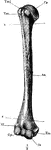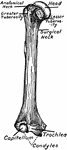This human anatomy ClipArt gallery offers 825 illustrations of the human skeletal system, including images of both the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. The human axial skeleton includes 80 bones formed by the vertebral column (spine), the thoracic cage (e.g., ribs, sternum), and the skull. The axial skeleton is responsible for the upright position of the body. The human appendicular skeleton is composed of 126 bones formed by the pectoral girdles, the upper and lower limbs, and the pelvic girdle. These bones function in locomotion as well as protection of vital organs.
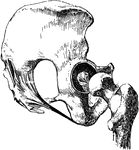
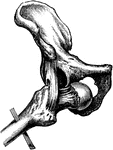
Hip Joint from Mesal Side
Right hip joint, from the mesal side. The bottom of the acetabulum had been chiseled away sufficiently…
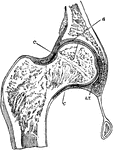
Hip Joint Section
Section through the hip-joint. Labels: a and b, articular cartilages; c, capsular ligament.
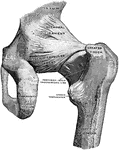
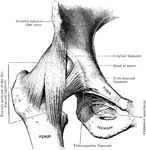
Back View of Hip Joint
Right hip joint, from behind. The joint capsule, except for strengthening ligaments, has been removed.
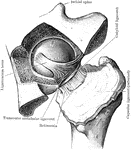
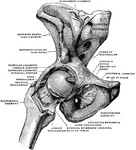
Dissection of Hip Joint
Dissection of hip joint with bottom of acetabulum removed, and capsule of the joint thrown outwards…
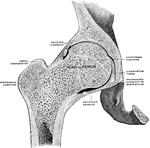
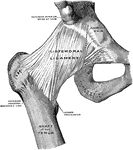
Frontal Section of Hip Joint
Right hip joint. Posterior half, viewed from in front. The joint surfaces have been somewhat pulled…
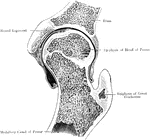
Frontal Section Through Hip Joint
A frontal section through the left hip joint of a boy. Front view.
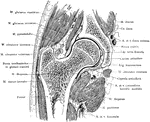
Frontal Section Through Hip Joint
Frontal section through the right hip joint, viewed from in front.
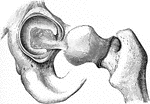
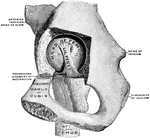
The Mechanism of the Hip Joint
The femur articulates with the hip bone by a ball-and-socket joint. The cup is deep, thus affording…
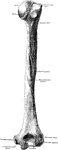
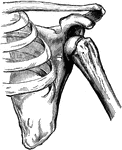
Humerus
"The humerus, which moves freely by a globular head upon the scapula, forming the shoulder-joint." —…
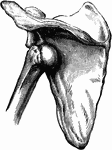
The Humerus
The humerus cut open. Labels: a, marrow cavity; b, hard bone; c, spongy bone; d, cartilage.
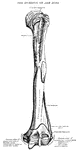
Humerus
Anterior view of humerus (bone of the leg) of the right side. Labels: 1, shaft or diaphysis; 2, the…
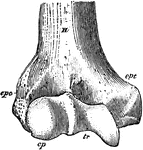
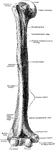
Humerus
"Anterior View, Distal End, of Right Humerus of a Man. H, humerus; epc, epicondyle, or external supracondyloid…
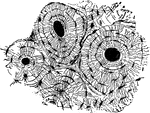
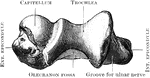
Bisection of the Humerus
The humerus bisected lengthwise. Labels: a, marrow-cavity; b, hard bone; c, spongy bone; d, articular…
The Human Humerus
The human humerus bone, the longest and largest bone of the upper leg. Labels: a, rounded head; gt,…
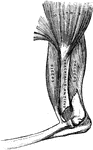
Longitudinal Section of Humerus
Longitudinal section of humerus showing relation of compact and spongy bone.

Section of Upper End of Humerus
Section of upper end of humerus, showing the external layer of compact bone surrounding the medullary…
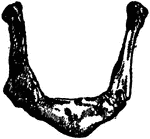
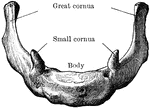
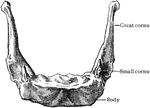
Human Hyoid Bone
The hyoid, os hyoides, or tongue bone, is an isolated, U-shaped bone lying in front of the throat, just…
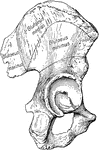
The Ilium Bone and Origin of the Gluteal Muscles
The origins of the three glutaei upon the dorsum of the ilium (part of the hip bone). The gluteal lines…

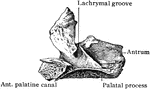
Inferior Turbinal Bones
Interior turbinal bones (or conchae nasales inferiores), which are situated in the nasal fossae.
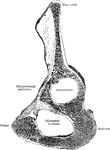
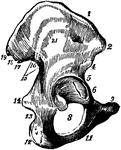
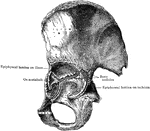
Sagittal Section of Innominate Bone
Oblique sagittal section of right innominate bone passing through bottom of acetabulum; inner surface.
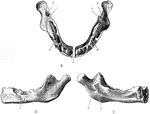
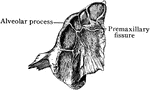
Jaw at Birth
The lower jaw at birth. A, As seen from above. B, As seen from outer side. C, As seen from inner side.…
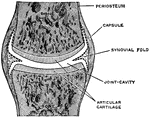
A Simple Complete Joint
A simple complete joint, one type of movable articulation. The synovial membrane is represented by dotted…
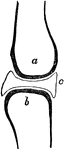
Joint
A joint between two bones (a and b). The ends of all bones are tipped with cartilage so that they may…

Human Joint, Dentated Suture
A toothed, or dentated suture. This is one type of immovable articulation. It is found in the union…
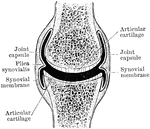
Diarthrodial Joint
Shown is a a diagram of a diarthrodial joint. In the diarthrodial group the extensive cavity has produced…
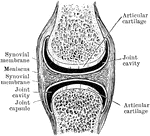
Diarthrodial Joint
In the diarthrodial group the extensive cavity has produced great interruption in the continuity of…
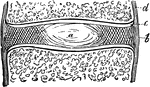
Human Joint, Mixed Articulation
A mixed articulation (slightly movable). In this form, the bony surfaces are usually joined together…