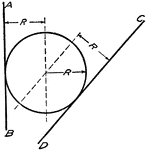
Draw Arc of Given radius R Tangent to Two Given Lines
"Draw lines parallel to AB and CD at distant R from them. The intersection of these lines will be center…
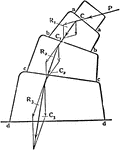
Buttress of Blocks
Uniting the theories of partial polygons of resistance and centres and lines of resistance, this buttress…
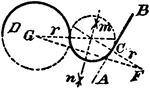
Construction Of A Center And Radius Of A Circle That Will Tangent A Given Circle And Line
An illustration showing how to construct the center and radius of a circle that will tangent a given…
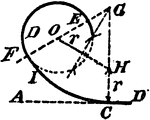
Construction Of A Center And Radius Of A Circle That Will Tangent A Given Circle And Line
An illustration showing how to construct the center and radius of a circle that will tangent a given…
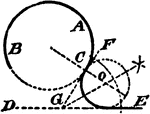
Construction Of A Center And Radius Of A Circle That Will Tangent A Given Circle
An illustration showing how to construct the center and radius of a circle that will tangent a given…
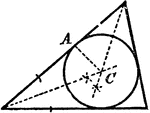
Construction Of The Center And Radius Of A Circle Tangent To Triangle Sides
An illustration showing how to construct a center and radius of a circle that will tangent the three…
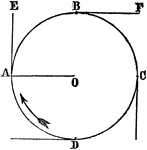
Centrifugal Force
"Attach a ball, for instance, to a cord; and , fastening the end of the cord at a point, O, give a quick…
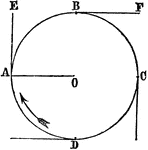
Centrifugal Force
"The instant one of the strings is let go, the centrifugal force carries off the stone in a tangent…
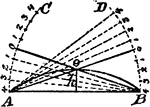
Construction Of A Circle Arc
An illustration showing how to construct a circle arc without recourse to its center, but its chord…
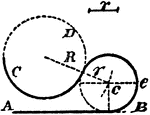
Construction Of A Circle Tangent To A Line And A Circle
An illustration showing how to construct a circle tangent to a given line and given circle. "Add the…
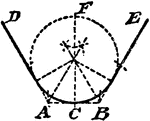
Construction Of A Circle That Tangents 2 Given Lines And Goes Through A Given Point
An illustration showing how to construct a circle that tangents two given lines and goes through a given…
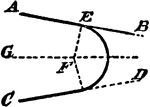
Construction Of A Circle That Tangents 2 Given Lines
An illustration showing how to construct a circle that tangents two given lines inclined to one another…
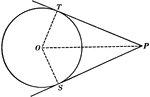
Equal Tangents to Circle Theorem
Illustration used to show that "If two tangents are drawn from any given point to a circle, those tangents…
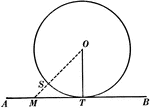
Tangent to Perpendicular Radius Circle Theorem
Illustration used to show that "A tangent to a circle is perpendicular to the radius drawn to the point…
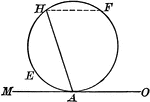
Circle With Chord and Tangent
Illustration of a circle showing an angle included by a tangent and a chord drawn from the point of…
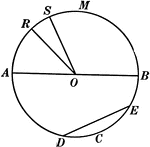
Chords, Diameters, and Radii of a Circle
Illustration of a circle with diameter AB. Radii are RO, SO, AO, and BO. ED is a chord.
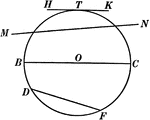
Chords, Secants, Diameters, and Tangents of a Circle
Illustration of a circle with diameter BC, chord DF, secant MN, and tangent HK.
