Daisy
The mountain daisy is a pretty little flower. It contains a multitude of little flowers close together.

Mountain Laurel flower
This is the flower cluster of the Mountain Laurel, Kalmia latifolia, (Keeler, 1915).

Mountain Goat
The Rocky Mountain Goat inhabits the most lofty peaks of the Rocky Mountains, (Smiley, 1839).
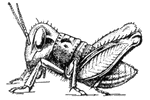
Locust development
Post-embryonic development of the Rocky Mountain locust. Successive developmental stage a.

Locust development
Post-embryonic development of the Rocky Mountain locust. Successive developmental stage b.
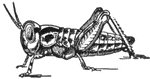
Locust development
Post-embryonic development of the Rocky Mountain locust. Successive developmental stage c.
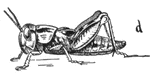
Locust development
Post-embryonic development of the Rocky Mountain locust. Successive developmental stage d.

Locust development
Post-embryonic development of the Rocky Mountain locust. Successive developmental stage e.
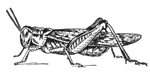
Locust development
Post-embryonic development of the Rocky Mountain locust. Successive developmental stage f.

Rocky Mountain Goat
A goat is allied to the sheep. The Rocky Mountain goat is a native of the western portion of the United…

General John M. Schoefield
He took part in the battles of Resaca, Dallas, Kenesaw Mountain and Atlanta. For his services at the…

Laurel Hill
"Advance of General Rosecrans's division through the forests of Laurel Hill to attack the Confederate…

Captain Knapp
"Captain Knapp's Battery engaging the Confederates at the battle of Cedar Mountain, August 9th, 1862-…

Battle of Cedar Mountain
"Gordon's and Crawford's Brigades driving the Confederate forces from the woods at the Battle of Cedar…

Battle of Cedar Mountain
"The Confederate batteries shelling the Federal position on the night of the Battle of Cedar Mountain,…

Seventy-ninth Regiment
"Taking away the colors of the Seventy-ninth New York Regiment for insubordination and mutiny, Washington,…

Battle of Cedar Mountain
"Battle of Cedar Mountain, fought Saturday, August 9th, 1862, between the Federal troops commanded by…

General Alfred Pleasonton
"General Pleasonton, born in Washington, D. C., June 7th, 1824, was graduated at the United States Military…

Kentucky Raid Rally
"The Confederate raid into Kentucky--excitement at Convington--gathering of armed Federal citizens at…

Village of Clarksburg
"Village of Clarksburg, Western Virginia, headquarters of General Rosecrans. Clarksburg, a post village,…

General Jesse L. Reno
"General Reno, born in Wheeling, W. Va., June 20th, 1823, died on South Mountain, Md., September 14th,…

General Christopher C. Augur
"General Augur, born in New York in 1821, was graduated from the United States Military Academy in 1843.…

Battle of South Mountain
"Federal artillery taking up position at the Battle of South Mountain. The Federal movement was admirably…

Thoroughfare Gap
"Thoroughfare Gap, Va., a pass in the mountains on the Manassas Gap Railroad, near Strasburg, held by…

General John Pope
"General Pope, born in Louisville, Ky., March 16th, 1822, was graduated from the United States Military…

Cumberland Gap
"Cumberland Gap and Heights, Tenn., from the Kentucky side. Cumberland Gap was a place of such importance…

Loudon Heights
"View from Loudon Heights, Va., showing Harper's Ferry, Maryland Heights, Bolivar, etc. Harper's Ferry,…

Hooker's Battle
"The war in Tennessee. Hooker's Battle above the clouds, and capture of the Confederate position on…

War in Georgia
"The war in Georgia- Stevenson, Ala., depot for General Rosecrans's Army. The campaign of General Rosecrans…

Capture of Lost Mountain
"The war in Georgia. Capture of Lost Mountain by General Hooker, June 16th, 1864. On June 14th General…

Sherman's Campaign
"Sherman's Campaign in Georgia- the attack of the Fourteenth, Sixteenth and Twentieth Army Corps on…

Battle of Resaca
"Battle of Resaca, Ga., May 14th, 1864. Geary's Second Brigade charging up the mountain."— Frank…

Campaign in Georgia
"The campaign in Georgia. A baggage train crossing the mountains in a storm. General Sherman, after…
Winchester Charge
"Sheridan's Campaign. Battle of Winchester- charge of Crook's Eighth Corps, September 19th, 1864- the…

War in Tennessee
"The war in Tennessee- Lookout Mountain and its vicinity, from the position of the Eleventh Army Corps."—…

Vulture Hawk
Genus Gypohierax, is about the size of a goose, and is found in Western Africa, particularly…

Lammergeyer
The lammergeyer (Swiss for "lamb-killer") is a member of the vulture family, but has a notably feathered…

Crested Pardalotte
Usually living around small mountain streams, large spiders have been known to attack and eat the vrested…

Rocky Mountain Goat
"Both male and female have small horns, and hair of a white color. They live in small flocks in the…

Battle of Rich Mountain
"The battle of Rich Mountain, Beverly Pike, Va., between a division of Major General McClellan's command,…

Argali
"It is remarkable, even among this active genus, for the agility with which it speeds along the rocks…

Sixteenth Regiment
"The Sixteenth Regiment, Ohio Volunteers, under Colonel Irwine, crossing the tray run viaduct, near…

Rock Thrush
Inhabiting the higher reaches of Southern Europe, the rock thrush descends to lower altitudes during…

Inghalla
"Is of a deep reddish-fawn color; its lives in pairs or small families, frequenting the reedy borders…

Abyssinian Mule
"The mule is in fact an exceedingly hardy, strong, and useful animals. In all mountain countries, for…

Front Royal
"Front Royal, Manassas Gap Railroad, Blue Ridge Mountains in the distance- the Federal army entering…

Battle of Lookout Mountain
"The Battle of Lookout Mountain, also known as the Battle Above the Clouds."—E. Benjamin Andrews…

William's Rock
William's Rock. This view is taken from the road, looking northward. In the distance is seen the highest…
Long Point
Long Point and vicinity. This little sketch was taken from the steam-boat , near the south end of Long…

Chimney Point
Chimney Point Landing. This view is taken from the green in front of the inn at Chimney Point, looking…
Western Line of Barracks
Western line of barracks. There were four large buildings used for barracks within the fort, the walls…

Beloeil Mountain
Beloeil Mountain, this sketch is taken from the southeast angle of old Fort chambly, showing the rapids…