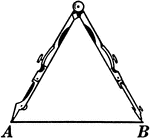
Compass and Line
Illustration of a compass with one leg at point A on the line segment and the other at Point B.
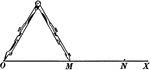
Compass and Line
Illustration of a compass with one leg at point O on the line segment and the other at Point M.
Star of Bethlehem Hyacinth
Of the hyacinth family (Hyacinthaceae), the Star-of-Bethlehem or Ornithogalum umbellatum.
Normal Sight
"Look through the rear-sight notch at the bull's-eye or mark and bring the top of the front sight on…

Peep Sight
"Look through the peep hole at the bull's-eye or mark and bring the top of the front sight to the center…
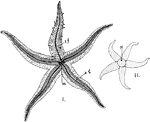
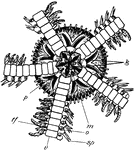
Starfish
"Starfish. I. Ventral surface; t.f., tube-feet extended; a.g., the ambulacral groove with the tube-feet…
Starfish Arm
"Diagrammatic cross-section of starfish arm. n., Radial nerve; b.v., radial blood vessel according to…
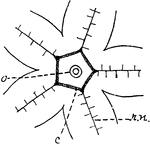
Ophiuroid
"Ventral surface of disc of an Ophiuroid (Ophiothrix fragilis). g., Openings of genital pockets or bursae;…
Starfish Nervous System
"Diagram showing arrangement of the nervous matter in Starfish. c, ganglionated ring about the mouth;…
Starfish Arm Section
"Transverse section of the arm of a Starfish near the disc. Diagrammatic. Lettering as in preceding…
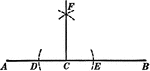
Construction Of A Perpendicular To A Straight Line
Illustration of the construction used to create a perpendicular to a straight line at a given point.
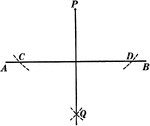
Construction Of A Perpendicular To A Straight Line
Illustration of the construction used to create a perpendicular to a straight line from a given point…
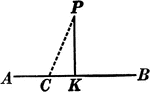
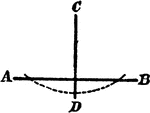
Perpendicular to Line Corollary
Illustration used to prove the corollary that "From a point outside a line there exists only one perpendicular…
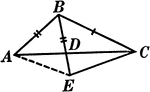
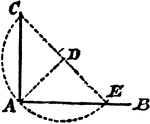
Segments Labeled In A Triangle
Illustration of triangle ABC with BE extended through the triangle at point D. Segment AB is equal to…
Decurrent Leaf
"Decurrent.--When leaves run down the stem to a point considerably below the place where they diverge…
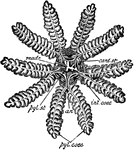
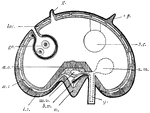
Common Starfish
"Asterias rubens. Digestive system. an, anus; card. st, cardiac division of the stomach; int. caec,…
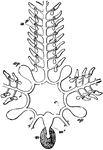
Ambulacral System
"Ambulacral system of a starfish. a, ampullae; ap, Polian vesicles; c, circular canal; m, madreporite;…

O. Lacertosa
"Ophioglypha lacertosa. A, outline, of the natural size; B, central disc, dorsal view; C, the disc,…
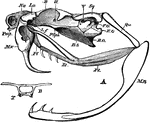
Rattlesnake Skull
"A, lateral view of skull of rattlesnake (Crotalus). B. O, basi-occipital; B. S, basi-sphenoid; E. O,…

Water Stargrass
Of the mud plantain family (Heteranthera), the water stargrass (Heteranthera dubia).
Reindeer age articles, Bone points and needles
Bone points and bone needles. Crafted during the Reindeer age.
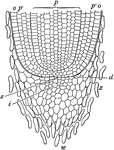
Corn Root Tip
"Lengthwise section through root-tip of Indian corn. w, root-cap; i, younger part of cap; z, dead cells…
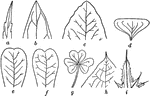
Leaf Tips
"Tips of leaves. a, acuminate or taper-pointed; b, acute; c, obtuse; d, truncate; e, retuse; f, emarginate…

Manufacturing of Turpentine
Tar is made from the turpentine by the smothered burning of the wood. When burning the wood, it is placed…

