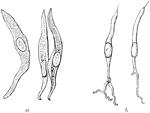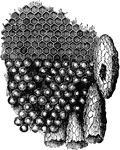
Portion of the Comb
"Portion of the comb, with the eggs occupying the cells. One of the royal cells has been opened by the…
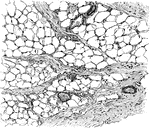
Adipose Tissue from Omentum
Adipose tissue from omentum. The fat cells are arranged as groups between the bundles of connective…

Carpenter Bee, Pupae, Eggs, Galleries and Nests
"The Carpenter Bee, or Wood Piercer, hollows out galleries in decayed wood, and builds in them cells…
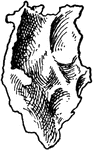
Inner Aspect of Lachrymal Bone
Right lachrymal bone, inner aspect. Upper part completes anterior ethmoidal cells, lower looks into…

A Species of Odynerus
"There are solitary wasps which make their cells in holes, which they scoop out in the ground or in…
Larva of the Odynerus Wasp
"There are solitary wasps which make their cells in holes, which they scoop out in the ground or in…

Nest of an Odynerus Wasp in the Stem of a Bramble
"There are solitary wasps which make their cells in holes, which they scoop out in the ground or in…
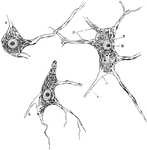
Neuron of Spinal Cord
Nerve cells of human spinal cord stained to show Nissl bodies. Labels: D, dendrites; A, axons; C, implantation…
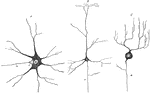
Various Forms of Neurons
Multipolar nerve cells of various forms. Labels: A, from spinal cord; B, from cerebral cortex; C, from…
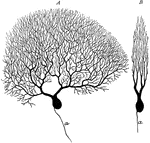
Purkinje Cell
Two purkinje cells from silver preparation of cerebellar cortex; A, side view; B, cell in profile; a,…
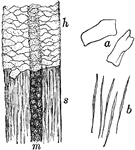
Shaft of Hair
Portion of shaft of hair. Labels: h, shaft covered with cuticle; s, cuticle removed to expose cortical…
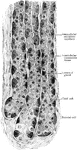
Gastric Gland from Fundus
Deeper portion of gastric glands from fundus, showing two varieties of lining cells and secretion capillaries…
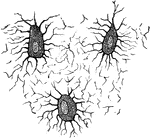
Osteoblasts
Nucleated none cells (osteoblasts) and their processes, contained in the one lacunae and their canaliculi…
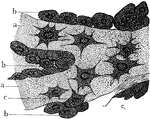
Osteoblasts from Embryo
Osteoblasts from the parietal bone of a human embryo thirteen weeks old. Labels: a, bony septa with…
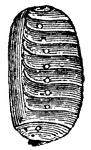
Pseudo Nymph of Sitaris Humeralis
"When the male bees have built the cells and furnished them with honey, the female, as we know, deposits…
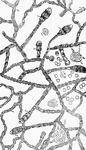
Stages of fungus growth
This illustration "represents its mycelium growth; 2,2 its budding cells, which terminate in fruit cells;…
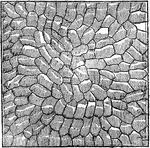
Microscopic view of a leaf
"The branch vascular bundles will be distinctly seen, resembling in some respects the arteries and veins…
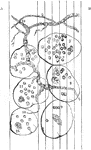
Microscopic view of a fermented apple
"Portions of the rotting pulp were placed on a microscopic slide, divided into hundredths and thousandths…
Cellular structure of peridia
"Under the power of about 90 diameters the general character of the peridia is seen. They are densely…

Potato Diseases at a Microscopic Level
"It is not unusual to fine a decayed spot in the center of potatoes otherwise apparently in good condition.…

Dendrophyllia Ramea (De Blainville)
"The Madrepores abound in all inter-tropical seas, taking a considerable part in the formation of the…

Dendrophyllia Ramea with Polypi (De Blainville)
"The Madrepores abound in all inter-tropical seas, taking a considerable part in the formation of the…
Dendrophyllia Ramea, Magnified (De Blainville)
"The Madrepores abound in all inter-tropical seas, taking a considerable part in the formation of the…

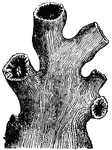
Porites Furcata (Lamarck)
"The polyp of the Porites is an animal somewhat pitcher-shaped, with twelve short tentacula,…
Muscle Fibers of the Heart
Anastomosing muscle fibers of the heart, seen in longitudinal section. On the right the limits of the…

Peptic Gastric Gland
The peptic gastric glands are distributed throughout the entire fundus and body, and may be found even…
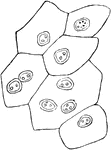
Superficial Layer of Bladder Epithelium
Superficial layer of the epithelium of the bladder. Composed of polyhedral cells of various sizes, each…
Deep Layer of Bladder Epithelium
Deep layers of the epithelium of the bladder, showing large club-shaped cells above, and smaller, more…

