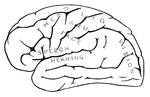
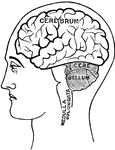
Human Brain
Side diagram of the human brain showing which parts of the brain control hearing, speech, vision, legs,…
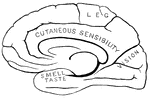
Human Brain
Side diagram of the human brain showing which areas perform the sense of taste, smell, and vision.

Saimiri
"Genus Saimiri. The animals of this genus are but about ten inches in length and are the most…
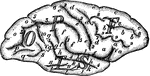
Human Brain
"The Brain is the encephalon, or center of the nervous system and the seat of consciousness and volition…

Female Gorilla
"The Gorilla is a celebrated anthropoid ape, generally belived to come nearer than any known one to…
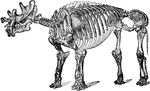
Tinoceras
"Tinoceras, or tinotherium, is a genus of mammals now extinct, found in the Eocene, and representing…
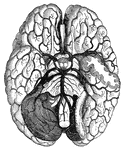
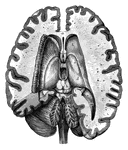
Blood vessels of the brain
"Arteries and their Branches at the Base of the Brain." — Blaisedell, 1904
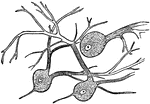
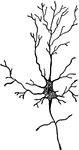
Nerve Cells of the Brain
"Wherever nerve cells are abundant, the nerve tissue has a gray color; in other places, it looks white.…

Nervous System
"Diagram illustrating the General Arrangement of the Nervous System. (posterior view.)" — Blaisedell,…
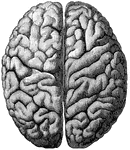
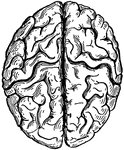
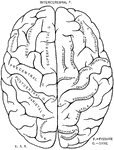
Cerebrum
"The Upper Surface of the Cerebrum. Showing its division into two hemispheres, and also of the convolutions."…
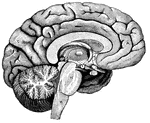
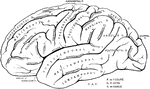
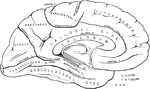
Left Half of the Brain
"A,frontal love of the cerebrum; B, parietal lobe; C, parieto-occipital lobe;…
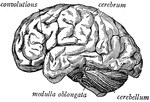
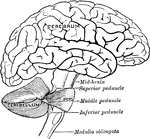
Side view of the brain
"The brain seen from the side, showing the three principal divisions." — Ritchie, 1918
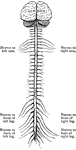
Central Nervous System
"Brain and spinal cord, with the thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves." — Tracy, 1888

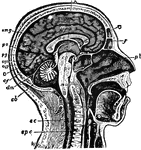
Side View of the Body
A side view of the two great cavities of the body and their organs. 1: The mouth. 2: The thorax. 3:…

