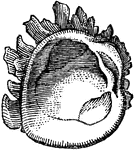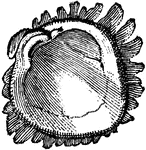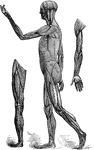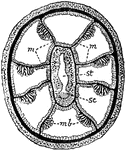
Alcyonarian
"Transverse section of an Alcyonarian zooid. mm, Mesenteries; mb, muscle banners; sc, sulcus; st, stomodaeum."…
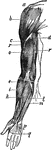
Arm Muscles
"abc, deltoid muscle; d, coraco branchfalls muacle; r, r, triceps; e, i, extensors of wrist and long…
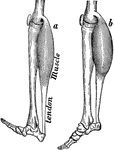
Muscles of the Arm
"Muscles on the front of the arm. Note the while cords, the tendons at the wrist." —Davison, 1910
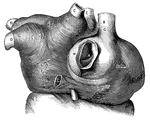
Muscular fibers of the auricle
L.A., left auricle; R.A., right auricle; A, opening of the inferior vena…

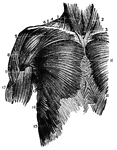
Muscles of the Back and Shoulder
"Some of the Larger Muscles on the Back of the Shoulder and the Arm." — Blaisedell, 1904
Back Forearm Muscles
The muscles of the back forearm. 1, biceps; 2, brachialis internus; 3, triceps; 4, pronator radii teres;…
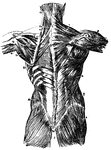
Back Muscles
Muscles of the back. 1, trapezius; 2, its origin; 3, spine of scapula; 4, latissimus dorsi; 5, delltoid;…
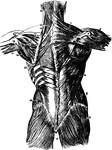
Muscles of the Back
Second layer of muscles of the back. Labels: 1, trapezius; 2, a portion of the ten dinous ellipse formed…
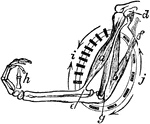
Muscular Cycle of the Biceps
A diagram showing the muscular cycle form by the biceps or flexor muscle, and the triceps or extensor…
Chest Muscles
A frontal view of the chest muscles. 1, sterno-hyoid; 2, sterno-mastoid; 3, sterno-thyroid; 4, sterno-mastoid;…
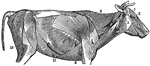
The Superficial Muscles of a Cow
In mammals the muscles in their general plain resemble those of humans. The superficial muscles of a…
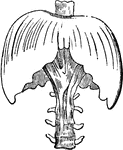
Diaphragm
"This is the name applied in anatomy to designate the transverse muscle which, in man and the mammalia…
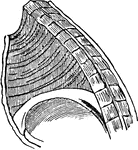
Diaphragm
"This is the name applied in anatomy to designate the transverse muscle which, in man and the mammalia…
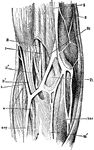
Elbow-Joint
"The superficial veins in front of the elbow-joint. B', tendon of biceps muscle; Bi, brachialis internus…
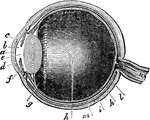
Eye
"Next in order is the aqueous humor, b, e, in the middle of which is the iris, d, c. Behind the pupil…
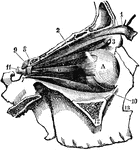
Eye Muscles
"The external bones of the temple are supposed to be removed in order to render visible the muscular…
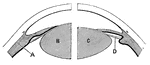
Lens of the eye
"Diagram showing the Change in the Lens during Accomadation. On the right the lens is arranged for distant…
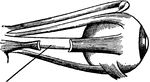
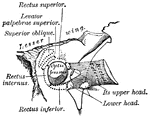
Muscles of the Eyes
"The eye is moved about by six muscles. The back ends of these muscles are attached to the eye sockets.…
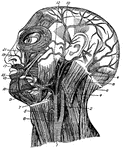
Facial Muscles
Muscles of the face, jaw and neck. 1, longus colli; 2, rapezius; 3, sterno-hyoid; 4, sterno-mastoid;…
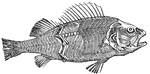
The Muscles of a Fish
In fish the chief masses of the muscular system are disposed on each side of the trunk in a series of…
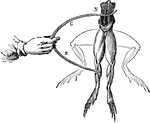
Frog Experiment
"Galvani found that whenever the nerves of a frog's leg were touched by one metal and the muscles by…
Front Forearm Muscles
The muscles of the back forearm. 1, biceps; 2, brachialis internus; 3, biceps; 4, supinator longus;…

