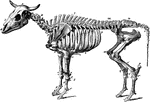
Ox Skeleton
The skeleton of an ox. Axial Skeleton. The skull. Cranial Bones- occipital, 1: b, parietal, 2; a, frontal,…
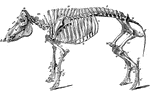
Skeleton of a Hog
Skeleton of the hog. Axial skeleton. The skull. Cranial bones- a, occipital, 1; b, parietal, 2; d, frontal,…
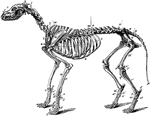
Skeleton of a Dog
The skeleton of the dog. Axial skeleton. The skull. Cranial bones- a, occipital, 1; b, parietal, 2;…
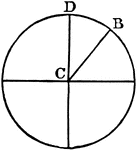
Sector
"In geometry: (a) A plane figure inclosed between the arc of a circle, ellipse, or other central curve…
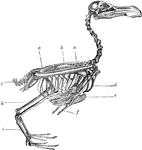
Skeleton of a Bird
The skeleton of a bird. Labels: a, radius and ulna; b, dorsal vertebrae; c, sacrum and pelvis; g, ploughshare…
Shuttle Shell
"A gastropod of the family Ovulidae and genus Radius, as R. volva, of long fusiform shape, the ends…
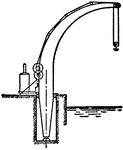
Fairbairn Steam Crane
The Fairbairn steam crane is a type of harbourside crane of an 'improved design', patented in 1850 by…
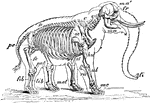
African Elephant Skeleton
"Skeleton and Outline of African Elephant (Elephas or Loxodon africanus). fr, frontal; ma, mandible;…
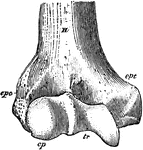
Humerus
"Anterior View, Distal End, of Right Humerus of a Man. H, humerus; epc, epicondyle, or external supracondyloid…
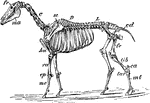
Horse Skeleton
"Skeleton of Horse (Equus caballus). fr, frontal bone; C, cervical vertebrae; D, dorsal vertebrae; L,…
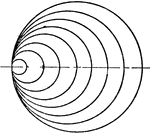
Geometric Inspection of Complex Numbers
Illustration showing complex numbers with a modulus equal to unity. The lines representing these numbers…
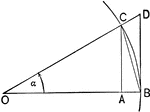
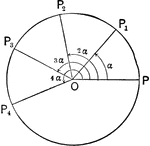
Triangles and Sectors in Quadrant I
Illustration of an angle &alpha with the vertex at the center, O, of a circle with radius OB. AC and…
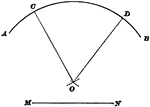
Construction Of Center
Illustration used to show how to find the center when given an arc and its radius.
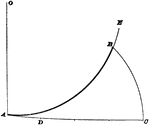
Construction Of Arc
Illustration used to show how to "find an arc of a circle having a known radius, which shall be equal…
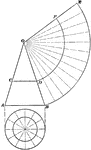
Development Of Cone
Illustration of the development of a cone along a stretchout described with the radius OB.
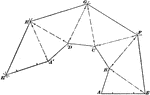
Irregular Solid With Triangular Surfaces
Illustration of an irregular solid form made up of triangular surfaces unfolded on a flat surface. A…
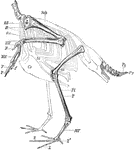
Skeleton of the Limbs and Tail of a Carinate Bird
"Skeleton of the Limbs and Tail of a Carinate Bird. (The skeleton of the body is indicated by dotted…
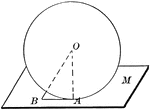
Sphere Tangent to Plane
Diagram used to prove the theorem: "A plane perpendicular to a radius at its extremity is tangent to…
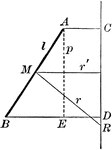
Area of Surface Generated by a Straight Line
Diagram used to prove the theorem: "The area of the surface generated by a straight line revolving about…
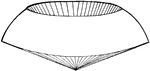
Spherical Cone
"If a sector revolves about its bounding radius as an axis, it generates what may be called a spherical…
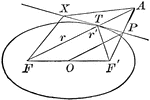
Tangent to an Ellipse
Diagram an ellipse with a tangent line that illustrates "A line through a point on the ellipse and bisecting…
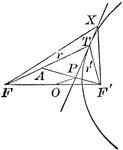
Tangent to a Hyperbola
Diagram part of a hyperbola with a tangent line that illustrates "A line through a point on the hyperbola…
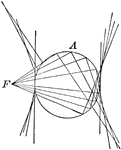
Construction of a Conic
Diagram showing how to construct a conic when given the focus and the auxiliary circle. If the focus…
Construction of Radii of a Circle
Illustration used to draw lines which are radii of a circle where the center is inaccessible.
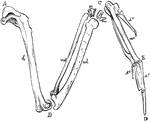
The Bones of the Right Wing of a Duck
"Fig 27. - Bones of the right wing of a duck, Clangula islandica, A, shoulder, omos; B, elbow, ancon;…
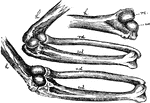
Mechanism of the Elbow-Joint
"Fig. 28. - Mechanism of elbow-joint. ..., where rc and uc show respectively the size, shape, and position…
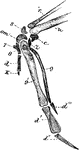
The Wing Bones of a Young Grouse
"Fig. 29., from a young grouse (Centrocercus urophasianus, six months old), is designed to show the…
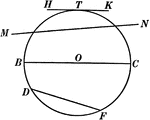
Chords, Secants, Diameters, and Tangents of a Circle
Illustration of a circle with diameter BC, chord DF, secant MN, and tangent HK.
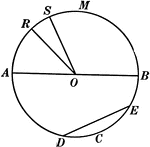
Chords, Diameters, and Radii of a Circle
Illustration of a circle with diameter AB. Radii are RO, SO, AO, and BO. ED is a chord.
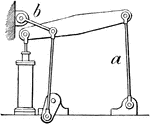
Grasshopper-Beam
"Grasshopper-beam. a, rocking pillar; b, radius-bar of the parallel motion which secures verticality…
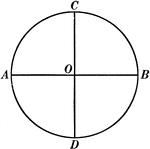
Circle With 2 Perpendicular Diameters
Illustration of a circle with center O and diameters AB and CD perpendicular to each other.
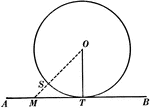
Tangent to Perpendicular Radius Circle Theorem
Illustration used to show that "A tangent to a circle is perpendicular to the radius drawn to the point…