Nerves
The cord-like structures composed of delicate filaments by which sensation or stimulative impulses are…
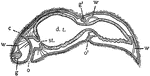
Stenostoma
In this Turbellarian the digestive tract (d.t.) is a blind sac. st., boundary of stomodaeum and mesenteron;…
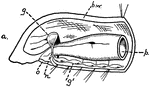
Oligochete Worm
This illustration shows the arrangement of the nervous material in the anterior end of an Oligochete…
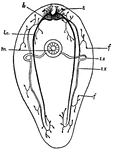
Turbellarian
This is a diagram of a Turbellarian, showing the general arrangement of the nervous structures and one…
Rotifer
This diagram shows a sagittal section of a Rotifer. b, brain; bl., excretory bladder; c, cloaca, the…
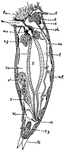
Annelid
This diagram shows a fresh-water annelid. a, appendages; br., brain; d, dissepiments; i, intestine;…
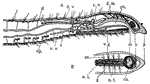
Annelid
This diagram shows the longitudinal section of the anterior end of the annelid. A, sagittal section;…
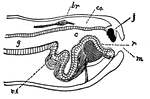
Snail
Diagram of the mouth of a snail, showing the lingual ribbon. br, brain; c, buccal cavity; co., caelom;…
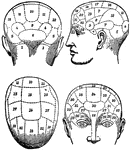
Phrenology
The term applied to the psychological theories of Gall and Spurzheim, founded upon 1, the discovery…
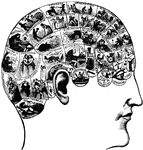
Phrenology
A theory which claims to be able to determine character, personality traits, and criminality on the…
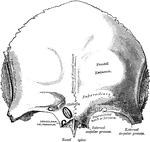
Frontal Bone
A bone in the human skull that consists of two portions, a vertical portion and a horizontal portion.…
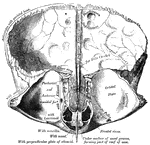
Frontal Bone
A bone in the human skull that consists of two portions, a vertical portion and a horizontal portion.…
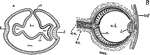
Vertebrate Eye
"Diagrams illustrating two stages in the development of the vertebrate eye. A, showing the relation…
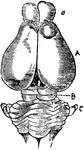
Opossum Brain
"The size of the hemispheres of the brain (A) is so small that they leave exposed the olfactory ganglion…
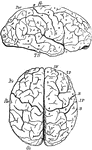
Brain
"Profile and vertex views of cerebrum. Dr, the frontal lobe; Par, parietal; Oc, occipital; Ts, temporo-sphenoidal…
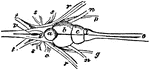
Perch Brain
"Brain of Perch. Upper aspect. a, cereoellum; b, optic lobes; c, hemispheres; e, lobi inferiores; f,…
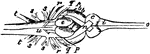
Perch Brain
"Brain of Perch. Lower aspect. a, cereoellum; b, optic lobes; c, hemispheres; e, lobi inferiores; f,…
Polypterus Brain
"Brain of Polypterus. Upper aspect. a, medulia; b, corpora restiformia; c, cerebellum; d, lobi optici;…
Polypterus Brain
"Brain of Polypterus. Lateral aspect. a, medulia; b, corpora restiformia; c, cerebellum; d, lobi optici;…
Polypterus Brain
"Brain of Polypterus. Lower aspect. a, medulia; b, corpora restiformia; c, cerebellum; d, lobi optici;…
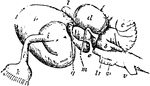
Carcharias Brain
"Brain of Carcharias. ae, nervus acousticus; b, corpus restiforme; c, cerebellum; d, lobus opticus;…
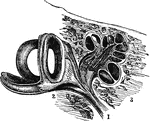
Auditory Nerve
"By anatomists, the auditory nerve is associated with the facial, and is the seventh in order of origin…
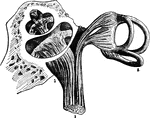
Auditory Nerve
"By anatomists, the auditory nerve is associated with the facial, and is the seventh in order of origin…
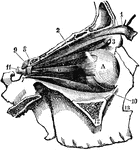
Eye Muscles
"The external bones of the temple are supposed to be removed in order to render visible the muscular…
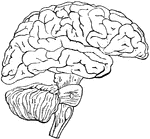
Brain
"Diagram illustrating the general relationships of the parts of the brain. A, fore-brain; b, midbrain;…
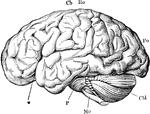
Brain
"The brain from the left side. Cb, the cerebral hemispheres forming the main bulkl of the fore-brain;…
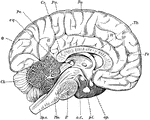
Brain
"Diagram of the left half of a vertical median section of the brain. H, H, convoluted inner surface…
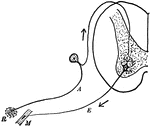
Reflex Arc
"Diagram of the simple reflex arc. R, receptor; A, afferent (sensory) neuron; E, efferent (motor) meuron;…
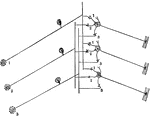
Sensory Neuron
"Diagram to illustrate how a single sensory neuron may communicate with several motor neurons, and a…