Decagon Circumscribed About A Circle
Illustration of a decagon circumscribed about a circle. This can also be described as a circle inscribed…
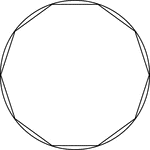
Decagon Inscribed In A Circle
Illustration of a decagon inscribed in a circle. This can also be described as a circle circumscribed…
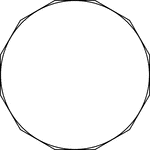
Dodecagon Circumscribed About A Circle
Illustration of a dodecagon circumscribed about a circle. This can also be described as a circle inscribed…
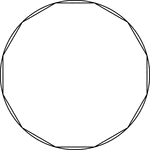
Dodecagon Inscribed In A Circle
Illustration of a dodecagon inscribed in a circle. This can also be described as a circle circumscribed…
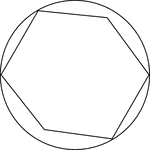
Hexagon In A Circle
Illustration of a hexagon in a circle. Four of the six vertices of the hexagon are bound by the circle…
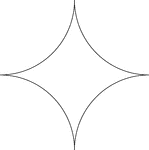
Reflected Arcs Of A Circle
A design created by dividing a circle into 4 equal arcs and reflecting each arc toward the center of…
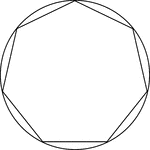
Regular Heptagon/Septagon Inscribed In A Circle
Illustration of a regular heptagon/septagon inscribed in a circle. This can also be described as a circle…
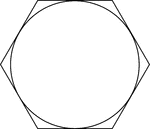
Regular Hexagon Circumscribed About A Circle
Illustration of a regular hexagon circumscribed about a circle. This can also be described as a circle…
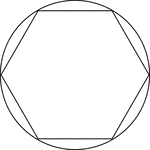
Regular Hexagon Inscribed In A Circle
Illustration of a regular hexagon inscribed in a circle. This can also be described as a circle circumscribed…
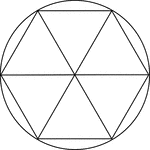
Regular Hexagon Inscribed In A Circle
Illustration of a regular hexagon inscribed in a circle. This can also be described as a circle circumscribed…
Regular Nonagon Circumscribed About A Circle
Illustration of a regular nonagon circumscribed about a circle. This can also be described as a circle…
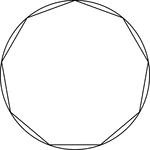
Regular Nonagon Inscribed In A Circle
Illustration of a regular nonagon inscribed in a circle. This can also be described as a circle circumscribed…
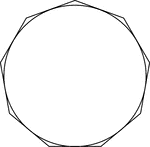
Regular Octagon Circumscribed About A Circle
Illustration of a regular octagon circumscribed about a circle. This can also be described as a circle…
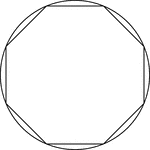
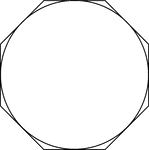
Regular Octagon Inscribed In A Circle
Illustration of a regular octagon inscribed in a circle. This can also be described as a circle circumscribed…
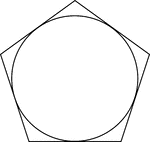
Regular Pentagon Circumscribed About A Circle
Illustration of a regular pentagon circumscribed about a circle. This can also be described as a circle…
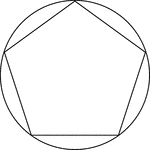
Regular Pentagon Inscribed In A Circle
Illustration of a regular pentagon inscribed in a circle. This can also be described as a circle circumscribed…
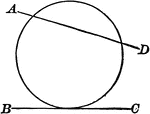
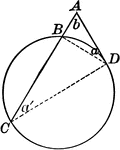
Circle with Secant and Point of Tangency
Illustrations of a circle with secant AD and line BC tangent to it.