Eurasian Sparrowhawk Muscles
"Muscles of a bird (accipiter nisus), after Carus, Tab. Anat. Comp., 1828, pl. 4. a, pharynx; b, trachea;…

Ellipse Curve French Curves
An ellipse French curve, or irregular curve, is used to draw short elliptical radius curves by using…
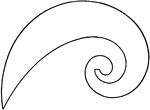
Logarithmic Spiral Curve French Curves
A Logarithmic Spiral French curve, or irregular curve, is used to draw short elliptical radius curves…
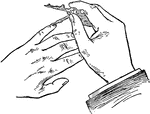
Guiding Needle Point of Compass to Little Finger
The little finger on the left hand can guide the needle point of the compass to the center.
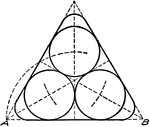
Drawing Tangent Circles and Lines with Compass and Triangles
"On base AB, 3 1/2" long construct an equilateral triangle, using the 60-degree triangle. Bisect the…
Drawing Tangent to Circle Arcs with Bow Compass
"Draw one and one-half inch square about center of space. Divide AE into four 3/16" spaces, with scale.…
Inscribe Regular Octagon in Given Square
"Draw the diagonals of the square. With the corners of the square as centers and radius of half the…
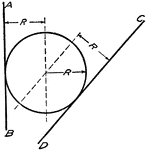
Draw Arc of Given radius R Tangent to Two Given Lines
"Draw lines parallel to AB and CD at distant R from them. The intersection of these lines will be center…
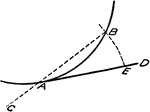
Approximating Length of Circle Arc using Straight Line
"At A draw the tangent AD and Chord AB produced. Lay off AC equal to half the chord AB. With center…
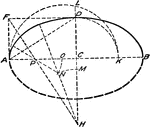
Approximate Ellipse with Five Centered Arc
"This (five centered arc) method is based on the principle that the radius of curvature at the end of…
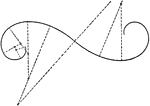
Curve Inked with Circle Arcs
"Any noncircular curve may be approximated by tangent circle arcs, selecting a center by trial, drawing…
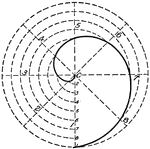
Draw Spiral of Archimedes
"Divide the circumference into a number of equal parts, drawing the radii and numbering the points.…
Side View of a Vehicle Wheel
A wheel is a circular device that is capable of rotating on its axis, facilitating movement and transportation.

Aeroplane Nose Spin Dive Flying
The illustration of the plane descending while spiraling down. The radius of the spiral spin is getting…
Turning Hand Wheels
An illustration of creating a hand wheel by spinning while moving threaded tool to the desired radius.
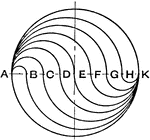
Curved Line with Circle Mechanical Drawing Exercise
A mechanical drawing exercise of drawing a curved line with circle in the middle. The image is drawn…
Mechanical Drawing Exercise Three Inscribed Squares with Rounded Corners using Triangle and Bow
"With a 45 degree triangle draw lines AC and BD through the center and construct three squares. Set…
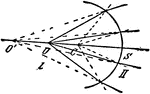
Virtual Image Formed on Spherical Surface
"O' is the virtual image of O formed at a spherical surface of centre C and radius CS." —Encyclopaedia…
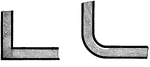
Pipe Diameter
When pipes are bent at ninety degree angles, a rounded bend is best as shown along with a radius as…
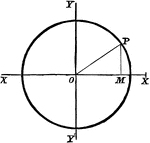
Circle Equation
To find the equation of a circle whose center is the origin and whose radius is 3 units in length.
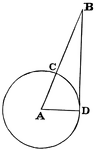
Circle with Secant
A secant is "a line which cuts a figure in any way. Specifically, in trigonometry, a line from the center…
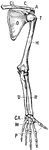
Bones of the Shoulder and Upper Extremity - Front View
"A, acromion; C, coracoid; CA, carpus; CL, clavicle; H, humerus; M, metacarpals; O, ventral surface…
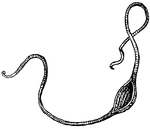
Sling
"An instrument for throwing stones or bullets, consisting of a strap and two strings attached to it.…
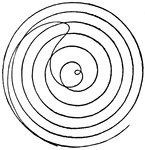
Fermat's Spiral
Also called a parabolic spiral, it is a type of Archimedean Spiral. A spiral is defined as "a plane…