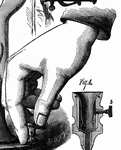
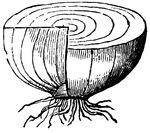
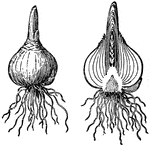
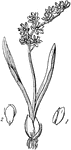Lily Bulb
From the bottom of the bulb, roots descend into soil to absorb moisture and other matter from it, while,…

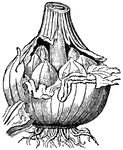
Garlic
Garlic is a perennial plant allied to the onion. Garlic is composed of a stalk, flower, bulb, and clove.
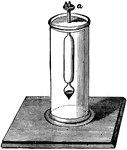
Hydrometer
"The Fahrenheit hydrometer of constant volume is made of glass, the bulb at the bottom being loaded…

Hydrometer of constant weight
"As generally made, a hydrometer of constant weight consists of a glass tube near the bottom of which…
Glass bulb
"An air thermometer consists essentially of a large glass bulb at the upper end of a tube of small but…

Tiger Lily
An ornamental plant of the genius lilium, characterized by an erect stem from a scaly bulb, numerous…

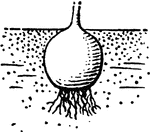
Onion
An edible bulb, produced by a biennial herb of the lily family. The plant has tubulated leaves, a pithy…
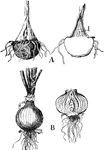
Onion
This illustration shows the shortened types of stems: A, corm of jack-in-the-pulpit. At left surface…

Lily
This illustration shows the scaly bulb of a Lily. Lilies are showy and large flowered plants that are…
White Lily
This illustration shows a radical leaf of the White Lily, with its base thickened into a bulb-scale,…

Tulip
This illustration shows a verticle section of the bulb of te tulip, showing its stem (a) and buds (b,…

Leslies Hygrometer
"Leslie's hygrometer, which is an adaptation of his differential thermometer, is formed by uniting two…
Regnaults Hygrometer
"It consists of a glass tube or capsule A, having on the bottom and a little way up a highly polished…
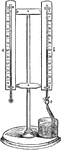
Bulb Hygrometer
"This hygrometer consists of two thermometers a and b similar to each other in all respects except that…
Hair
A hair. 1: External part; 2: Sac in skin; 3: Surface of Cuticle; 4: Sebaceous membrane; 5: Bulb at base;…
Clavate Antenna
A feeler is clubbed, or clavate, when the joints toward or at the tip suddenly or gradually…
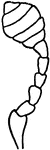
Capitate Antenna
A feeler is clubbed, or capitate, when the joints toward or at the tip suddenly or gradually…
White Lily
A ground leaf of White Lily, its base (cut across) thickened into a bulb-scale. This plainly shows that…
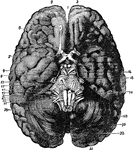
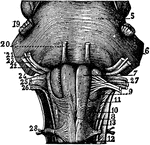
Base of Brain
The base of the brain. Labels: 1, longitudinal fissure; 2, 2, anterior lobes of cerebrum; 3, olfactory…
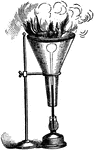
Funnel with Inverted Mercury Thermometer
"Pass the tube of an air thermometer or of an inverted mercury thermometer through a cork in the neck…
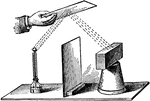
Heat Reflection
"About two feet away from an air thermometer, place an inverted flower pot. Midway between the two,…
!["Incandescence lamps operate essentially on the principle...[that] the current being sent through some substance that, because of its high resistance, becomes intensely heated and brilliantly incandescent. The only suitable substance known for such a resistance filament is carbon, which, carefully prepared and bent into a loop, is enclosed in a glass bulb from which the air is exhausted to prevent oxidation, i.e., combustion." -Avery 1895](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/36000/36079/incand_36079_mth.gif)
Incandescence Lamp
"Incandescence lamps operate essentially on the principle...[that] the current being sent through some…
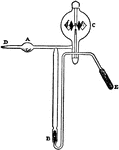
Washing Out a Radiometer
"Configuration used to wash out a radiometer using oxygen. A, bulb containing perchlorate of potash;…
Thermometer
"A bulb of liquid is placed in the base of the glass graduated tube. As temperature increases, the volume…
Differential Thermometer
"Used to compare the temperature between two environments. As the temperature in one bulb increases,…
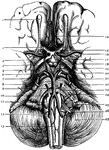
Base of the Brain
The base of brain. Labels: 1. Olfactory Bulb; 2. Second, or Optic Nerves; 3. Anterior Perforated Space;…
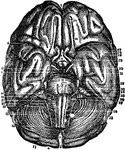
Base of the Brain
Base of the Brain. Labels: 1,2, longitudinal fissure; 3, anterior lobes cerebrum; 4, middle lobe; 5,…

