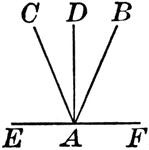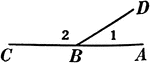
Relationships Between 4 Angles
Illustration showing four angles that can be used to define different relationships, such as adjacent,…
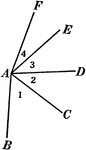
Relationships Between 4 Angles
Illustration showing four angles that can be used to define different relationships, such as adjacent,…
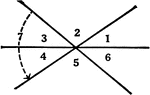
Relationships Between 6 Angles
Illustration showing six angles that can be used to define different relationships, such as adjacent,…
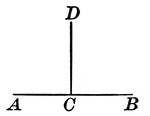
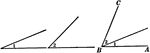
Right Angles With Same Vertex
An illustration showing when one straight line meets another straight line and makes the adjacent angles…
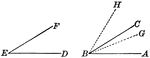
Superposition of Angles
Illustration of the superposition of two angles to compare magnitudes of the same kind.
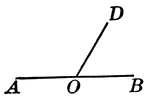
Supplementary Angles
Illustration of supplementary angles. Two angles whose sum is a straight angle.
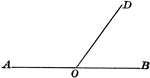
Supplementary Angles
Illustration of supplementary angles. Two angles whose sum is a straight angle. This can be used tow…
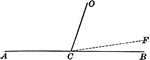
Supplementary Angles
Illustration of supplementary angles. Two angles whose sum is a straight angle. This can be used tow…
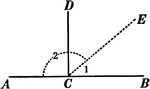
Supplementary and Right Angles
Illustration showing angles 1 and 2 are supplementary and angles ACD and DCB are supplementary. Also,…
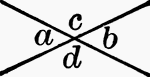
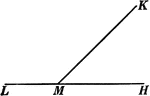
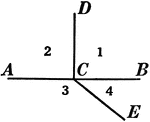
Vertical Angles
Vertical angles are when two angles have the same vertex, and the sides of the one are prolongations…
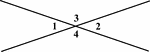
Vertical Angles
Illustration showing that angles 1 and 2 are vertical and angles 3 and 4 are vertical.
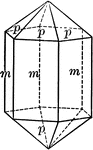
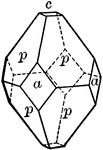
Apatite
"Hexagonal; tri-pyramidal. Crystals usually long prismatic in habit; sometimes short prismatic or tabular.…
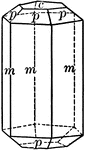
Apatite
"Hexagonal; tri-pyramidal. Crystals usually long prismatic in habit; sometimes short prismatic or tabular.…
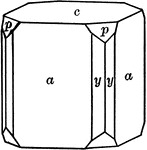
Apophyllite
"Tetragonal. Usually shows a combination of prism of second order, pyramid of first and basal plane."…
Aragonite
"Orthorhombic. Acicular pyramidal; consisting of a prism terminated by a combination of a very steep…
Aragonite
"Orthorhombic. Tabular; consisting of prominent brachypinacoid faces modified by a prism and a low brachydome."…
Arch
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…
Arch
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…
Arch
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…
Arch
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…
Area of Circle with Triangles
"In the triangle above, the line AB is its altitude. Since we know how to find the area of one triangle,…
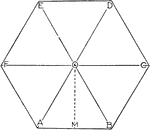
Area of Hexagon
Illustration showing how to find the area of a hexagon using the triangles that make it up.
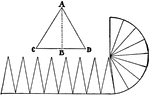
Area of Sphere
"It is found that the cord covering the curved surface is twice as long as the one covering the flat…

Area of Sphere
"The bases of the pyramids are considered as forming the surface of the sphere, while the altitude of…

Arrow Pointing Left
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…
Arrow Pointing Left
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…
Arrow Pointing Left
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…
Arrow Pointing Left
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…
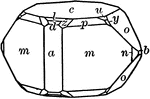
Arsenopyrite
"Orthohombric. Usually in tabular diamond-shaped crystals, formed by a short prism terminated by low…
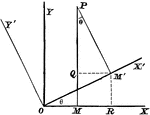
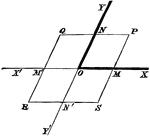
Rectangular Axes
Transforming from one set of rectangular axes to another with the same origin, but different direction.
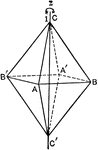
Symmetry axis
"A crystal has a center of symmetry if an imaginary line is passed from some point on its surface through…
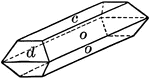
Barite
"Orthohombic. Crystals usually tabular parallel to base; often diamond shaped because of the presence…
Barite
"Orthohombic. Crystals usually tabular parallel to base; often diamond shaped because of the presence…

Bear
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…
Bear
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…

Bear
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…
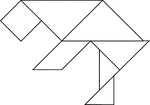
Bear
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…
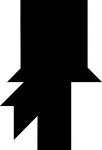
Bearded Man in a Tophat
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…
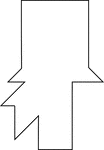
Bearded Man in a Tophat
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…
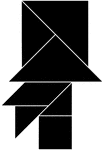
Bearded Man in Tophat
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…
Bearded Man in Tophat
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…
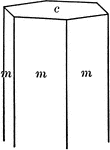
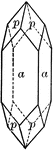
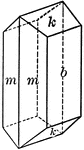
Beryl
"Hexagonal. Strong prismatic habit. Frequently vertically striated and grooved. Forms usually present…
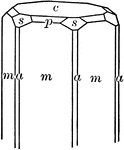
Beryl
"Hexagonal. Strong prismatic habit. Frequently vertically striated and grooved. Forms usually present…
Beta Fish
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…
Beta Fish
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…
Beta Fish
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…
Beta Fish
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…
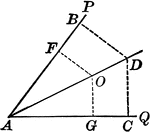
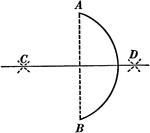
Angle Bisector
Illustration showing that the bisector of a given angle is the locus of points equidistant from the…