British Coin
British coin of the time period of the Roman invasion in the Gallic War, B.C. 54. Back.

Byzantine court
"Constantine, the first Christian emperor, removed the capital of the world-empire from Rome to Byzantium,…

Caesar in England
"All histories of England commence with the invasion of Julius Caesar, the earliest event in that quarter…

Julius Caesar
An image depicting Julius Caesar, a Roman general and statesman. He was a key component to the shift…

Julius Caesar (profile)
An illustration of Caesar. A politician of the populares tradition, he formed an unofficial triumvirate…

Capitoline and Cloaca Maxima
The Capitoline Hill is a Roman hill between the Forum and the Campus Martius. The Cloaca Maxima was…

Capitoline Hill in Rome
The Capitoline Hill, between the Forum and the Campus Martius, is one of the seven hills of Rome. By…
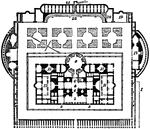
Baths of Caracalla
The ground plan of the baths of Caracalla. The Baths of Caracalla were Roman public baths, or thermae,…

Hall in Baths of Caracalla
"Marcus Aurelius Antoninus Caracalla was eldest son of the Emperor Severus, born in Lyons, A.D. 188.…

Ruins of the Baths of Caracalla
The ruins of the baths of Caracalla were roman public baths built in Rome, Italy between AD 212 and…

Cavalryman Charging
Charging cavalryman pictured trampling an enemy soldier and holding a spear in the Gallic War.

Roman Centurion
A Centurio was a low-to-middle ranking officer in charge of a "century," ideally 100 men but ranging…
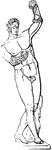
Boxer with cestus
"The cestus was used by boxers from the earliest times. It consisted of thongs of raw ox-hide, or of…
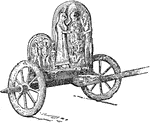
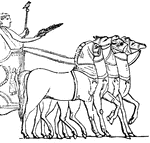
A Graeco-Ertuscan Chariot
"The chariot was discovered in 1903 in an Ertuscan cemetery near Rome. It dates from perhaps 600 B.C.…

Charlemagne
The King of the Franks from 768 and the Emperor of the Romans from 800 until his death in 814.

Christians Given to the Lions in the Roman Amphitheater
"More particularly was the new sect of Christians selected as the objects of vengeance. These people…

Marcus Tullius Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero (106-43 BC) was a Roman philosopher, statesman, and lawyer.

Circus Maximus
"Chariot-racing was a favorite amusement, and the great circuses were arranged especially for such contests.…
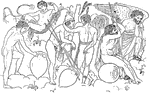
Fircoronian cista
"Part of the Fircoronian Cista. Third century B.C. Found near Palestrina in 1774. Now in the Museo Kircheriano,…
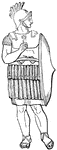
Roman Clypeus
"The following cut represents a Roman clypeus, from the column of Trajan. The projection in the centre…

Roman Colosseum
This Roman Colosseum is located in Rome, Italy. It is the largest elliptical amphitheater that was built…