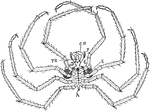
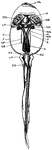
Nymphon Sea Spider
"Male of Nymphon. PR., Proboscis; CH., chelophores; P., pedipalps; E., eggs carried on ovigerous legs;…
Californian Hagfish
"Bdellostoma stouti (Californian hag), enveloped in sheath of mucus. b., barbules e., eyes m. mucus;…
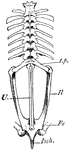
Bullfrog Vertebrae
"Vertebral column and pelvic girdle of bull-frog. t.p., Transvers processes of sacral vertebra; Il.,…
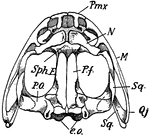
Upper Surface of Frog Skull
"Skull of frog. Upper surface-- Pmx., premaxilla; N., nasal; M., maxilla; Sq., squamosal; Q.j., quadrato-jugal;…
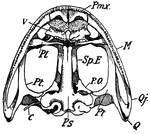
Lower Surface of Frog Skull
"Skull of frog. Lower surface-- Pmx., premaxilla; M., maxilla; Q.j., quadrato-jugal; Q., quadrate; Pt.,…
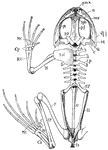
Frog Skeleton
"Skeleton of frog. The half of the pectoral girdle, and fore- and hind-limb of the right side are not…
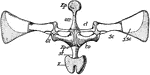
Frog Pectoral Girdle
"Pectoral girdle of Rana esculenta. The cartilaginous parts are dotted. Ep., Episternum; om., omosternum;…
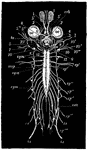
Frog Nervous System
"Nervous system of frog. 1-10, The cranial nerves; oc., eyes; crb., in front of optic chiasma; to.,…
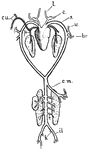
Frog Arterial System
"Arterial system of frog. l., Lingual; c., carotid; s., systemic; cu., cutaneous; p., pulmonary; v.,…
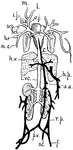
Frog Venous System
"Venous system of frog. m., l., Mandibular and lingual; e.j., external jugular; i.j., internal jugular;…
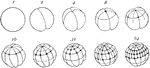
Frog Ovum Division
"Division of frog's ovum. The numbers indicate the number of cells or blastomeres." -Thomson, 1916
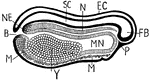
Frog Embryo
"Longitudinal vertical section of frog embryo, shortly before closure of blastopore. FB., fore-brain;…
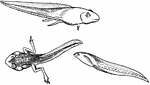
Tadpole Dissection
"Dissection of tadpole. DL., Lower lip; H., ventricle of heart; DE., oesophagus; NA., head kidney; A.,…
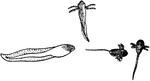
Frog Stage 2
"Life history of a frog. Newly hatched forms hanging to water-weeds. Stages with external gills." -Thomson,…
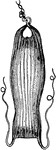
Blood Particle
A particle of human blood as it appears when transparent and floating. 2. the same, seen as illuminated.…
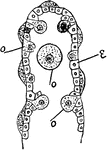
Sea Urchin Ovary
"Diagram of a portion of the ovary of Sea-urchin showing the eggs arising from the epithelium (reproductive…
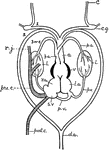
Frog Heart
"Diagram of the heart and branchial arches in the Frog. c.g., carotid gland; l., lungs; l.a., left auricle;…
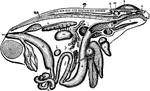
Frog Viscera
"General view of the viscera of a male frog, from the right side. a, stomach; b, urinary bladder; c,…
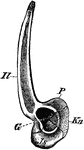
Edible Frog Shoulder Girdle
"Rana esculenta. The shoulder girdle from the ventral aspect. Co, coracoid; Co', epicoracoid; Cl, clavicle;…
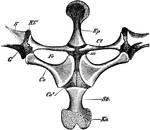
Edible Frog Pelvic Girdle
"Rana esculenta. Pelvic girdle from the right side. G, acetabulum; Il, P, ilium; Is, ischium; Kn, pubis."…
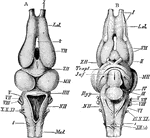
Edible Frog Brain
"Rana esculenta. The brain. A, from above; B, from below. ch. opt, optic chiasma; HH, cerebellum; Hyp,…
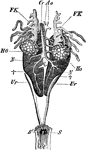
Male Edible Frog Genital Organs
"Rana esculenta. Urinogenital organs of the male. Ao, dorsal aorta; Cl, cloaca; Cv, post-caval vein;…
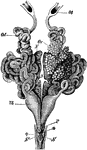
Female Edible Frog Genital Organs
"Rana esculenta. Urinogenital organs of the female. N, kidneys; Od, oviduct; Ot, its coelomic aperture;…

