A plugin is a piece of software that acts as an add-on to a web browser and gives the browser additional functionality. Plugins can allow a web browser to display additional content it was not originally designed to display.
An example of a plugin is the free Macromedia Flash Player, a plugin that allows the web browser to display animations using the Flash format. As the Web has become more commercial, Flash has become a popular format for displaying ads in web pages. As a result, many web users have been prompted to download the Flash plug in and have it installed on their systems.
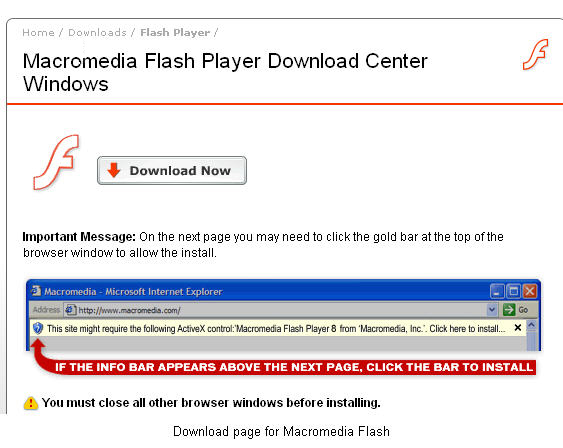
Other popular plugins include Quicktime Player (available on the Apple website) and Acrobat Reader (which in addition to being a plugin for the major browsers is also a stand alone application used to display files using the PDF format).
Most plugins are available as free downloads. To install the plugin, you visit the website of the plugin’s developer and click on a link that will download the installer for the plugin you have selected. You can save the installer to an easy to find location such as the Desktop or a specific folder you have created to organize all of your downloads. Once you have downloaded the installer, you can open it and follow the prompts to install the plugin on your system. You may have to restart your web browser to enable the additional functionality provided by the plugin.