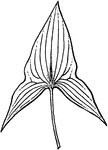
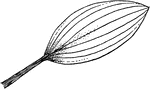
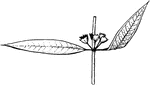
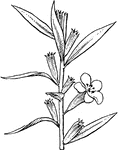
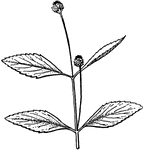
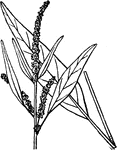
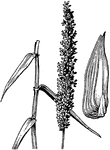
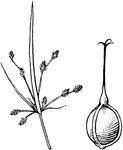
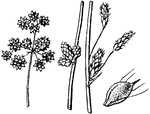
Nemastylis
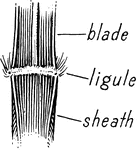
Flowers violet, over 3cm scross; leaves equitant at base; that is coming in two ranks, making the base…
Eriocaulon
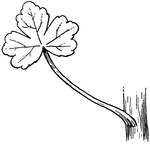
Leave from base of scrape bearing button like whitish heads of minute flowers; roots with cross-constrctions.

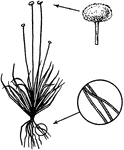
Sagittaria
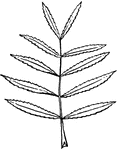
Leaves from base of scape bearing evident white flowers in racemes; roots without crss-constrictions.

Acrobasis
"a, case containing caterpillar; b, cases in winter; c, head and thoracic joints of larva, enlarged;…
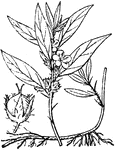
Hydrolea
Sepals united at base into a tube enclosing the ovary and later the fruit; leaves with spines in axils.

Amphora
"A jar with two handles; Among the Greek and Roman, a vessel, usually tall and slender having two handles…

Amphora
"A jar with two handles; Among the Greek and Roman, a vessel, usually tall and slender having two handles…

honey-comb
"The comb is made of wax, found in various plants, but which is also secreted by the bees themselves…

Anamorphoscope
"An optical toy consisting of a vertical cylindrical mirror which gives a correct image of a distorted…

Angelfish
"A plagiostomous fish. It is from 6 to 8 feet long, has a flat, roundish head, terminal mouth, and teerh…
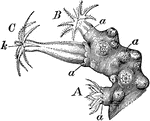
Anthozooids
"End of a branch of red coral of commerce, Corallium rubrum, with three anthozooids, A, B, C, in different…

Half-Mourning Butterfly
"The Galatea Butterfly, P. Galatea, A Euoprean species, called The Half-Mourning Butterfly,…
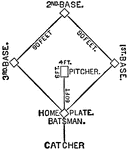
Baseball Diamond
"Base Ball is a field game played principally in the United States. It originated in the English school-boy…
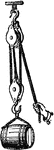
Block and Tackle
"A Block is a pulley or a system of pulleys rotating on a pintle mounted in its frame or shell with…

Shrimp
"They are distinguished by the possession of a large oval or triangular appendage which covers the base…

Sea-anemone
"Their tentacles, which are disposed in regular circles, and tinged with a variety of bright lively…

Mouth of the sea-anemone
"Their tentacles, which are disposed in regular circles, and tinged with a variety of bright lively…
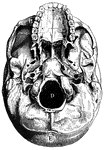
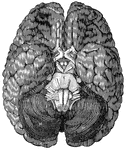
Base of skull
"A, Palate process of upper jawbone; B, zygoma, forming zygomatic arch; C, condyle, for forming articulation…
Transverse section of the small intestine
"In the figure on the left are seen the artery and vein of a villus. In the right figure are represented…
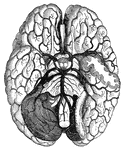
Blood vessels of the brain
"Arteries and their Branches at the Base of the Brain." — Blaisedell, 1904

Pompeiian House
"House construction consists mainly of concrete or brick, and sometimes of stone blocks, especially…

Apex
"A cap worn by the flamines and salii at Rome. The essential part of the apex, to which alone the name…

Sawfish Head
"The Sawfish is so called from the saw-like weapon into which the snout is produced. They are common…

Spoonbill
"Spoonbill is the popular name of the birds of the genus Platalea, belonging to the heron family (Ardeidæ),…
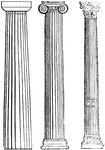
Columna
"A pillar or column. The use of the trunks of trees placed upright for supporting buildings, unquestionably…

Fastigium
"An ancient Greek or Roman temple, of rectangular construction, is terminated at its upper extremity…

Pompeii
"The following cut gives a view of of a portion of the paved street at the entrance of Pompeii. The…
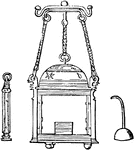
Laterna
"In later Greek, a lantern. Two bronze lanterns, constructed with nicety and skill, have been found…

Eyebright
A genus of plants of natural order Scropulariaceæ. having a tubular calyx, the upper lip of the…
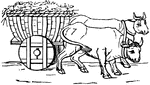
Plaustrum
"A cart or wagon. It had commonly two wheels, but sometimes four, and it was then called the plaustrum…
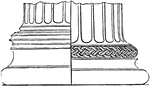
Spira
"Spira, the base of a column. in the Tuscan and the Roman Doric the base consisted of a single torus,…

Spur Winged Plover
The wing is armed with a horny tubercle or spine, sometimes rudimentary; the base of the bill in most…
Stock, top view
"The parts are the butt, A; small, B; magazine well, C; barrel bed, D; air chamber, E, which reduces…
Stock, right side view
"The parts are the butt, A; small, B; magazine well, C; barrel bed, D; air chamber, E, which reduces…
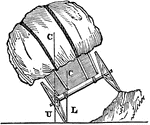
Vehicle on hill
"A loaded vehicle is represented as crossing the side of a hill, which has been raised one wheel above…

Yellow Billed Cuckoo
A bird with a moderately curved beak, wide at th base and compressed beyond it, long pointed wings,…
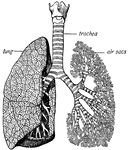
Trachea and lungs
"The trachea has in its walls stiff rings of cartilage that hold it open so that the air can…
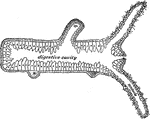
Section of a hydra
"Longitudinal section of a Hydra; b, bud which will form a young one; ba, base by…