Psychrometer
The psychrometer (showing wet and dry bulb thermometers) is an instrument used for determining the humidity…
Nematode
"Diagram of the structure of a male Nematode. M., mouth; OE., oesophogus; GA., nerve ring; B., bulb…
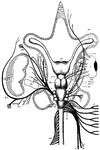
Skate Nerves
"Dissection of nerves of skate. CH., Cerebral hemispheres; O.TH., optic thalami; OL., optic lobes; M.,…
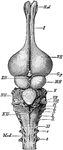
Alligator Brain
"Brain of alligator, from above. B. ol., olfactory bulb; G. p, epiphysis; HH, cerebellum; Med, spinal…
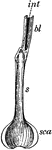
Onion Leaf
"Longitudinal section of an onion leaf. sca, thickened base of leaf, forming a bulb-scale; s, thin sheath…
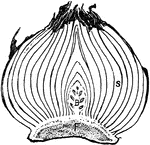
Tulip Bulb
"Tulip bulb; longitudinal section. F, solid stem; B, flower bud; S, leaf-bases serving as bud-scales,…
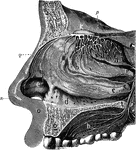
Olfactory System
The olfactory system. Labels: a, b, c, d, interior of the nose, which is lined by a mucous membrane;…

Pacinian Corpuscle of a Cat
The Pacinian bodies or corpuscles are elongated oval bodies situated on some of the cerebrospinal and…
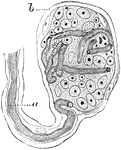
End-bulb of Krause
End-bulbs are oval or spheroidal, and are composed of medullated nerve fibers, which terminate in corpuscles…
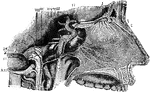
Nerves of the Septum Nasi
Nerves of the septum nasi, seen from the right side. I, the olfactory bulb; 1, the olfactory nerves…

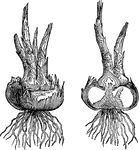
Dog's-Tooth Violet Stages
"Dog's-tooth violet (Erythronium americanum). Stages of development from the seed. 1-5 show the stage…
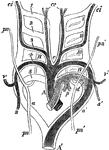
Aortic Arches in a Mammal
Diagram of the aortic arches in a mammal, showing transformations which give rise to the permanent arterial…
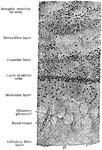
Transverse Section of Olfactory Bulb
Transverse section of olfactory bulb; drawing includes part of bulb lying ventral to atrophic ventricular…
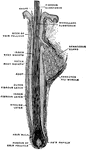
Hair of the Head
A hair of the head still in the course of growth, with hair bulb in longitudinal section.
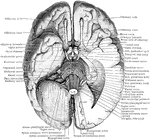
Base of the Brain
The base of the brain. The under part of the left temporal and occipital lobes has been sliced off so…

Thomas Alva Edison
Thomas Alva Edison (February 11, 1847 – October 18, 1931) was an American inventor and businessman…
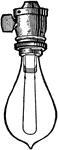
Incandescent Lamp
The incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe is a source of electric light…