Singular Star Fish
" The most singular of all the star fishes is the splendid Astrophyton. Its center is not unlike the…
Construction Of A Perpendicular
An illustration showing the construction used to erect a perpendicular from a point to a line. "With…
Construction Of A Perpendicular
An illustration showing the construction used to erect a perpendicular at the end of a line. "With the…
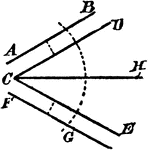
Construction Of A Divided Angle
An illustration showing the construction used to divide an angle into two equal parts when the lines…
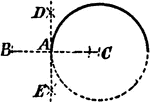
Construction Of Tangent To Circle
An illustration showing how to construct a tangent to a circle through a given point in a circumference.…
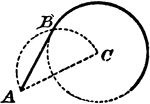
Construction Of Tangent To Circle
An illustration showing how to construct a tangent to a circle through a given point outside of a circumference.…
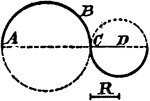
Construction Of Circle Tangent To Circle
An illustration showing how to construct a tangent circle to a circle with a given radius. "Through…

Proteus Anguinus
"The Proteus anguinus attains a length of about 1 foot. The body is smooth, naked, and eel-like, the…
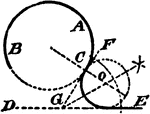
Construction Of A Center And Radius Of A Circle That Will Tangent A Given Circle
An illustration showing how to construct the center and radius of a circle that will tangent a given…
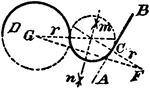
Construction Of A Center And Radius Of A Circle That Will Tangent A Given Circle And Line
An illustration showing how to construct the center and radius of a circle that will tangent a given…
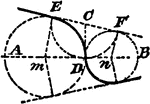
Construction Of Two Circles That Tangent Themselves and 2 Given Lines
An illustration showing how to construct two circles that tangent themselves and two given lines. "Draw…
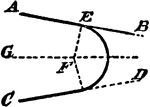
Construction Of A Circle That Tangents 2 Given Lines
An illustration showing how to construct a circle that tangents two given lines inclined to one another…
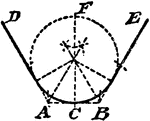
Construction Of A Circle That Tangents 2 Given Lines And Goes Through A Given Point
An illustration showing how to construct a circle that tangents two given lines and goes through a given…
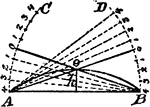
Construction Of A Circle Arc
An illustration showing how to construct a circle arc without recourse to its center, but its chord…
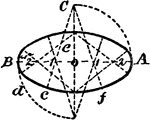
Construction Of An Isometric Ellipse
An illustration showing how to construct an isometric ellipse by compass and six circle arcs. "Divide…
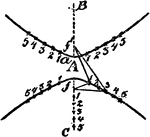
Construction Of A Hyperbola
An illustration showing how to construct a hyperbola by plotting. "Having given the transverse axis…

Starry Ray
The Starry Ray is so called for having a number of spines on its upper surface rising from rayed or…
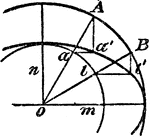
Construction Of An Ellipse
An illustration showing how to construct an ellipse. "With a as a center, draw two concentric circles…
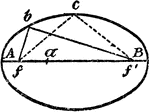
Construction Of An Ellipse
An illustration showing how to construct an ellipse. Given the two axes, set off half the long axis…
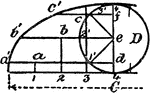
Construction Of A Cycloid
An illustration showing how to construct a cycloid. "The circumference C=3.14D. Divide the rolling circle…
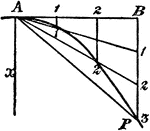
Construction Of A Parabola
An illustration showing how to construct a parabola. "Given the vertex A, axis x, and a point P. Draw…
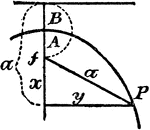
Construction Of A Parabola
An illustration showing how to construct a parabola. "Given the axis of ordinate B, and vertex A. Take…
Table Wheel
This table wheel would be used to practice the six tables. The teacher would rapidly point to the surrounding…
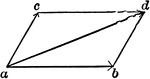
Vector Addition
Illustration showing two component forces ab and ac acting upon point a. The result is the vector ad…
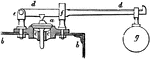
Lever Safety-valve
A safety-valve, in which a weight is employed. Here a is the valve, b b the boiler, c c the valve-seat,…
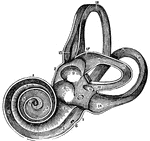
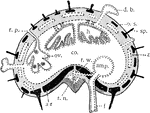
View of the Labyrinth Laid Open
A view of the labyrinth laid open. Labels: 1, The cochlea. 2, 3, Two channels that wind two and half…
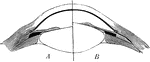
The Use of the Crystalline Lens
A convex lens, bends the ray of light which pass through it, so that they meet at a point called a focus.…
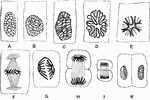
Karyokinesis
Karyokinesis. Labels: a, ordinary nucleus of a columnar epithelial cell; B, C, the same nucleus in the…