The Amphibian Anatomy ClipArt gallery features 61 illustrations of amphibian skeletal and organ system views, diagrams of movement in water, and related images.
Archegosaurus Head
Archegosaurus is a genus of amphibian which lived during the Asselian to Wuchiapingian ages of the Permian,…
Dorsal Vertebrae of the Archegosaurus
Archegosaurus is a genus of amphibian which lived during the Asselian to Wuchiapingian ages of the Permian,…
Dorsal Vertebra of Branchiosaurus
Branchiosaurus (Greek for "gill lizard") is a genus of small, lightly-built early prehistoric amphibians.…
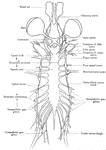
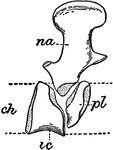
Bullfrog Vertebrae
"Vertebral column and pelvic girdle of bull-frog. t.p., Transvers processes of sacral vertebra; Il.,…
Capillaries in Frog's Foot
Capillaries (C) in the web of the frog's foot connecting a small artery (A) with a small vein (V).
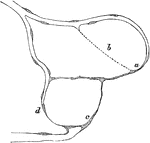
Development of Capillaries of a Tadpole
Development of capillaries in the regenerating tail of a tadpole. a b c d, sprouts and cords of protoplasm.

Development of Capillaries of a Tadpole
Development of capillaries in the regenerating tail of a tadpole. a b c d, sprouts and cords of protoplasm.…
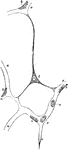
Capillary Blood Vessels of Larval Frog
Capillary blood vessel of the tail of a young larval frog. a, capillaries permeable to blood; b, fat…

Circulation in a Frog's Foot
Circulation in frog's foot under a microscope. Labels: A, walls of capillaries; B, tissue of web lying…
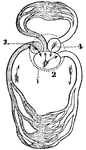
Circulation of a Frog
A diagram of the circulation of a frog. Labels: 1, The pericardium. 2, The single ventricle. 3, The…
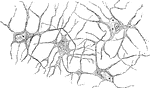
Magnified Frog Cornea Showing Branched Corpuscles
Horizontal preparation of cornea of frog; showing the network of branched cornea-corpuscles. The ground…

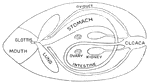
Dissected Frog
"Frog with the left side cut away and some of the organs pulled downward. a, aorta leading from the…
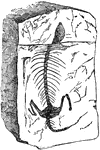
Fossil
This illustration shows the ancient fossile of an amphibian. Fossils are the mineralized or otherwise…
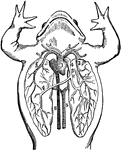
Frog
The heart and lungs of a frog. 1: Heart. 2: Arch of the aorta. 3: Pulmonary artery. 4: Pulmonary veins.…
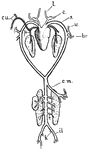
Frog Arterial System
"Arterial system of frog. l., Lingual; c., carotid; s., systemic; cu., cutaneous; p., pulmonary; v.,…

Frog Blood Corpuscles
Blood corpuscles of a frog. Highly magnified. The appearance of blood cells in different animals varies…
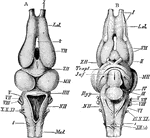
Edible Frog Brain
"Rana esculenta. The brain. A, from above; B, from below. ch. opt, optic chiasma; HH, cerebellum; Hyp,…
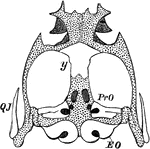
Frog Chondrocranium
"Chondrocranium of Frog (Rana esculenta). y, girdle-bone or os en ceinture; EO, exoccipital; PrO, proötic;…

