Auditory Nerve
"By anatomists, the auditory nerve is associated with the facial, and is the seventh in order of origin…
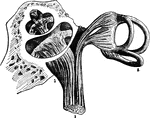
Auditory Nerve
"By anatomists, the auditory nerve is associated with the facial, and is the seventh in order of origin…
Auditory Nerve
"a, the osseous septum grooved for the passage of the cochlear nerve b, which terminates by a free end…

A Back View of the Brain and Spinal Cord
A back view of the brain and spinal cord. Labels: 1, The cerebrum. 2, The cerebellum. 3, The spinal…
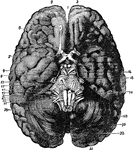
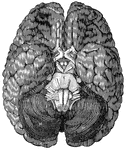
Base of Brain
The base of the brain. Labels: 1, longitudinal fissure; 2, 2, anterior lobes of cerebrum; 3, olfactory…
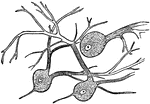
Nerve Cells of the Brain
"Wherever nerve cells are abundant, the nerve tissue has a gray color; in other places, it looks white.…
Cardiac Plexuses
The constitution of the cardiac plexuses. Labels: Sy, cervical sympathetic cord; C.1, superior cervical…

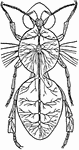
Carmarina
"Carmarina (Geryonia) hastata, one of the Trachomedusae. a, nerve-ring; a', radial nerve; b, tentaculocyst;…
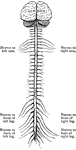
Central Nervous System
"Brain and spinal cord, with the thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves." — Tracy, 1888
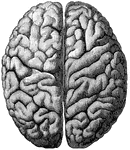
Cerebrum
"The Upper Surface of the Cerebrum. Showing its division into two hemispheres, and also of the convolutions."…
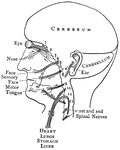
Distribution of the Cranial Nerves
"The cranial nerves are thus arranged in pairs: 1, olfactory nerves, special nerves of smell; 2, optic…
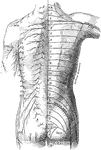
Posterior View of the Cutaneous Nerves of Trunk
The distribution of cutaneous nerves n the back of the trunk. On the left side the distribution of the…
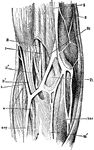
Elbow-Joint
"The superficial veins in front of the elbow-joint. B', tendon of biceps muscle; Bi, brachialis internus…
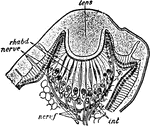
Euscorpius Italicus
"Section through the lateral eye of Euscorpius italicus. lens, Cuticular lens. nerv.c, Retinal cells…
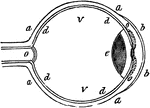
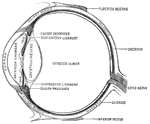
Eye
"a, sclerotic membrane; b, cornea; d, retina; o, optic nerve; v, vitreous humor." -Comstock 1850
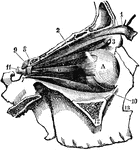
Eye Muscles
"The external bones of the temple are supposed to be removed in order to render visible the muscular…
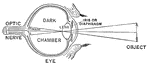
Diagram of the Eye
"Diagram illustrating the Manner in which the Image of an Object is inverted on the Retina." — Blaisedell,…
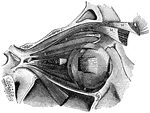
Muscles of the eyeball
"A, attachment of tendon connected with the four recti muscles; B, external rectus,…
Facial Nerve
"(1) The facial nerve at its emergence from stylo-mastoid foramen; (2) temporal branches communicating…
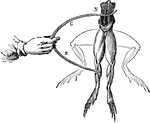
Frog Experiment
"Galvani found that whenever the nerves of a frog's leg were touched by one metal and the muscles by…

Sensory Nerves to the Head and Neck
Distribution of sensory nerves to the head and neck. Labels: Ophth, ophthalmic division of the fifth…
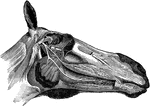
Head of a Horse Showing Nerves
Nerves of the right side of the head- the maxillary ramus and cheek being removed. Labels: a, superior…

Head of a Horse Showing Nerves
Left side of the face- showing the distribution of the facial portions of the fifth and the seventh…

