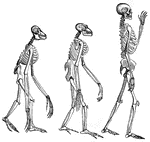
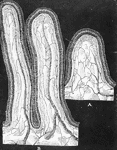
The Comparative Anatomy ClipArt gallery offers 228 images of anatomy comparing numerous parts of humans and animals, showing similarities and differences among species and between different taxonomic orders.
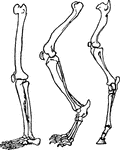
Skeletal Feet
The part of the limb upon which an animal stands when resting. A comparison of the foot in various animals…
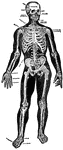
Skeleton
The framework of animals, which in vertebrates is composed of bone and cartilage. It serves to support…
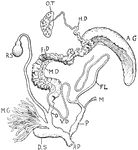
Snail Reproductive Organs
"Reproductive organs of Helix pomatia. O.T., Ovotestis; H.D., hermaphrodite duct; A.G., albumen gland;…
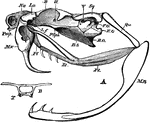
Rattlesnake Skull
"A, lateral view of skull of rattlesnake (Crotalus). B. O, basi-occipital; B. S, basi-sphenoid; E. O,…

Spermatozoa
"Forms of spermatozoa (not drawn to scale). 1 and 2. Immature and mature spermatozoa of snail; 3. of…
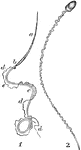
Spermatozoa of a Salamander and Human
Spermatozoa of the salamander (1) and human (2). Labels: a, long pointed head; b, elliptical structure…

The Lower Jaw of a Squirrel
The backward and forward movement of the jaws and the great size and strength of the lower jaw, adapt…
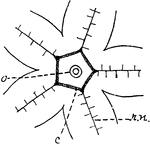
Starfish Nervous System
"Diagram showing arrangement of the nervous matter in Starfish. c, ganglionated ring about the mouth;…
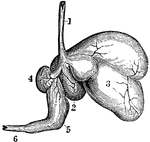
The Stomach of a Sheep
Ruminants (those animals that chew the cud), as the sheep, have a stomach with four cavities. Labels:…
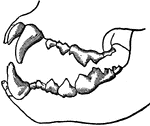
Teeth of a Carnivorous Animal
Teeth of a carnivorous animal that lives on flesh alone. The front teeth are designed for tearing, while…
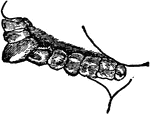
Teeth of a Frugivore
Teeth of a frugivore (fruit-eating animal). Animals that live on soft fruits do not need such grinders…

Teeth of an Herbivore
Teeth of an herbivore, showing the rough surface of some of these teeth. Herbivores have no tearing…

Comparing Teeth of Carnivora and Insectivora Animals
The image on the left are the teeth of a carnivora or flesh-eating animal. The teeth on the right belong…
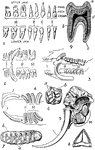
Teeth of Man and Several Animal Species
1. Dentition (teeth) of man. 2. Dentition of hyena. 3. Dentition of pig. 4. Dentition of Patagonian…
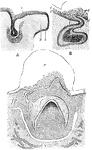
Development of Teeth
The first step in the development of teeth consists in a downward growth from the Rete Malpighi or the…
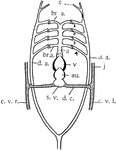
Teleost Heart
"Diagram of the heart, the branchial arches, and the principal veins in the Teleosts. Ventral view.…
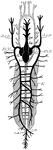
Teleostean Circulation
"Diagram of Teleostean circulation. A., auricle; V., ventricle; v.a., ventral aorta; a.br., afferent…

Teleostean Gill
"Section of a Teleostean gill. G.F., Gill-filament; A., artery (venous blood); V., vein (pure blood);…
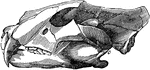
Jaws of a Tiger
Jaws of a tiger, showing that when the jaws are closed the ends of the teeth do not press upon the ends…