Sacred Beetle
An extensive genus of coleopterous insects tribes, and answering to the section Lamellicornes of Latereille.…

Frog Blood Corpuscles
Blood corpuscles of a frog. Highly magnified. The appearance of blood cells in different animals varies…
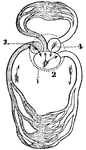
Circulation of a Frog
A diagram of the circulation of a frog. Labels: 1, The pericardium. 2, The single ventricle. 3, The…
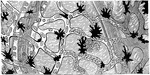
Circulation of Blood in a Frog's Foot
The circulation of the blood in the web of a frog's foot. A, an artery; B, capillaries crowded with…
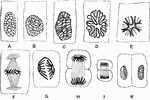
Karyokinesis
Karyokinesis. Labels: a, ordinary nucleus of a columnar epithelial cell; B, C, the same nucleus in the…
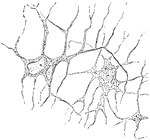
Branched Cornea Corpuscles of a Frog
Horizontal preparation of the cornea of frog, stained in gold chloride; showing the network of branched…

Connective Tissue Cells from a Frog
Flat, pigmented, branched connective tissue cells from the sheath of a large blood vessel of a frog's…
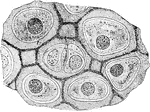
Hyaline Cartilage Cells
The matrix of hyaline cartilage has a dimly granular appearance like that of ground glass, and in man…
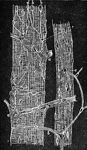
Striped Muscle Fibers of a Frog
Two striped muscle fibers of the hyoglossus of frog. Labels: a, Nerve end plate; b, nerve fibers leaving…
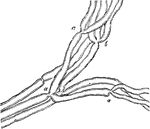
Muscular Nerve Showing Division of Fiber
Small branch of a muscular nerve of the frog, near its termination, showing division of the fibers.…

Effect of Acetic Acid on Red Blood Cells
Acetic acid (dilute) causes the nucleus of the red blood cells in the frog to become more clearly defined;…
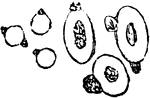
Effect of Tannin on Red Blood Cells
When a 2 percent fresh solution of tannic acid is applied to frog's blood it causes the appearance of…
Effect of Boric Acid on Red Blood Cells
A 2 percent solution of boric acid applied to nucleated red blood cells of a frog will cause the concentration…

Effect of Gases on Red Blood Cells
If the red blood cells of a frog be first exposed to the action of water vapor (which renders their…
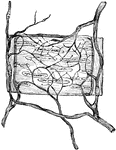
Nerves in the Artery of a Frog
Ramifications of nerves and termination in muscular coat of a small artery of the frog.

Surface View of an Artery
Surface view of an artery from the mesentery of a frog, ensheathed in a perivascular lymphatic vessel.…
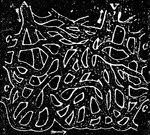
Capillaries in Frog's Foot
Capillaries (C) in the web of the frog's foot connecting a small artery (A) with a small vein (V).
Capillaries Showing Emigration of Leucocytes
A large capillary from the frog's mesentery eight hours after irritation had been set up, showing emigration…
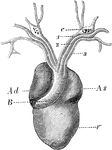
Heart of a Frog
The heart of a frog (Rana esculenta) from the front. Labels: V, ventricle, Ad, right auricle; As, left…
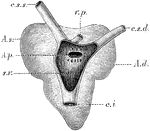
Heart of a Frog
The heart of a frog (Rana esculenta) from the back. Labels: s.v., sinus venosus opened; c.s.s., left…
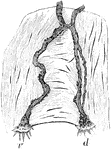
Nerves of the Heart of a Frog
Course of the nerves in the auricular partition wall of the heart of a frog. Labels: d, dorsal branch;…
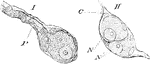
Nerve Cells
The nerve cells that compose the ganglia are generally unipolar, and seldom bipolar; sometimes two cells…