To search for files on your computer using Windows XP’s search feature, select Start, Search.
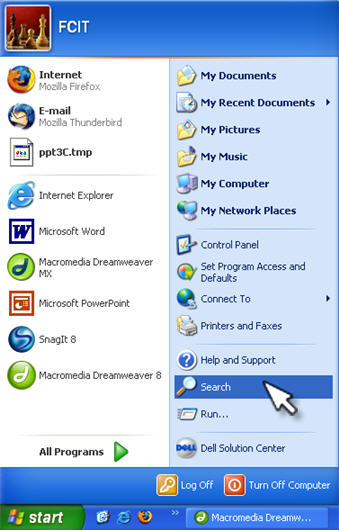
In the window that opens up, you will see the search assistant on the left, and the results window on the right. Click on “All files or folders” in the Search Assistant area unless you know the type of file you are looking for. If you know the type of file you are searching for, then use one of the first two links, “Pictures, music, or video” to search for those kinds of files or “Documents” to search for Word files and the like.

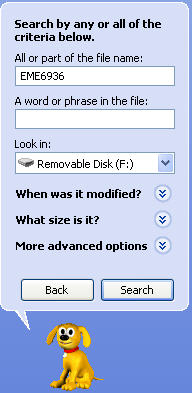
In the next window displayed by the Search Assistant, you can enter the name of the file you are looking for under “All or part of the file name.” You can also search the contents of a file for a particular word or phrase by entering them in the second search field. Under “Look in” you can change the drive to search from the default of the “C:” drive to a CD or a USB drive.
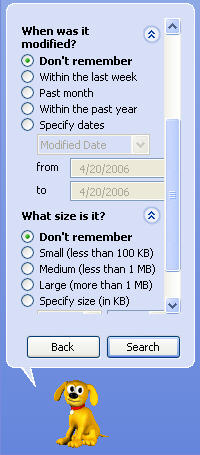
The links below the drive selection menu allow you to set more specific criteria for your search. If you select “When was it modified?” you can search only files modified in the last week, the last month, or the last year using the radio buttons. You can also select “Specify dates”, and enter a date range using the “from” and “to” fields. This date range can cover when you think the file was created, last modified, or last accessed. You can select one of these three options using the pull-down menu above the date range fields. The next link allows you to specify some file size criteria. For example, you can tell Windows to only look for files that are at least a certain size by selecting the “Specify size” option, selecting “at least”, and entering a file size.
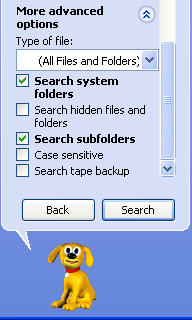
If you click on “More advanced options” you can tell Windows to search within system folders (where operating system files are stored) or to search hidden files and folders. By default, Windows is set up to search within subfolders.
If you only know part of the name of a file or folder you are searching for, you can use wild cards such as “*” or “?”. The asterisk can replace a whole group of letters or numbers, while the question mark only replaces one character. For example, typing “books.*” in the search box will find files such as books.doc and books.pdf. Typing in book*.pdf may find files such as books.pdf as well as bookkeeping.pdf. Typing in book?.pdf will only find books.pdf, but not bookkeeping.pdf. That’s because the question mark can only replace one character in the file name.