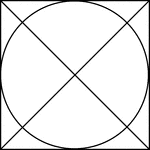
Square Circumscribed About A Circle
Illustration of a square, with diagonals drawn, circumscribed about a circle. This can also be described…
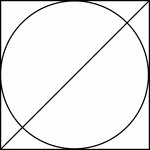
Square Circumscribed About A Circle
Illustration of a square, with 1 diagonals drawn, circumscribed about a circle. This can also be described…
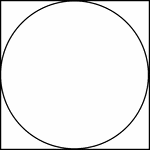
Square Circumscribed About A Circle
Illustration of a square circumscribed about a circle. This can also be described as a circle inscribed…
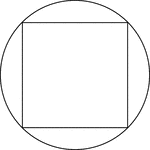
Square Inscribed In A Circle
Illustration of a square inscribed in a circle. This can also be described as a circle circumscribed…
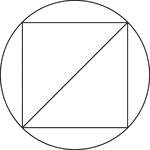
Square Inscribed In A Circle
Illustration of a square inscribed in a circle. This can also be described as a circle circumscribed…
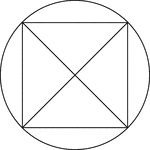
Square Inscribed In A Circle
Illustration of a square, with diagonals drawn, inscribed in a circle. This can also be described as…
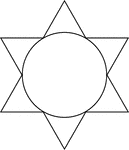
Star Circumscribed About A Circle
Illustration of a 6-point star (convex dodecagon) circumscribed about a circle. This can also be described…
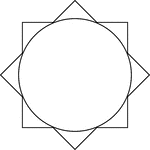
Star Circumscribed About A Circle
Illustration of an 8-point star (convex polygon) circumscribed about a circle. This can also be described…
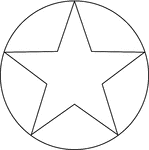
Star Inscribed In A Circle
Illustration of a 5-point star inscribed in a circle. This can also be described as a circle circumscribed…
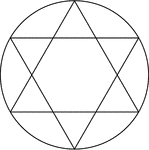
Star Inscribed In A Circle
Illustration of a 6-point star created by two equilateral triangles (often described as the Star of…
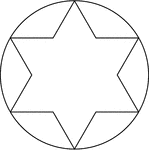
Star Inscribed In A Circle
Illustration of a 6-point star (convex dodecagon) inscribed in a circle. This can also be described…
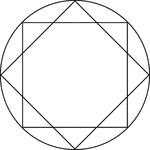
Star Inscribed In A Circle
Illustration of an 8-point star, created by two squares at 45° rotations, inscribed in a circle.…
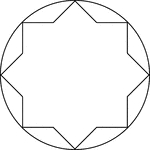
Star Inscribed In A Circle
Illustration of an 8-point star, or convex polygon, inscribed in a circle. This can also be described…
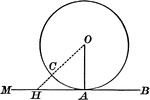
Circle With Tangent Line Drawn
Illustration of a circle with a tangent drawn - a straight line perpendicular to a radius at its extremity.
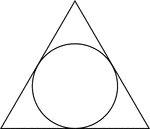
Triangle Circumscribed About A Circle
Illustration of an equilateral triangle circumscribed about a circle. This can also be described as…
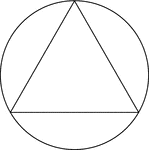
Triangle Inscribed In A Circle
Illustration of an equilateral triangle inscribed in a circle. This can also be described as a circle…
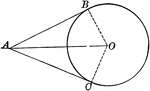
Circle With Two Tangents Drawn From an External Point
Illustration of a circle which illustrates that the tangents to a circle drawn from an external point…
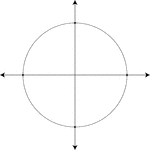
Unit Circle
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane. The…
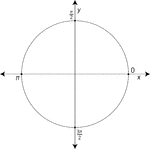
Unit Circle Labeled At Quadrantal Angles
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
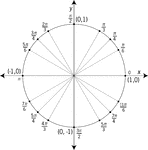
Unit Circle Labeled At Special Angles
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
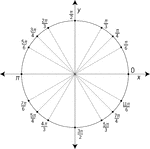
Unit Circle Labeled At Special Angles
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
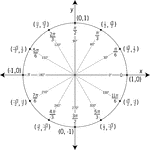
Unit Circle Labeled In 30° Increments With Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
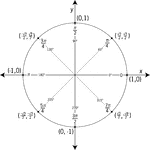
Unit Circle Labeled In 45 ° Increments
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
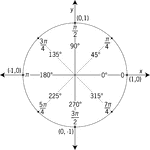
Unit Circle Labeled In 45° Increments With Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…