
Chicago Art Institute
The Art Institute of Chicago is one of America's premier fine art museums. It was founded in 1879.

Jefferson Davis's First Message
Jefferson Davis', the President of the Confederate States of America, first message.

Cortez and the Ambassadors of Montezuma
On November 8, 1519, Cortez reached Tenochtitlan and was graciously received by Montezuma, the Aztec…

William Richardson Davie
William Richardson Davie (June 22, 1756–November 5, 1820) was the Governor of North Carolina from…

The Contrast Between American Liberty and French Liberty
A political cartoon contrasting American liberty and French liberty.

Church of All Saints, Wilden, Worcestershire
All Saints Church in Wilden, Worcestershire about one mile to the north east of Stourport. It was designed…

Jonathan Edwards
Jonathan Edwards (October 5, 1703 – March 22, 1758) was a colonial American Congregational preacher,…

Whitehall in the Seventeenth Century
Whitehall is a road in Westminster in London, England. It is the main artery running north from Parliament…

Federal Hall
Federal Hall, located at 26 Wall Street in New York City, was the first capitol of the United States…

The Pine Tree Flag
The "Pine Tree Flag" is a generic name for a number of flags used by Massachusetts and by New England…

Procession to the Tower of London
Her Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress, more commonly known as the Tower of London (and historically…

Giant's Causeway
The Giant's Causeway is an area of about 40,000 interlocking basalt columns, the result of an ancient…
Biscayne Bay
An illustration of Biscayne Bay, is a lagoon that is approximately 35 miles (56 km) long and up to 8…

Royal Palm
Roystonea (Royal Palm) is a genus of 10 species of monoecious palms, native to tropical regions of Florida,…

Brown Pelican and Sea Gull
An illustration of a brown pelican with a fish in it's mouth and a sea gull resting on his back. The…

Westover Plantation
Westover Plantation is located on the north bank of the James River in Charles City County, Virginia.…
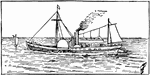
Fulton's Clermont
The first commercial steamboat, the North River Steamboat later known as the Clermont.

Thomas Gage
Thomas Gage (1719 - April 2, 1787) was a British general and commander in chief of the North American…

Conrad Alexandre Gérard
Conrad Alexandre Gérard de Rayneval (12 December 1729—16 April 1790), also known as Conrad…

Louis Malesherbes Goldborough
Louis Malesherbes Goldsborough (February 18, 1805 - February 20, 1877) was an admiral in the United…

The Battlefield of Guilford
The Battle of Guilford Court House was a battle fought on March 15, 1781 inside the present-day city…

George Whitefield
George Whitefield (December 16, 1714 – September 30, 1770), was a preacher in the Church of England…

John Wesley
John Wesley (June 28 1703 – March 2, 1791) was an Anglican minister and Christian theologian who was…

The New Houses of Parliament
After a fire in 1834, the present Houses of Parliament were built over the next 30 years. They were…
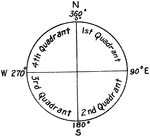
Cardinal Directions
The four cardinal directions or cardinal points are north, south, east, and west.
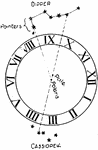
Astronomical Compass
The North Star (Polaris) varies so slightly from the true north that we may, for practical purposes,…
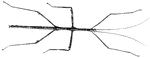
Stick Insect
The Phasmatodea (sometimes called Plasmodia) are an order of insects, whose members are variously known…

Calabash Tree
An illustration of a Calabash tree and ways to utilize the shell of the fruit it produces. Crescentia…

Ground Beetle
Ground beetles or carabids are collective terms for the beetle family Carabidae. This is a large family,…

Zachary Taylor's Residence at Baton Rouge
Zachary Taylor (November 24, 1784 – July 9, 1850) was an American military leader and the twelfth…
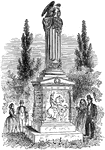
Richard Mentor Johnson's Monument
Richard Mentor Johnson (October 17, 1780 or 1781 – November 19, 1850) was the ninth Vice President…

Chattanooga, Tennessee in 1862
Chattanooga, "the Scenic City", is the fourth-largest city in Tennessee (after Memphis, Nashville, and…

Non Importation Act
Newspapers and speakers especially condemned the "land embargo" — the cutting-off trade with Canada.…
Ticonderoga and the Lake, from Mount Defiance
The crossing between Lakes George and Champlain had been used by natives for thousands of years. The…

United States of America War Office
The seal of the War Office of the United States of America. The term "War Office" used during the Revolution,…

Colorado Potato Beetle
The Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata), also known as the Colorado beetle, ten-striped…

John Paul Jones
John Paul Jones (July 6, 1747 – July 18, 1792) was America's first well-known naval fighter in…

Gold Medal Awarded to John Paul Jones (Back)
The Congressional Gold Medal awarded to John Paul Jones, America's first well-known naval fighter in…

Medal Awarded to John Paul Jones (Front)
The Congressional Gold Medal awarded to John Paul Jones, America's first well-known naval fighter in…

Hessian Fly
The hessian fly or barley midge, Mayetiola destructor, is a species of fly that is a significant pest…

Cedar Waxwing Hatchling
The Cedar Waxwing (Bombycilla cedrorum) is a member of the family Bombycillidae or waxwing family of…

Cedar Waxwing (3 Weeks)
The Cedar Waxwing (Bombycilla cedrorum) is a member of the family Bombycillidae or waxwing family of…

Young American Robins
The American Robin, Turdus migratorius, is a migratory songbird of the thrush family. It is named after…

Crows
The true crows are large passerine birds that comprise the genus Corvus in the family Corvidae. Ranging…
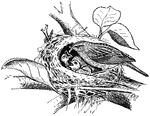
Chipping Sparrow Feeding Young
An illustration of a chipping sparrow feeding its young. The Chipping Sparrow (Spizella passerina) is…

Field Mouse
The Meadow Vole (Microtus pennsylvanicus), sometimes called the Field Mouse or Meadow Mouse, is a small…

Blue Jay
The Blue Jay (Cyanocitta cristata) is a passerine bird, and a member of the family Corvidae native to…

Ruffed Grouse
The Ruffed Grouse, Bonasa umbellus, is a medium-sized grouse occurring in forests from the Appalachian…

View at King's Mountain Battleground
The Battle of Kings Mountain, October 7, 1780, was an important Patriot victory in the Southern campaign…

Monument on King's Mountain
The Battle of Kings Mountain, October 7, 1780, was an important Patriot victory in the Southern campaign…

Samuel Kirkland
Rev. Samuel Kirkland (1741 – 1808) was a Presbyterian missionary among the Oneida and Tuscarora…

Thaddeus Kosciuszko
Andrzej Tadeusz Bonawentura Kościuszko was a Polish, Lithuanian and American national hero and general.…

Cecropia Moth
The cecropia moth is one of the largest moths found in North America. It is a member of the Saturniidae…
Larva of Cecropia Moth
An illustration of the larva of a ceropia moth. The cecropia moth is one of the largest moths found…
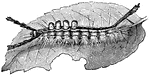
White-marked Tussock Caterpillar
Orgyia leucostigma, the White-marked tussock moth, is a moth in the family Lymantriidae. The caterpillar…