Tongue of Human and Rabbit
A, Section through papilla vallata of a human tongue. B, Section through part of the papilla foliata…
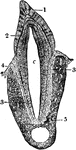
Premolar Tooth
Section through a premolar tooth of a cat still embedded in its socket. Labels: 1, enamel; 2, dentine;…
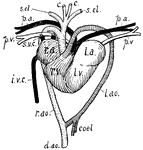
Tortoise Heart
"Heart and associated vessels of tortoise. r.a., Right auricle; superior venae cavae (s.v.c.) and inferior…
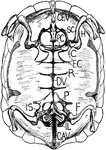
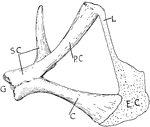
Tortoise Skeleton
"Internal view of tortoise skeleton. H., humerus; SC., scapula running dorsally; PC., precoracoid; C.,…
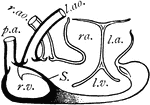
Turtle Heart
"Dissection of Chelonian heart. r.v., Right half of ventricle; S., septum; l.v., left half of ventricle;…
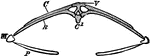
Turtle Hyoid
"Hyoid apparatus of a Chelonian. BH., Body of the hyoid (basihyal); H., representing another part of…
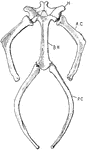
Turtle Pectoral Girdle
"Pectoral girdle of a Chelonian. G., Glenoid cavity; SC., scapula; P.C., procoracoid fused to the scapula;…
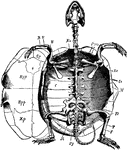
Green Turtle Skeleton
"Chelone midas. Transverse section of skeleton. C, costal plate; C', centrum; M, marginal plate; P,…
Marsh Turtle Skeleton
"Cistudo lutaria. Skeleton seen from below; the plastron has been removed and is represented on one…
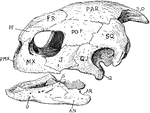
Turtle Skull
"Skull of turtle. "S.O., supra-occipital; PAR., parietal; FR., frontal; P.F., pre-frontal; PO.F., post-frontal;…
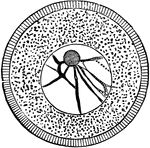
Sea Urchin Ovum
"Ovum of a Sea-Urchin, showing the radially striated cell-membrane, the protoplasm, containing yolk-granules,…
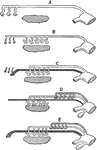
Urinogenital Organs of a Vertebrate
Diagrams illustrating the development of the urinogenital organs of a vertebrate. A, pronephros and…
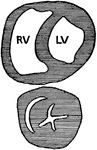
Transverse Section through the Ventricle of a Dog's Heart
Transverse section through the middle of the ventricles (right and left) of a dog's heart in diastole…
Vertebra of a Fish
The vertebra of a fish, which is very different from that of a human. It has but two processes, …
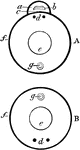
Vertebrate and Invertebrate
A, Diagrammatic transverse section through the body of a vertebrate. B, A similar section through a…
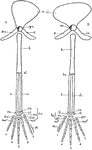
Vertebrate Appendages
"Diagrams of the girdles and appendages in a typical Vertebrate. A, anterior; B, posterior. ac., acetabulum,…
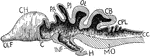
Vertebrate Brain
"Partial section of a Vertebrate brain (diagrammatic). OLF., Olfactory lobe; CH., cerebral hemispheres;…
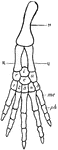
Vertebrate Fore Limb
"Ideal fore limb. H., Humerus; R., radius; U., ulna; r'., radiale; u'., ulnare; i., intermedium; c.,…
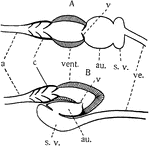
Vertebrate Heart
"Diagrams of the structure of the heart in the lower Vertebrates. A, primitive condition; B, the position…
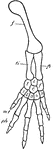
Vertebrate Hind Limb
"f., Femur; ti., tibia; fi., fibula; i., intermedium; t., tibiale (astragalus); f., fibulare (os calcis);…
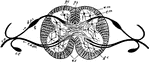
Vertebrate Spinal Cord
"Diagrammatic section of spinal cord. p.f., Posterior fissure; p.c., posterior column of white matter;…
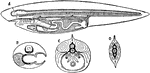
Section of Vertebrate
Diagrammatic sections of the ideal vertebrate. A, sagittal section showing the brain and spinal cord…
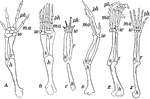
Forearms of vertebrates
"Fore limbs of vertebrates showing similarity of structure. A, salamander; B, turtle;…
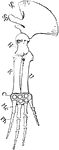
Whale Forelimb
"Left fore-limb of Balaenoptera. Sc., Sca pula with spine (sp.); H., humerus; R., radius; U., ulna;…
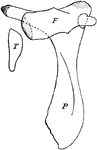
Greenland Whale Pelvis
"Pelvis and hind-limb of Greenland whale (Balaena). P., Pelvis; F., femur; T., tibia." -Thomson, 1916