The Superficial Muscles of a Hawk
In birds the muscles system is remarkable for their marked line of attachment to their tendons. Labels:…
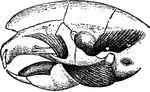
Hystrix Eristata
"Skull of Hystrix Eristata. t, temporal muscle; m, masseter. m', portion of masseter transmitted through…
Spindle Cell of Involuntary Muscle
"The involuntary muscles consist of ribbon-shaped bands which surround hollow tubes or cavities…
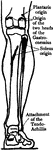
Leg Muscles
The muscles of the front of the leg. 1, tendon of quadriceps; 2, spine tibia; 3, tibialis anticus; 4,…
Muscles of the leg
"Muscles of the leg showing how they pass into tendons at the ankle." —Davison, 1910
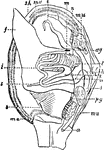
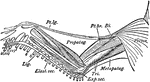
Mollusc Anatomy
"Anatomy of an Acephalous Mollusc (Mactra): s, stomach; ii, intestine; ag, anterior ganglions; pg, posterior…
Muscle Diagram
"Diagram illustrating the muscles (drawn in thick black lines) which pass before and behind the joints…
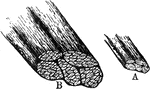
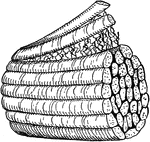
Muscle Fibers
A small bit of muscle composed of five primary fasciculi (bundles). Labels: A, natural size; B, the…
Muscle Fibers
A small piece of muscular fiber highly magnified. At a the fiber has been crushed and twisted so as…
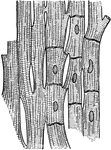
Muscle Fibers
Muscle fibers from the heart showing the striations and the junctions of the cells, highly magnified.
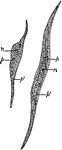
Muscle Fibres
"Plain muscle fibres. n, nucleus of muscle cell; p, undifferentiated cell protoplasm; p', the differentiated…
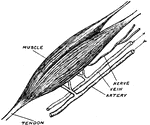
Bicep Muscle
The upper bicep of the right arm. Included are the tendons, blood vessels, and its nerve.
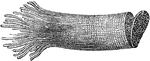
Microscopic View of a Muscle
A microscopic view of a muscle showing, at one end, the fibrillae; and at the other, the disk, or cells…
Smooth Muscle
Three sections of smooth muscle. M C is muscle cells and N is nucleus. Smooth muscles are slow to contract.…
Striated Muscle
Striped, or striated, muscle which quickly contracts causing the alternating black and white lines.…
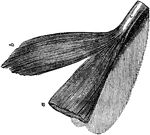
Two Portions of Muscle
Two portion of muscle; one of which, a, is covered with membrane; the other, b, is uncovered; c, the…
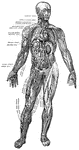
Muscles and Blood Vessels
"Principal Muscles on the Right, Certain Organs of the Chest and Abdomen, and the Larger Blood Vessels…

Back View of the Muscles of the Body
Muscle of the body, back view: The fascia is left upon the left limbs, removed from the right.

Front View of the Muscles of the Body
Muscle of the body, front view: On the right half, the superficial muscles; left half, deep-seated muscles.
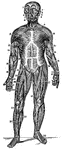
Front View of the Superficial Muscles of the Body
A front view of the superficial muscles of the body. Labels: 1, The frontal swells of the occipito-frontalis.…
Muscles of the forearm
"The extensor muscles on the back of the forearm. Note the tendons at the wrist." —Davison, 1910
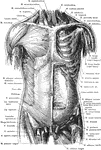
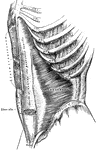
Anterior View of the Muscles of the Trunk
Superficial and deep muscles of the trunk. The sternocleidomastoid, pectoralis major, anterior portion…
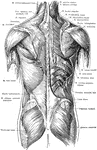
Posterior View of the Muscles of the Trunk
Superficial and deep muscles of the trunk. The latissimus dorsi and trapezius on the right side have…