Frog Egg
"The Tadpole is the larva of the anurous amphibia, sometimes so far extended as to include larvaæ…
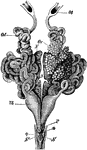
Female Edible Frog Genital Organs
"Rana esculenta. Urinogenital organs of the female. N, kidneys; Od, oviduct; Ot, its coelomic aperture;…
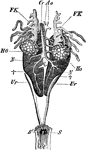
Male Edible Frog Genital Organs
"Rana esculenta. Urinogenital organs of the male. Ao, dorsal aorta; Cl, cloaca; Cv, post-caval vein;…
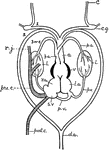
Frog Heart
"Diagram of the heart and branchial arches in the Frog. c.g., carotid gland; l., lungs; l.a., left auricle;…
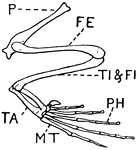
Leg of Frog
This illustration shows the leg of a frog. P. Pelvis, FE. Femur, TI. Tibia, FI. Fibula, TA. Tarsus,…
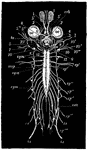
Frog Nervous System
"Nervous system of frog. 1-10, The cranial nerves; oc., eyes; crb., in front of optic chiasma; to.,…
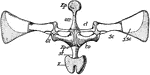
Frog Pectoral Girdle
"Pectoral girdle of Rana esculenta. The cartilaginous parts are dotted. Ep., Episternum; om., omosternum;…
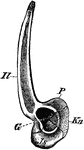
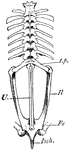
Edible Frog Pelvic Girdle
"Rana esculenta. Pelvic girdle from the right side. G, acetabulum; Il, P, ilium; Is, ischium; Kn, pubis."…
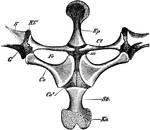
Edible Frog Shoulder Girdle
"Rana esculenta. The shoulder girdle from the ventral aspect. Co, coracoid; Co', epicoracoid; Cl, clavicle;…
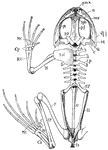
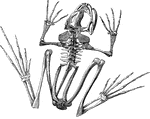
Frog Skeleton
"Skeleton of frog. The half of the pectoral girdle, and fore- and hind-limb of the right side are not…
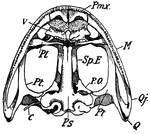
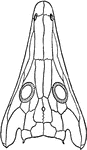
Lower Surface of Frog Skull
"Skull of frog. Lower surface-- Pmx., premaxilla; M., maxilla; Q.j., quadrato-jugal; Q., quadrate; Pt.,…
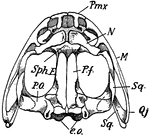
Upper Surface of Frog Skull
"Skull of frog. Upper surface-- Pmx., premaxilla; N., nasal; M., maxilla; Sq., squamosal; Q.j., quadrato-jugal;…
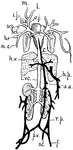
Frog Venous System
"Venous system of frog. m., l., Mandibular and lingual; e.j., external jugular; i.j., internal jugular;…
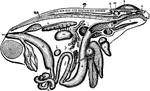
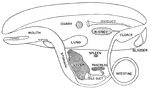
Frog Viscera
"General view of the viscera of a male frog, from the right side. a, stomach; b, urinary bladder; c,…
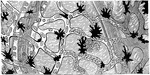
Circulation of Blood in a Frog's Foot
The circulation of the blood in the web of a frog's foot. A, an artery; B, capillaries crowded with…
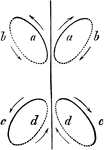
Ellipses of Swimming Frog
A diagram showing the motions a young frog makes while swimming. In this stage of life, the frog makes…
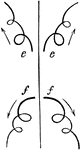
Loops of Swimming Frog
A diagram showing the motions a young frog makes whilst swimming. In this stage of the frog's life,…
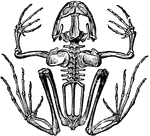
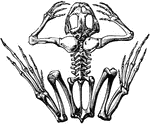
Skeleton of a Frog
"The skull in reptiles is flat, and the cerebral cavity is not filled with brains. There are no ribs."
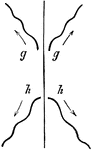
Swim Lines of Frog
A diagram demonstrating the motion a frog makes whilst swimming. In this stage of the frog's life, the…
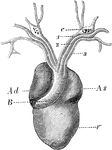
Heart of a Frog
The heart of a frog (Rana esculenta) from the front. Labels: V, ventricle, Ad, right auricle; As, left…
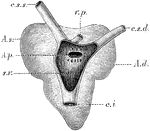
Heart of a Frog
The heart of a frog (Rana esculenta) from the back. Labels: s.v., sinus venosus opened; c.s.s., left…
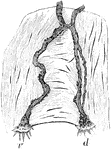
Nerves of the Heart of a Frog
Course of the nerves in the auricular partition wall of the heart of a frog. Labels: d, dorsal branch;…
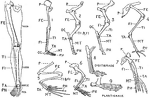
Human Leg (Front View), and Comparative Diagrams showing Modifications of the Leg
This illustration shows a human leg (front view), and comparative diagrams showing modifications of…

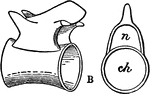
Vertebral Column of Hymenochirus
African dwarf frogs of genus Hymenochirus, also known as dwarf aquatic frogs, are frogs native to Sub…
Head of Ichthyophis Glutinosus
Ichthyophis glutinosus or Ceylon Caecilian is a species of amphibian in the Ichthyophiidae family. Pictured…
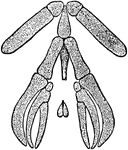
Hyoid and Branchial Apparatus of the Common Mudpuppy
The Common Mudpuppy (Necturus maculosus) is a species of aquatic salamander found throughout the northeastern…
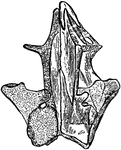
Cranium of the Common Mudpuppy (Dorsal View)
The Common Mudpuppy (Necturus maculosus) is a species of aquatic salamander found throughout the northeastern…

Cranium of the Common Mudpuppy (Lateral View)
The Common Mudpuppy (Necturus maculosus) is a species of aquatic salamander found throughout the northeastern…

Cranium of the Common Mudpuppy (Ventral View)
The Common Mudpuppy (Necturus maculosus) is a species of aquatic salamander found throughout the northeastern…
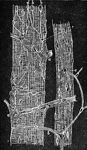
Striped Muscle Fibers of a Frog
Two striped muscle fibers of the hyoglossus of frog. Labels: a, Nerve end plate; b, nerve fibers leaving…
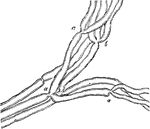
Muscular Nerve Showing Division of Fiber
Small branch of a muscular nerve of the frog, near its termination, showing division of the fibers.…
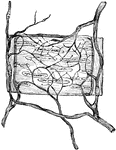
Nerves in the Artery of a Frog
Ramifications of nerves and termination in muscular coat of a small artery of the frog.
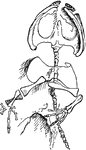
Raniceps Lyellii
This illustration represents a skeleton of another species of ancient amphibian reptiles.