This human anatomy ClipArt gallery offers 825 illustrations of the human skeletal system, including images of both the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. The human axial skeleton includes 80 bones formed by the vertebral column (spine), the thoracic cage (e.g., ribs, sternum), and the skull. The axial skeleton is responsible for the upright position of the body. The human appendicular skeleton is composed of 126 bones formed by the pectoral girdles, the upper and lower limbs, and the pelvic girdle. These bones function in locomotion as well as protection of vital organs.
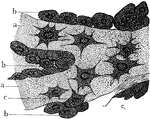
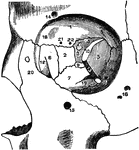
Osteoblasts from Embryo
Osteoblasts from the parietal bone of a human embryo thirteen weeks old. Labels: a, bony septa with…
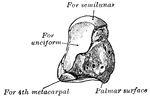
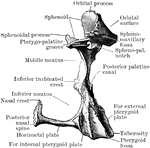
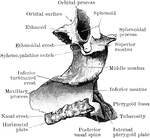
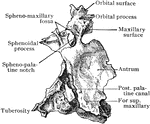
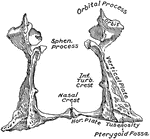
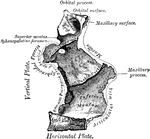
Human Palate Bone
Palate bone. Palate bones form the back part of the roof of the mouth; part of the floor and outer wall…

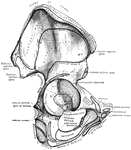
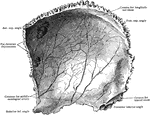
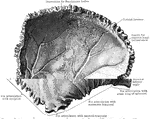
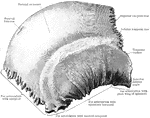
Parietal Bone of the Human Skull
Parietal bone of the human skull, inner surface. The parietal bones form the greater part of the sides…

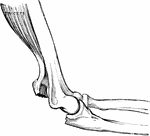
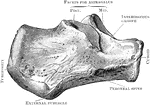
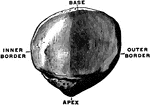
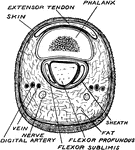
Patella
View of the posterior surface of the right patella, showing diagrammatically the areas of contact with…
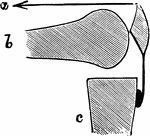
Mechanism of Fracture of the Patella by Muscular Action
Diagram to show mechanism of fracture of the patella by muscular action. a, Line of action of quadriceps…
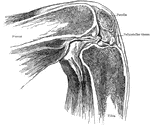
Position of Patella in Relation to Condyles of Femur with Knee Flexed
Showing position of patella in relation to condyles of femur with knee flexed at a right angle.
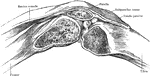
Position of Patella in Relation to Condyles of Femur with Knee Partially Flexed
Showing position of patella in relation to condyles of femur with knee partially flexed.
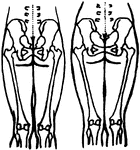
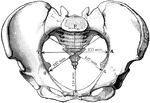
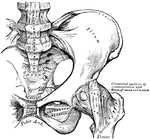
Position of the Pelvic and Thigh Bones in the Male and Female
Diagram showing the position of the pelvic and thigh bones in back view in the male and female.
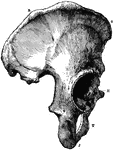
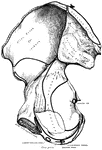
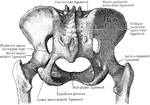
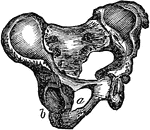
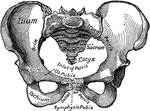
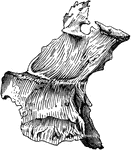
Part of the Human Pelvic Bone
The Os Innominatum, or nameless bone, so called from bearing no resemblance to any known object, is…
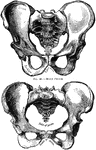
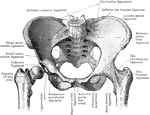
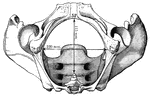
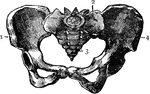
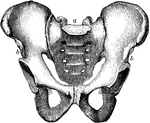
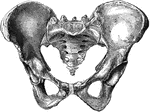
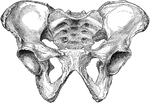
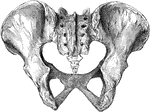
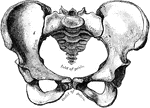
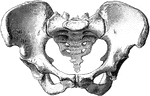
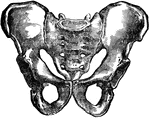
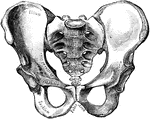
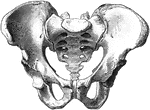
Human Pelvis, Male and Female
Male pelvis (top) and female pelvis (bottom). The pelvis is stronger and more massively constructed…
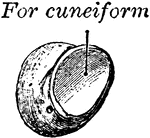
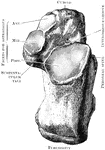
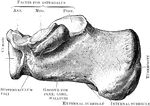
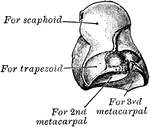
Pisiform Bone
The pisiform may be known by its small size and by its presenting a single articular facet. It is situated…