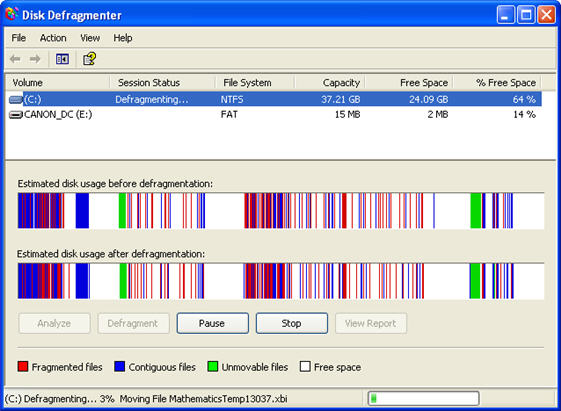
separate non-consecutive pieces to store them on the hard drive. This happens when you create and save a file, then go back at a later time and add to it so that it is larger in size. Windows will probably have already saved other files after the original file, so the only way it can store the modified file to disk is by splitting it into separate pieces and saving the new part in another location on the hard drive. A part of the operating system called the file table keeps track of where the different pieces of a file are stored.
Defragmenting is the process of scanning your hard drive and joining the different file fragments stored on the disk. When files are stored in consecutive pieces your operating system can access them much faster. Defragmenting your hard drive can increase your PC’s performance when performed on a regular basis.
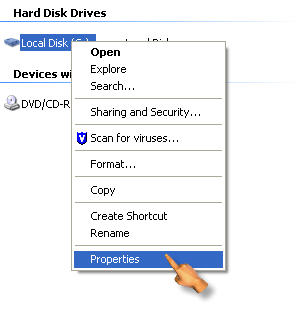
To defragment your hard drive, open My Computer (Start, My Computer) and then right-click on the drive you want to defragment and select Properties.
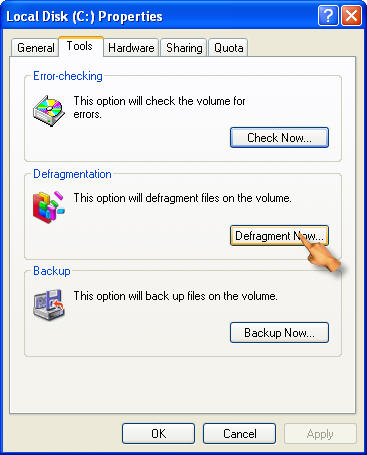
Select the Tools tab and then click on Defragment Now to open the Disk Defragmenter window. Click on Defragment to start defragmenting the drive.
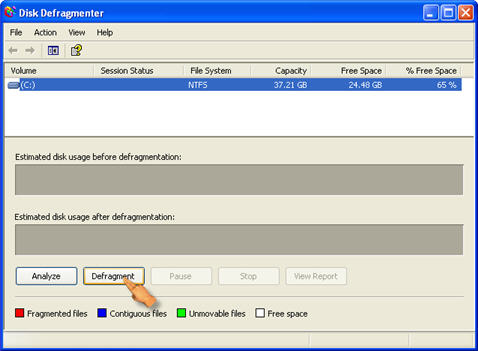
Note that depending on the size of your hard drive this process could take a while. It helps to shut down your antivirus software and other applications to speed it up. Otherwise, your computer may restart defragmenting each time these programs try to access your hard drive.