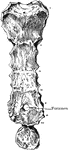This human anatomy ClipArt gallery offers 825 illustrations of the human skeletal system, including images of both the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. The human axial skeleton includes 80 bones formed by the vertebral column (spine), the thoracic cage (e.g., ribs, sternum), and the skull. The axial skeleton is responsible for the upright position of the body. The human appendicular skeleton is composed of 126 bones formed by the pectoral girdles, the upper and lower limbs, and the pelvic girdle. These bones function in locomotion as well as protection of vital organs.
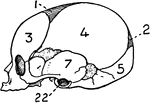
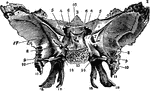
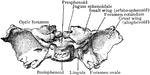
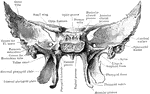
Base of the Skull
The base of the skull. "The lower jaw has been removed. At the lower part of the figure is the hard…
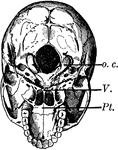
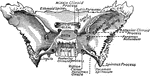
Base of the Skull
The base of the skull. The lower jaw has been removed. At the lower part of the figure is the hard palate…
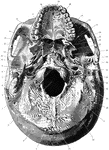
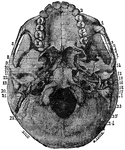
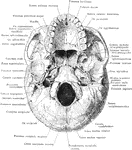
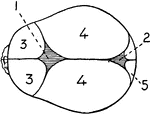
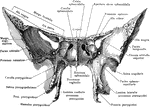
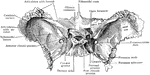
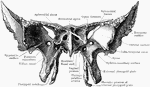
Base of the Skull
Shown is norma basalis, which refers to the base of the cranium. Labels: 1, external occipital crest;…
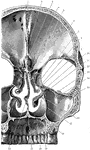
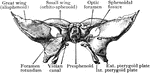
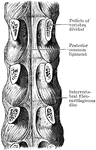
Coronal Section of Skull
Shown is a coronal section passing inferiorly through interval between between the first and second…
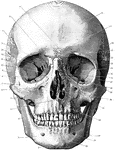
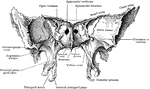
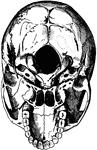
Front of the Skull
Shown is norma frontalis, which refers to the front of the skull. Labels: 1, mental protuberance; 2,…

Hochelagan Skull
A front view of a Hochelagan skull, surrounded by the outline, on a larger scale, of the Cromagnon skull.
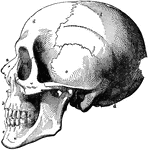
Human Skull
The skull. Labels: a, nasal bone; b, superior maxillary; c, inferior maxillary; d, occipital; e, temporal;…
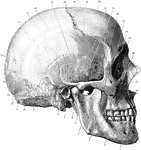
Side of the Skull
Shown is norma lateralis, which refers to the side of the skull. Labels: 1, mental foramen; 2, body…
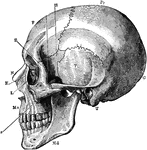
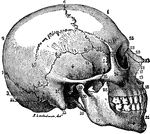
Side View of the Skull
A side view of the skull. Labels: O, occipital bone; T, temporal; Pr, parietal; F, frontal; S, sphenoid;…
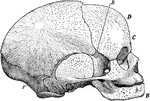
Side View of Fetal Skull
Side view of a fetal skull. The coronal suture extends from the top of the head downwards on either…
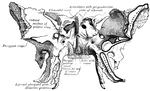
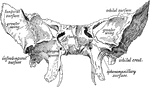
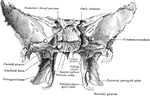
Sphenoid Bone
A bone situated at the base of the skull in front of the temporals and basilar part of the occipital.
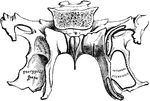
Sphenoid Bone
A bone situated at the base of the skull in front of the temporals and basilar part of the occipital.
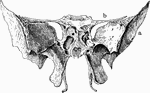
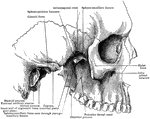
Sphenoid Bone of the Human Skull
Sphenoid bone, situated the anterior part of the base of the skull, articulating with all the other…
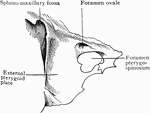
Sphenoid Bone Showing Foramen Pterygospinosum
Portion of sphenoid bone, showing the foramen pterygospinosum.
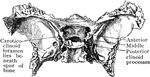
Abnormal Sphenoid Bone
Sphenoid bone, showing abnormal development of middle clinoid processes, especially on the left side.
Spinal Column
Side view of the spinal column, with the vertebrae numbered: C1-7, cervical vertebrae; D1-12, dorsal…
Spinal Column
Lateral view of the spinal column. Labels: 1, atlas; 2, dentata 3, seventh cervical vertebra; 4, twelfth…
The Spinal Column
View of the entire spinal column. The bodies of the vertebrae are in the front with the spinous processes…
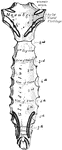
Human Spinal Column
Side view of spinal column, without sacrum and coccyx. Labels: 1 to 7, cervical vertebrae; 8 to 19,…
Side View of the Spinal Column
Side view of the spinal column. Labels: C 1-7, cervical; D 1-12, dorsal; L 1-15 lumbar; S 1, sacrum;…
Spinal Divisions
A lateral view of the spine divided into its cervical, dorsal, and lumbar portions.
The Spine
The spine showing the seven vertebrae of the neck, cervical; the twelve of the back, dorsal; the five…
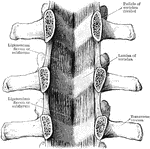
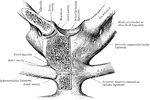
Ligamenta Subflava of the Spine
Ligamenta subflava as seen from the front after removal of he bodies as the vertebrae by sawing through…
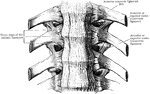
Ligaments of the Spine
Anterior common ligament of the vertebral column, and the costo vertebral joints as seen from in front.
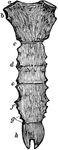
Sternum
The sternum in this cut consists of two bones. The first is broad and thick above, and contracts as…
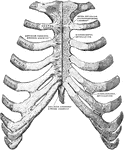
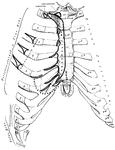
Sternum and Ribs
Sternum and ribs with ligaments, from in front. In the right half of the figure the most anterior layer…
Human Sternum Bone
Sternum, front and side view. The sternum, or breast bone, is a flat narrow bone, situated in the median…