Head of a Horse Showing Nerves
Ninth, tenth, eleventh, and twelfth cranial, first cervical, and part of the sympathetic nerves- the…
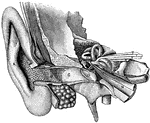
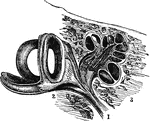
General view of organ of hearing
"A, pinna; B, cavity of the concha, showing the openings of a great number of sebaceous…
Leg of a Horse Showing Nerves
Carpal and metacarpal nerves-internal aspect. q, external branch of median; r, internal branch of median,…
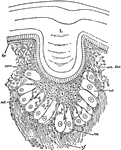
Limulus
"Section through one of the central eyes of a young Limulus. L, Cuticular or corneous lens. hy, Epidermic…
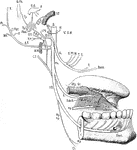
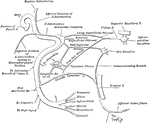
Inferior Maxillary Nerve
Scheme of the course and distribution of the inferior maxillary nerve. Labels: V.I.M, inferior maxillary…
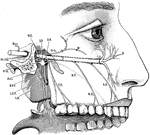
Superior Maxillary Nerve
Scheme of the course and distribution of the superior maxillary nerve. Labels: Rec, recurrent branch…
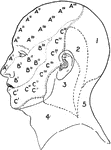
Nerve Areas of the Face and Scalp
Nerve areas of the face and scalp. Labels: A, Distribution of the first division of the fifth cranial…
Nerve Cells
"Nerve tissue is really made up of a great number of distinctive units called nerve cells.…
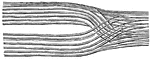
Portion of a medullated nerve fiber
"The axis cylinder is in the center. On either side is seen the medullary sheath, represented by dark…
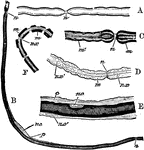
Nerve Fibers
To illustrate the structure of nerve fibers. Labels: A, nerve fiber examined fresh; n, node. B, nerve…
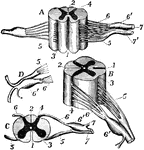
Nerve Roots
"The spinal cord and nerve-roots. A, a small portion of the cord seen from the ventral side; B, the…
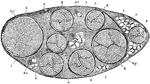
Nerve Trunk
Each nerve trunk is composed of a variable number of different sized bundle (funiculi) of nerve fibers…
Nerve trunks
"The Main Nerve Trunks of the Right Forearm, showing the Accompanying Radial and Ulnar Arteries. (Anterior…
Great Nerve
"A Great Nerve (Posterior Tibial) on the Back of the Leg, with its Accompanying Artery of the Same Name."…

Great Nerve
"A Great Nerve (Crural) and its branches on the Front of the Thigh. The femoral artery with its cut…
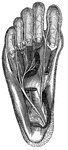
Great Nerve
"A Great Nerve (Plantar) and its Branches which supply the Bottom of the Feet. Note the cut tendons…
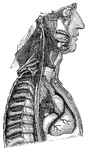
Sympathetic nerve
"The Cervical and Thoracic Portions of the Sympathetic Nerve and their Main Branches. In the center…
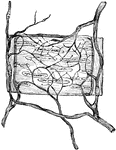
Nerves in the Artery of a Frog
Ramifications of nerves and termination in muscular coat of a small artery of the frog.
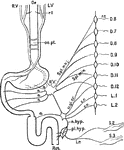
Nerves of the Alimentary Canal
Diagrammatic representation of the nerves of the alimentary canal. Oe to Rct, the various parts of the…
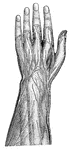
Superficial Nerves of the Forearm and Hand
"Superficial, or Cutaneous, Nerves on the Back of the Left Forearm and Hand." — Blaisedell, 1904
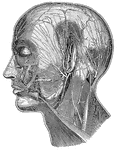
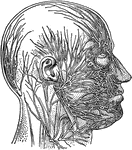
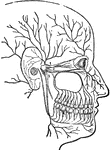
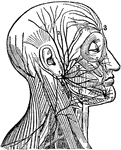
Superficial Nerves of the Head
"Showing some of the superficial nerves on the left side of the neck and the head. A few superficial…
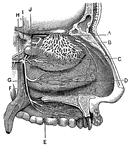
Nerves of the Nostril
"A, branches of the nerves of smell; B, nerves of touch to the nostrils; E, F,…
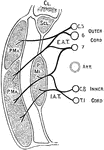
Nerves of the Pectoral Muscles
Diagram of the origin and distribution of the nerves to the pectoral muscles. E.A.T., external thoracic…