Roman Soldiers
The distinction between rank and unit type doesn't seem to have been as precise as in a modern-day army,…

Tetratheca
"Tetratheca hirsuta. 1. the stamens; 2. the pistil, with one of the cells laid open." -Lindley, 1853
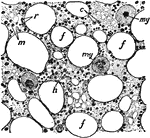
Section of Bone Marrow
Section of bone marrow. Labels: f, fat vacuole; e, eosinophile cells; ,y, myeloplaxes; r, red corpuscles;…

Reproduction of Cells
Successive stages of mitosis or karyokinesis. A, B, C, D, and E illustrate the phenomena of the prophase;…
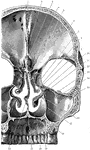
Coronal Section of Skull
Shown is a coronal section passing inferiorly through interval between between the first and second…

Pyramidal Cells of the Brain
The developmental stages exhibited by a pyramidal cell of the brain. Labels: a, neuroblast with rudimentary…

Section Through Spinal Cord Showing Neuroglial Cell
Section through the central canals of the spinal cord of a human embryo, showing ependymal (A) and neuroglial…
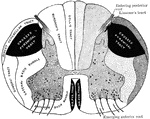
Transverse Section Through Spinal Cord
Diagrammatic representation of a transverse section through the spinal cord. The nerve tracts in the…
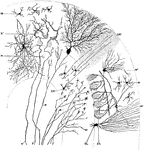
Sagittal Section Through Cerebellar Folium
Transverse section through a cerebellar folium. Labels: A, axon of cell Purkinje; F, moss fibers; K…
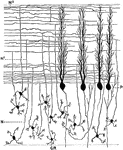
Sagittal Section Through Cerebellar Folium
Section through the molecular and granular layers in the long axis of a cerebellar folium. Labels: P,…

Minute Structure of Cerebral Cortex
Diagram to illustrate minute structure of the cerebral cortex. Labels: A and B, neuroglia cells; C,…

Prisoners and Guard
An illustration of two prisoners with chains around their ankles walking past an armed guard.

Mouth of French Creek
General Jacob Brown made camp at French Creek on October 29th, 1813. Brown's force was the advance guard…
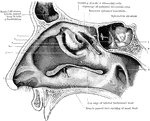
Outer Wall of Nose
View of the outer wall of the nose. The turbinated bones having been removed. Labels: 1, vestibule,…
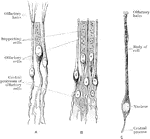
Olfactory and Supporting Cells
Olfactory and supporting cells in a frog and a human. A. Frog. B. Human. C. Human.
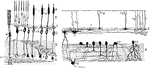
Section of Retina
Perpendicular section of mammalian retina. Labels: A, layer of rods and cones; B, outer nuclear layer;…
Development of a Tooth
Diagram to illustrate the development of a tooth. I. Shows the downgrowth of the dental lamina D.L.…
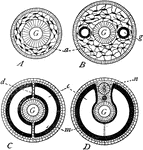
Body Layers and Cavities
Diagrams of the body layers and cavities in A, coelenterates; B, flatworms; C, annelids; D, vertebrates.…
Protonephridium
Structure of the protonephridium (excretory organ) of a flatworm. A, part of the excretory apparatus…
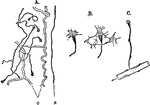
Eyepit of Limpet
A, section through the open eyepit of a limpet. B, the two kinds of retinal cells, pigmented and sensory.
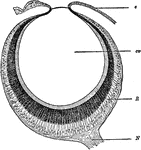
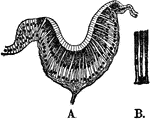
Eye of Waterbeetle
Section through the eye of a waterbeetle. Labels: l, chitinous lens; cv, transparent cells; pg, pigment…
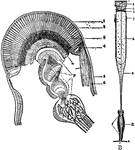
Eye of a Crayfish
A, section through the compound eye of a crayfish. Labels: 1, cornea; 2, crystaline cones; 3, retinulae;…

David Wooster
David Wooster (March 2, 1710 – May 2, 1777) was an American general in the American Revolutionary…

Ellsworth Zouave
Zouave was the title given to certain infantry regiments in the French army, normally serving in French…

Two-Handed Sword
The two-handed sword or German Zweihänder, here of the 15th century showing the Second Guard or…

Remains at Fort Schlosser
Fort Schlosser was a fortification built in Western New York in the USA around 1760 by British Colonial…
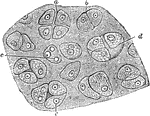
Hyaline Cartilage
Section of hyaline cartilage. Labels: a, four separating cells; b, two cells in apposition; c, nuclei;…
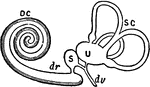
Membranous Labyrinth
The membranous labyrinth is lodged within the bony labyrinth and has the same general form; it is, however,…